Abstract
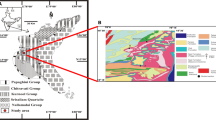
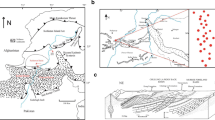
The present study brings out the reappraisal of mode of depositional conditions of the Talchir sediments from Savarla village of Bandar Basin, Chandrapur district of Maharashtra. These sediments correspond to four lithofacies namely, (i) basal massive diamictite (bmd), (ii) stratified diamictite and sandstones (sds), (iii) medium- to fine-grained sandstones (mfs) and (iv) siltstones-shale. The bmd facies characterizing laterally discontinuous, unstratified and matrix- to clast-supported sediments represent the continental tills. The sds facies corresponding to melting of glaciers at outwash plains reveal the decrease in the boulder and cobble clasts and increase in pebble clasts. The mfs facies associated with the very thin, fine-grained sand and varves represent glacio-lacustrine depositional conditions with suitably developed still water bodies and even ice-dammed lakes. The petrographic characteristics of these sediments, which bring out textural immaturity and depiction of QFR triangular diagram, divulge interior type of continental block provenance with cold-arid palaeoclimate. The microtextures like high relief, conchoidal breakage pattern, arc shaped steps, semi parallel steps, globular protuberances as well as striations along with ‘v’ shaped indentations noted from SEM photomicrograph clearly point out towards the glaciogenetic influence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J.B. (1983) Ancient glacial-marine deposits: their special and temporal distribution. In: Molnia, B.F., (Ed.), Glacial-marine sedimentation. Plenum press, New York.
Banerjee, I. (1966) Turbidites in a glacial sequence: A study from the Talchir Formation, Raniganj Coal field, India. Jour. Geol., v.74(5), pp.593–606.
Benn, D. L. and Evans, D. J. A. (1998) Glaciers and Glaciations. Arnold, London.
Bhattacharya, H.N., and Bhattacharya, B. (2006) A Permo-Carboniferous Tide-Storm Interactive System: Talchir Formation, Raniganj Basin, India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.27, pp.303–311.
Bhattacharya, H.N. and Bhattacharya, B. (2010) Soft-sediment deformation structures from an ice-marginal storm-tide interactive system, Permo-Carboniferous Talchir Formation, Talchir Coal basin, India. Sediment. Geol., v.223, pp.380–389.
Bhattacharya, H.N. and Bhattacharya, B. (2011) Sole marks in storm beds from a glacially influenced late Paleozoic shallow sea, Talchir Formation, Talchir Basin, India. Indian Jour. Geosciences, v.65(3), pp.175–188.
Bhattacharya, H.N. and Bhattacharya, B. (2015) Lithofacies architecture and paleogeography of late Paleozoic glacio-marine Talchir Formation, Raniganj Basin, India. Jour. Palaeogeo., v.4(3), pp.269–283.
Bhattacharya, B. and Bhattacharya, H.N. (2007) Implications of trace fossil assemblages from Late Paleozoic glacio-marine Talchir Formation, Raniganj Basin, India. Gondwana Res., v.12, pp.509–524.
Bhattachrya, H. H., Mukhopadhyay, G. and Bose, P.K. (1989) Hummocky cross stratification and its hydraulic and climatic implications in Talchir Formation, Dudhi nala, Hazaribag, Bihar, India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.34, pp.398–404.
Blanford, W. T., Blanford, H. F. and Theobald, W. (1856) On the geological structure and relations of the Talchir coal field in the district of Cuttack. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.1, pp.33–89.
Carver, R. E. (1971) Heavy mineral separation. In: Carver, R. E. (Ed.), Procedure in sedimentary petrology. John Wiley and Sons, pp.427-452.
Casshyap, S. M. and Qidwai, H.A. (1974) Glacial sedimentation of Late Paleozoic Talchir diamictite, Pench Valley Coal field, Central India. Bull. Geol. Soc. Amer., v.85, pp.749–760.
Casshyap, S. M. and Srivastava. V. K. (1987) Glacial and proglacial Talchir sedimentation in Son-Mahanadi Gondwana basin: paleogeographic reconstruction. Amer. Geophys. Union, pp.167-181.
Das, D., Saha, T. and Bhattacharya, R. (1993) Sedimentological studies of sub-surface Gondwana sediments of Bengal Basin. Gond. Geol. Mag., Birbal Sahni Center. Nat. Symp. Spec. v.2, pp.19–23.
