Abstract
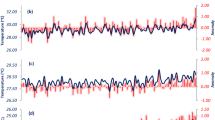
Direct information about climate change from meteorological surface air temperature records are available in India only since 1901 A.D. Meteorological surface air temperature (SAT) data for the period 1901–2006 from 49 sites in peninsular India have been combined with the geothermal data from 146 sites to extract a baseline (or pre-observational mean, POM) surface temperature prior to the existence of the observational record in the region. Periodicities of 5, 11 and 22 years in the SAT time series have little influence on the combined analysis to infer long-term climate change. The best estimate of the long-term average temperature for the 19th Century is 0.7 °C lower than the 1961–1990 mean temperature. Considering the additional warming of 0.38°C relative to the 1961–1990 mean over a 10-year window centred on the year 2000, the hybrid POM-SAT method suggests that the total surface warming in peninsular India from mid-1800s to early- 2000s is about 1.1 °C. The study provides new evidence for significant warming prior to the establishment of widespread meteorological stations in peninsular India.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akkiraju, V.V. and Roy, S. (2011) Geothermal Climate Change Observatory in South India 1: Borehole temperatures and inferred surface temperature histories. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, v.36, pp.1419–1427.
Akkiraju, V.V., Roy, S. and Shalivahan (2018) Ground surface warming in peninsular India: evidence from geothermal records. Curr. Sci. (in press).
Carslaw, H.S. and Jaeger, J.C. (1959) Conduction of Heat in Solids. Second Edition, Oxford University Press, New York, 386p.
Chisholm, T.J., Chapman, D.S. (1992) Climate change inferred from analysis of borehole temperatures: An example from western Utah. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.97, pp.14,155–14,175.
Chapman, D.S., Chisholm, T.J. and Harris, R.N. (1992) Combining borehole temperature and meteorologic data to constrain past climate change. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol., v.98, pp.269–281.
Chapman, D.S. and Harris, R.N. (1993) Repeat temperature measurements in borehole GC-1, Northwestern Utah: Towards isolating a climate-change signal in borehole temperature profiles. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.20(18), pp.1891–1894.
Davis, M.G., Harris, R.N. and Chapman, D.S. (2010) Repeat temperature measurements in boreholes from northwestern Utah link ground and air temperature changes at the decadal time scale. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.115, B05203, doi:10.1029/2009JB006875.
Hansen, J., Lebedeff, S. (1987) Global trends of measured surface air temperatures. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.92, pp.13,345–13,372.
Harris, R.N. (2007) Variations in air and ground temperature and the POMSAT model: results from the Northern Hemisphere. Clim. Past, 3, 611–621.
Harris, R.N., Chapman, D.S. (1995) Climate change on the Colorado Plateau of eastern Utah inferred from temperatures. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.100, pp.6367–6381.
Harris, R.N. and Chapman, D.S. (2001) Mid-Latitude (30°–60° N) climatic warming inferred by combining borehole temperatures with surface air temperatures. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.28, pp.747–750.
Harris, R.N. and Chapman, D.S. (1997) Borehole temperatures and a baseline for 20th-century global warming estimates. Science, v.275, pp.1618–1621.
Harris, R.N. and Chapman, D.S. (1998a) Geothermics and climate change: 1. Analysis of borehole temperatures with emphasis on resolving power. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.103, pp.7363–7370, doi:10.1029/97JB03297.
Harris, R.N. and Chapman, D.S. (1998b) Geothermics and climate change: 2. Joint analysis of borehole temperatures and meteorological data. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.103, pp.7371–7383. doi:10.1029/97JB03296.
Harris, R.N. and Gosnold, W.D. (1999) Comparisons of borehole temperaturedepth profiles and surface air temperatures in the northern plains of the USA, Geophys. Jour. Internat., v.138, pp.541–548.
Hingane, L.S., Rupakumar, K. and Ramamurthy, B.V. (1985) Long term trends of surface air temperature in India. Jour. Climatol., v.5, pp.521–528.
Lachenbruch, A.H., Cladouhos, T.T. and Saltus, R.W. (1988) Permafrost temperature and the changing climate, in Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Permafrost, Trondheim, v.3, pp.9–17.
Lachenbruch, A.H. and Marshall, B.V. (1986) Changing climate: Geothermal evidence from permafrost in the Alaskan Arctic. Science, v.234, pp.689–696, doi:10.1126/science.234.4777.689.
Roy, S. and Chapman, D.S. (2012) Borehole temperatures and climate change: Ground temperature change in south India over the past two centuries. Jour. Geophys. Res. v.117, doi: 10.1029/2011JD017224.
Roy, S., Harris, R.N., Rao, R.U.M. and Chapman, D.S. (2002) Climate change in India inferred from geothermal observations. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.107, doi: 10.1029/2001JB000536.
Rupa Kumar, K., Krishna Kumar, K. and Pant, G.B. (1994) Diurnal asymmetry of surface temperature trends over India. Geophys. Res. Lett., v.21, pp.677–680.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkiraju, V.V., Roy, S., Tiwari, V.M. et al. A 19th Century Baseline Temperature Estimate for Peninsular India from Combined Analysis of Geothermal and Meteorological Records. J Geol Soc India 92, 542–547 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1064-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1064-x