Abstract
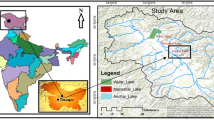
River estuarine samples are a complex repository of terrestrial and nearshore geophysical changes. Sediment core raised from the Gad river estuary, situated in Maharashtra state of India, was analyzed to understand their rock magnetic, particle size and geochemical characteristics. These three parameters are closely related to one another signifying detrital model of deposition, devoid of soft diagenetic changes. The magnetic grain size and particle grain size constraining the domain structure and physical structure respectively, are both in consonance with chemical elements that are amenable largely to physical comminution. The integrated approach of this nature has been tried for the first time on estuarine samples of India. Mineral magnetism utilises the magnetic behaviour of a material to interpret environmental processes acting upon it.
The study unraveled two-tier climate-induced modifications to erosional activity, suggesting abrupt change at 20 cm depth in a 45 cm core. The magnetic characteristics are seen to be controlled by the presence of ferrimagnetic minerals. Rock magnetic results (χlf, ARM, SIRM) and Curie temperature reveal that low-coercivity magnetite (and/or titanomagnetite) is the dominant magnetic mineral. χlf is more at the bottom and less at the top. Magnetic grain size is coarse at the top and fine at the bottom. Clay and silt proportion is more at the top of the core and that of sand is more at the bottom. Concentration of detrital geochemical elements like Al, Ti and Cr are less at the top and more at the bottom of the core, corroborated by chemical index of weathering and chemical index of alteration. Thus, it is clear from χlf that magnetic minerals are more at the bottom and so are the detrital minerals like Al, Ti and Cr, along with sand. This reveals energy conditions were vigorous at the time of the deposition of these entities at the bottom, which eased out at the top and are corroborated by the presence of clay and silt, having correspondingly low Al, Ti and Cr with low χlf.
Micromorphological features revealed abrasion pits, grooves and bumped edges on sub-angular grains, which indicate moderate transport distance under moderate to low energy conditions revealing terrestrial origin of this material. Thus, similar studies in other estuarine complexes can be used as a proxy to understand monsoonal or environmental changes initiated by neotectonic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, E. (1972) Coastal geomorphology of India, (Orient Longman, Bombay). pp.222.
Blake, W.H., Wallbrink, P.J., Doerr, S.H., Shakesby, R.A., Humphreys, G.S. (2006) Magnetic enhancement in wildfire-affected soil and its potential for sediment-source ascription. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, v.31, pp.249–264.
Blundell, A., Dearing, J.A., Boyle, J.F., Hannam, J.A. (2009) Controlling factors for the spatial variability of soil magnetic susceptibility across England and Wales. Earth Sci. Rev., v.95, pp.158–188
Booth, C.A., Fullen, M.A., Walden, J., Smith, J.P., Hallett, M.D., Harri, J., Holland, K. (2005) Magnetic Properties of Agricultural Topsoils of the Isle of Man: Their Characterization and Classification by Factor Analysis. Soil Science and Plant Analysis, v.36, pp.1241–1262.
Bradák, B., Thamó-Bozsó, E., Kovács, J., Márton, E., Csillag, G., Horváth, E. (2011) Characteristics of Pleistocene climate cycles identified in Cérna Valley loess- paleosol section (Vértesacsa, Hungary). Quaternary Internat., v.234, pp.86–97.
Caitcheon, G.G. (1993) Sediment source tracing using environmental magnetism: A new approach with examples from Australia. Hydrological Processes, v.7, pp.349–358.
Caitcheon G.G. (1998) The significance of various sediment mag.etic mineral fractions for tracing sediment sources in Killimicat Creek. Catena, v.32, pp.131–142.
Crosby, C.J., Booth, C.A., Appasamy, D., Fullen, M.A., Farr, K. (2014) Mineral magnetic measurements as a pollution proxy for canal sediments (Birmingham Canal Navigation Line). Environ. Tech. (UK), v.35, pp.432–445.
Dearing, J., Livingstone, I.P., Bateman, M.D., White, K. (2001) Palaeoclimate records from OIS 8.0-5.4 recorded in loess-palaeosol sequences on the Matmata Plateau, southern Tunisia, based on mineral magnetism and new luminescence dating. Quaternary Internat., v.76–77, pp.43–56
Dixit, K.R. (1976) Drainage basins of Konkan—forms and characteristics. Natl. Geogr. Jour. India, v.22, pp.79–105.
Dürr, H.H., Laruelle, G.G., van Kempen, C.M., Slomp, C.P., Meybeck, M., Middelkoop, H. (2011) Worldwide typology of nearshore coastal systems: defining the estuarine filter of river inputs to the oceans. Estuaries Coasts, v.34, pp.441–458.
Evans, M.E. and Heller, F. (2003) Environmental Magnetism: Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics. Academic Press, San Diego, USA
Engstrom, D.R. and Wright, H.E. (1984) Chemical stratigraphy of lake sediments as a record of environmental change. In Lund, J. W. G. and Haworth, E.Y. (Eds.), Lake Sediments and Environmental History, University of Leicester Press, Leicester, pp.11–67.