Davis, J.C. (2002) Statistics and data analysis in geology. John Wiley and Sons Deshpande, G.G. (1971) On the occurrence of stromatilitic limestone boulders in the Talchir Boulder Bed, Nagpur. Proc. Indian Sci. Cong., v.3, pp.29–30.
Deshpande, G. G. (1996) Geology of Maharashtra. Geol. Soc. India, Bangalore, 223p.
Dickinson, W.R. and Suczek, C.A. (1979). Plate tectonics and sandstone composition. Bull. Amer. Assoc. Petrol. Geol., v.63, pp.2164–2182.
Dutta, A.B. (1965) Fenestella sp. From Talchirs of Daltonganj coal field, Bihar. Quat. Jour. Geol. Min. Metal Soc. India, v.37, pp.124–133.
Edwards, M. (1986). Glacial environment. In: Reading, H.G. (Ed.), Sedimentary environments and facies. Blackwell scientific publications, Oxford, London, Edinburgh, Boston, Melbourne. pp.445–470.
Eyles, N., Eless, C.H. and Miall, A.D. (1993) Lithofacies type and vertical profile models: an alternative approach to the description and environmental interpretation of glacial diamict and diamictite sequence. Sedimentology, v.30, pp.394–410.
Folk, R.L. and Ward, W.C. (1957). Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. Jour. Sed. Pet., v.27(1), pp.3–26.
Folk, R.L. (1965) Petrology of sedimentary racks. Hemphill’s Austin, Texas, 159p.
Frakes, L.A. (1979) Climate throughout geological time. Elsevier scientific publishing company, New York.
Ghosh, S. K. (1954) Discovery of new locality of marine Gondwana formation. Sci. Cult. 19, 620p.
Ghosh, S.K. (2003) First Record of Marine Bivalves from the Talchir Formation of the Satpura Gondwana Basin, India: Palaeobiogeographic Implications. Gondwana Res., v.6(2), pp.312–320.
Gustavson, T.C., Ashley, G.M. and Bothroyal, J.C. (1975) Depositional sequences in glaciaolacustrine delta. In: Jopling, A.V. (Ed.), Glacio-fluvial and glacio-lacustrine sedimentation. Soc. Eco. Pal. Min. Spl. Pub., v.23, pp.123-136.
Hambrey, M.J. and Glasser, N.F. (2003) Glacial sediments: processes, environment and facies. In: Middleton, G.V. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of sediments and sedimentary rocks. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Doerdrecht.
Hota, R.N. (2011) Practical approach to petrology. CBS Publishers and distributors Pvt Ltd. New Delhi.
Ingram, R.L. (1971) Seive analysis. In: Carver, R.E. (Ed.), Procedures in sedimentary petrology. John Wiley and Sons, New York, London, pp.49–68.
Kriensley, D.H., Pye, K., Boggs, S.Jr. and Tovey, N.K. (1998) Backscattered scanning electron microscopy and image analysis of sediments and sedimentary rocks. Cambridge University Press, London, 193p.
Krinsley, D.H., and Doornkamp, J.C. (1973) Atlas of quartz surface textures. Cambridge University Press, London, 91P.
Lindholm, R.C. (1987) A practical approach to Sedimentology. Allen and Unwin, London, 276p.
Maejima, W., Das, R., Pandya, K. L. and Miako Hayashi. (2004) Deglacial control on sedimentation and basin evolution of Permo-Carboniferous Talchir Formation, Talchir Gondwana Basin, Orissa, India. Gondwana Res., v.7(2), pp.339–352.
Miller, J.M.G. (2012) Glacial sediments. In: Reading, H.G. (Ed.), Sedimentary Environments: processes, facies and Stratigraphy Wiley India.
Mukhopadhyay, G. and Bhattachrya, H. H. (1996) Facies analysis of Talchir sediments (Permo-Carboniferous), Dudhi nala, Hazaribag, Bihar, India-A glacio-marine model. Ninth Internat. Gond Symp. Hyderabad, India, v.2, pp.737–753.
Murkute, Y.A. (2003) Sedimentological Attributes of Sandstones from Talchir Formation, Chimur Area, Chandrapur District, Maharashtra. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.61, pp.471–456.
Murkute, Y.A. (2009) Petrography of Upper Member Barakar Sediments, Umrer coal Basin, Nagpur District. Gondwana Geol. Mag., v.24(1), pp.19–27.