Fassbinder, J.W.E., Stanjek, H. (1994) Magnetic properties of biogenic soil greigite (Fe3S4). Geophys. Res. Lett., v.21, pp.2349–2352
Foster, I.D.L., and Walling, D.E. (1994) Using reservoir deposits to reconstruct changing sediment yields and sources in the catchment of the Old Mill Reservoir, South Devon, UK, over the past 50 years. Hydrological Sci., v.39, pp.347–368
Gathorn-Hardy, F.J., Erlendsson, E., Langdon, P.G., Edwards, K.J. (2009) Lake sediment evidence for late Holocene climate change and landscape erosion in western Iceland. Jour. Paleolimnology, v.42, pp.413–426
Geiss, C.E., Umbanhowar, C.E., Cammil, P., Banerjee, S.K. (2003) Sediment magnetic properties reveal Holocene climate change along Minnesota prairie-forest ecotone. Jour. Paleolimnol, v.30, pp.151–166
Gujar Anup, R., Nawso V. Ambre, Premchand, G. Mislankar and Sridhar D. Iyer (2010) Ilmenite, Magnetite and Chromite Beach Placers from South Maharashtra, Central West Coast of India. Resource Geol., v.60(1), pp.71–86.
Gurney, S.D. and White, K. (2005) Sediment magnetic properties of glacial till deposited since the Little Ice Age maximum for selected glaciers at Svartisen and Okstindan, northern Norway. Boreas, v.34, pp.75–83.
Hannam, J.A., Dearing, J.A. (2008) Mapping soil magnetic properties in Bosnia and Herzegovina for landmine clearance operations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.274, pp.285–294.
Harnois, L. (1988) The CIW index: a new chemical index of weathering. Sediment. Geol., v.55, pp.31–32.
Heller, F. and Evans, M.E. (1995) Loess magnetism. Reviews of Geophysics, v.33, pp.211–240.
Hounslow, M.W., Morton, A.C. (2004) Evaluation of sediment provenance using magnetic mineral inclusions in clastic silicates: comparison with heavy mineral analysis. Sediment. Geol., v.171, pp.13–36
Jenkins, P.A., Duck, R.W., Rowan, J.S. and Walden, J. (2002) Fingerprinting of bed sediment in the Tay Estuary, Scotland: an environmental magnetism approach. Hydrology and Earth System Sci., v.6, pp.1007–1016.
Kotlia, B.S., Sanwal, J., Bhattacharya, S.K. (2008) Climatic record between ca. 31 and 22 ka BP in east-central Uttarakhand Himalaya, India. Himalayan Geol., v.29, pp.25–33.
Maher, B.A. (1998) Magnetic properties of modern soils and Quaternary loessic paleosols: paleoclimatic implications. Palaeogeo., Palaeoclimat., Palaeoeco., v.137, pp.25–54
Maher, B.A. and Taylor, R.M. (1988) Formation of ultra fine-grained magnetite in soils. Nature, v.336, pp.368–370.
Maher, B.A., Thompson, R., Hounslow, M.W. (1999) Quaternary Climates, Environments and Magnetism. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Maher, B.A., Alekseev, A., Alekseeva, T. (2003) Magnetic mineralogy of soils across the Russian Steppe: climatic dependence of pedogenic magnetite formation. Palaeogeo. Palaeoclimat. Palaeoeco. v.201, pp.321–341.
Maher, B.A. (2007) Environmental magnetism and climate change. Contemp. Phys., v.48, 247–274.
Maher, B.A., Moore, C., Matzka, J. (2008) Spatial variation in vehicle-derived metal pollution identified by magnetic and elemental analysis of roadside tree leaves. Atmospheric Environment, v.42, pp.364–373.
Mitchell, S.B., Jennerjahn, T.C., Vizzini, S., Zhang, W. (2015) Changes to processes in estuaries and coastal waters due to intense multiple pressures - an introduction and synthesis. In: Mitchell, S.B., Jennerjahn, T.C., Vizzini, S., Zhang, W. (Eds.), Changes to Processes in Estuaries and Coastal Waters Due to Intense Multiple Pressures (Special Issue) Estuar Coastal Shelf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2014.12.027.
Mühs, D.R., Bertis, E.A., Been, J., McGeehin, J.P. (2001) Impact of climate and parent material on chemical weathering in loess derived soils of the Mississippi river valley. Soil Sci. Soc. Amer., v.J65, pp.1761–1777
Nesbitt, H.W., Young, G.M. (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of Lutites. Nature, v.299, pp.715–717
Nolan, S.R., Bloemendal, J., Boyle, J.F., Jones, R.T., Oldfield, F., Whitney, M. (1999) Mineral magnetic and geochemical records of late Glacial climatic change from two northwest European carbonate lakes. Paleolimnology, v.22, pp.97–107
Ojala, A.E.K., Kubischta, F., Kaakinen, A., Salonen, V.P. (2011) Characterization of diamictons on the basis of their mineral magnetic properties in Murchisonfjorden, Nordaustlandet, Svalbard. Sediment. Geol., v.233, pp.150–158
Oldfield, F. (1991) Environmental Magnetism - A personal perspective. Quaternary Sci. Rev., v.10, pp.73–85.