Murkute, Y.A. (2013) Sediment characteristics and depositional environments of Lower Gondwana Sediments, Chandrapur District, Maharashtra. Gondwana Geol. Mag. v.28(2), pp.131–140.
Murkute, Y.A. (2015) Report on Glaciogenic Talchir Deposits from Koradi Area, Nagpur District, Central India: Lithofacies and Petrography. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.85 (4), pp.439–449.
Nichols, G. (2012) Sedimentology and Stratigraphy. Wiley-Blackwell, India Niyogi, D. (1961) Pattern of Talchir sedimentation in Burhari Gondwana basin, Bihar. Jour. Sed. Petrol., v.31(1), pp.63–71.
Pandya, K.L. (1987) Some usual structures in the Talchir Group, Talchir Gondwana basin, Orissa. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.30, pp.305–308.
Pandya, K. L. (1990) Lithofacies and environments of deposition of a part of Talchir Group, Gondwana Basin, Orissa. Jour. Geol. Soc. India. v.36(2), pp.175–186.
Pettijohn, F. J. (1984) Sedimentary rocks. CBS publishers and Distributors, Delhi, 628p.
Potter, P. E. and Pettijohn, F. J. (1977) Paleocurrent and Basin Analysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Rains, R. B., Selby, M. S. and Smith, C. J. R. (1980) Polar desert sandar, Antarctica. NZ. Jour. Geol. Geophy., v.23, pp.595–604.
Raiverman, V. (1986) Depositional model of Gondwana sediments in Pranhita-Godavari graben, South India. Bull. Geol. Min. Met. Soc. India, v.54, pp.66–90.
Raja Rao, C.S. (1982) Coal resources of Tamil-Nadu, Andhra pradesh, Orissa and Maharashtra. Coal fields of India. Geol. Surv. India., Bull. Ser. A 15, pp.62-93.
Reed, F. R. C. (1928) A Permo-Carboniferous marine fauna from Umaria coal field. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.60(4), pp.469–476.
Reineck, H. E. and Singh, I. B. (1973) Depositional sedimentary environments. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heideberg, New York, 549p.
Saha, R. and Shingate, S. K. (1994) Deposition history of Kamthi basin, northern part of Pranhita-Godavari valley graben, Maharashtra, India. Ninth Internat. Gond. Symp. Hyderabad, v.2, pp.723–736.
Sarkar, S., Ghosh, S.K. and Chakraborty, C. (2009) Ichnology of a Late Palaeozoic ice-marginal shallow marine succession: Talchir Formation, Satpura Gondwana basin, central India. Paleogeography, Paleoclimetology, Paleoecology, v.283(1–2), pp.28–45.
Sen, D.P. and Hatim, A. (1977) Talchir (Lower Gondwana) sedimentation in Daltonganj coalfield, Bihar, India. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.18, pp.563–569.
Setlow, L. W. and Karpovich, R. P. (1972) Glacial micro-textures on quartz and heavy mineral sand grains from the littoral environment. Jour. Sed. Pet., v.42(4), pp.864–875.
Soman, G. R. and Kale, M. G. (1993). Sedimentological studies of Talchirs from Ghonad area, Pranhita-Godavari Basin. Gond. Geol. Mag. Birbal Sahni Cente. Net. Symp. Spl. vol., pp.100-115.
Suttner, I. J. and Dutta, P. K. (1986) Alluvial sandstones composition and palaeoclimate framework mineralogy. Jour. Sed. Pet., v.56, pp.329–345.
Tewari, R. C., Hota, R. N. and Maejima, W. (2012) Fluvial architecture of Early Permian Barakar rocks of Korba Gondwana basin, eastern-central India. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.52, pp.43–52.
Trewin, N. (1988) Use of the scanning electron microscope in sedimentology. In: Tucker, M. (Ed.), Techniques in sedimentology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, London, Edinburgh, Boston, Palo, Alto, Melbourne, pp.229–394.
Whalley, W.B. and Krinsley, D.H. (1974) A scanning electron microscope study of surface textures of quartz grains from glacial environments. Sedimentology, v.21(1), pp.87–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murkute, Y.A. Reappraisal on Depositional Environments of Glaciogenic Talchir Sediments around Savarla Village from Bandar Basin, Chandrapur District, Central India. J Geol Soc India 94, 367–374 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1324-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1324-4