Oldfield, F. (1994) Toward the discrimination of fine grained ferrimagnets by magnetic measurements in lake and near-shore marine sediments. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.99, pp.9045–9050.
Oldfield, F. (2007) Sources of fine grained magnetic minerals in sediments. A problem revisited. Holocene, v.17(8), pp.1265–1271.
Oldfield, F., Battarbee, R.W., Boyle, J.F., Cameron, N.G., Davis, B., Evershed, R.P. (2010) Terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem responses to late Holocene climate change recorded in the sediments of LochanUaine, Cairnorms, Scotland. Quaternary Sci. Rev., v.29, pp.1040–1054
Peters, C. and Dekkers, M.J. (2003) Selected room temperature magnetic parameters as a function of mineralogy, concentration and grain size. Phys. Chem. Earth., v.28, pp.659–667.
Paranjpe, S.C. (2000) Climatic classification of Maharashtra State based on methods proposed by Thronwaite. In: Groundwater Surveys and Development Agency Seminar volume “Integrated approach for strengthening and protecting drinking water sources”, IUCCA, Pune, pp.489–498.
Robinson, S.G. (1986) The Late Pleistocene paleoclimatic record of North Atlantic deep-sea sediments revealed by mineral-magnetic measurements. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., v.42, pp.22–47.
Sagnotti, L., Florindo, F., Wilson, G.S., Roberts, A.P., Verosub, K.L. (1998) Environmental magnetism of lower Miocene strata from the CRP-1 core, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Terra Antarctica, v.5, pp.661–667
Snowball, I.F. (1991) Magnetic hysteresis properties of greigite (Fe3S4) and a new occurrence in Holocene sediments from Swedish Lappland. Phys. Earth Planet. Int., v.68, pp.32–40
Snowball, I., Thompson, R. (1990) A stable chemical remanence in Holocene sediments. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.95, pp.4471–4479
Sukhtankar, R.K. (1995) An evolutionary model based on geomorphologic and tectonic characteristics of the Maharashtra Coast, India. Quaternary Internat., v.26, pp.131–137.
Sun, D., Bloemendal, J., Yi, Z., Zhu, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Wang, F., Han, F., Zhang, Y. (2011) Palaeomagnetic and palaeoenvironmental study of two parallel sections of late Cenozoic strata in the central Taklimakan Desert: Implications for the desertification of the Tarim Basin. Palaeogeo., Palaeoclimat., Palaeoeco., v.300, pp.1–10
Thompson, R. and Oldfield, F. (1986) Environmental magnetism. Allen & Unwin, London
Valero-Graces, B.L., Gonzalez-Samperiz, P., Delgado-Huertas, A., Navas, A., Machin, J., Kelts, K. (2000) Late glacial and late Holocene environmental and vegetational change in Salada Mediana, central Ebro basin, Spain. Quaternary Internat., v.74, pp.29–46
Walden, J.F., Oldfield, F., Smith, J. (1999) Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide, No.6. Quaternary Res. Assoc., London, 243p.
Walden, J. and Ballantyne, C.K. (2002) Use of environmental magnetic measurements to validate the vertical extent of ice masses at the Last Glacial Maximum. Jour. Quaternary Sci., v. 17, pp.193–200
Wang, X.S. (2013) Heavy metal pollution in urban top soils: Mineralogical analyses and magnetic characterization. Environ. Earth Sci., v.70, pp.3155–3161
Weinert, H.H. (1965) Climatic factors affecting the weathering of igneous rocks. Agric. Meteorol., v.2, pp.27–42
White, A.F., Blum, A.E. (1995) Effects of climate on chemical weathering in watersheds. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.59, pp.1729–1747
Zabel, M., Schneider, R.R., Wagner, T., Adesina, A.T., Vries, U., Kolonic, S. (2001) Late Quaternary climatic changes in central Africa as inferred from terrigenous input to the Niger Fan. Quaternary Res., v.56, pp.207–217.
Zhang, C., Huang, B., Piper, J.D.A., Luo, R. (2008) Biomonitoring of atmospheric particulate matter using magnetic properties of Salixmatsudana tree ring cores. Science of the Total Environment v.393, pp.177–190.
Acknowledgements
IIG Director Prof. D.S. Ramesh is thanked for permission to publish this research article, and for constant encouragement and support. Dr P.T. Hanamgond, acknowledges the financial support by University Grants Commission, New Delhi (F.No.33-42/2007 (SR)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gawali, P.B., Hanamgond, P.T., Lakshmi, B.V. et al. Applicability of Magnetic and Geochemical Characterization Techniques to Assess the Evolution of Estuarine Systems: A Case Study of Gad River Estuary Sediments, Maharashtra. J Geol Soc India 94, 267–274 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1306-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1306-6