Abstract
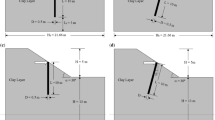
Slope stability has been identified as a major obstacle to construction in the rapidly developing countries of Indonesia and Malaysia. In these countries, slope failure has been identified as one of the most commonly occurring natural disasters, leading to financial losses and deaths. Slope failure is often related to prolonged rainfall events where rainfall infiltration increases pore water pressure, reducing soil strength. This failure mechanism will accelerate with the existence of cracks, which are usually caused by differential settling, drying and shrinking of soil, and associated construction activities, among other causes. The existence of cracks on slopes usually provides an easy pathway for rainfall infiltration into soil, allowing rain to infiltrate to deeper layers than in the absence of cracks. The moisture content in deep layers is therefore higher in cracked slopes than in slopes without cracks. To address this issue, we investigated the effects of cracks on slope stability when subjected to rainfall. The influence of crack location, depth, size, and direction on pore water pressure distribution and slope stability was studied by imposing different rainfall intensities. Analysis of seepage and stability were conducted using the GEO STUDIO 2007 softwares SEEP/W and SLOPE/W. Results suggested that pore water pressure and slope stability were influenced by the existence of cracks. Analysis showed that slope factors of safety decreased sharply when cracks were located adjacent to the slope crest, as compared to when cracks were located in the middle of the slope. Furthermore, slope factors of safety decreased with increasing crack depth. Pore water pressure and slope factors of safety decreased further when slopes were subjected to small rainfall intensities for long periods, as compared to when slopes were subjected to high rainfall intensities for short periods. The present study shows that study of cracks should be an integral part of the slope stability analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, A.W. (1967) Progressive failure-with special references to the mechanism causing it. Proceedings of the Geotechnical Conference of Oslo, Norway. Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Oslo, Norway, v.2, pp.142–150.
Fan, P., Liu, Q., Li, J. and Sun, J. (2005) Numerical analysis of rainfall infiltration in the slope with a fracture. Science in China Series E Engineering & Materials Science,v. 48(1), pp.107–120.
Fredlund, D.G., Morgenstern, N.R. and Widger, R.A. (1978) The shear strength of unsaturated soils. Canadian Geotechnical Jour., v.15(3), pp.313–321.
Fredlund, D. G. and Rahardjo, H. (1993) Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils, New York, John Wiley & Sons.
Gavin, K. and Xue, J. (2008) A simple method to analyze infiltration into unsaturated soil slopes. Computer and Geotechnics. v.35(2), pp.223–230.
Geo-slope International Ltd., (2012a) Seep/W, Groundwater seepage analysis. GEO-SLOPE International Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Geo-slope International Ltd., (2012b) Slope/W, Slope stability analysis. GEOSLOPE International Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Gue, S.S. and Tan, Y.C. (2006) Land slides: Case histories, lessons learned and mitigation measures. Land slide, Sinkhole, Structure Failure: Myth or Science, pp.1–18.
Gui, M.W. and Han, K.K. (2008) A case study on infiltration effect on the stability of two slopes. Land slides and Engineered Slopes. pp.1737–1743.
Mukhlisin, M., and Aziz, N.A.A. (2016) Study of horizontal drain effect on slope stability. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.87(4), pp.483–490.
Nurly, G., Lee, M.L. and Asof, M. (2006) Transient seepage and slope stability analysis for rainfall-induced land slide: A case study. Malaysian Jour. Civil Engg., v.18(1), pp.1–13.
Reddi, L.N. (2003) Seepage in Soils, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New Jersey.
Richards, L.A. (1931) Capillary conduction of liquid through porous medium. Jour. Physics 1, v.1(5), pp.318–333.
Robertson, A.M.G. (1971) Accounting for Cracks in Slope Stability Analysis, Fifth Regional Conference for Africa on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering.Luand a Angola (Portuguese West Africa): pp.1–7.
Suryo, E.A., Gallage, C., Trigunarsyah, B., Indrasurya, B.M. and Ria, A.A.S. (2011) Application of Electrical Resisitivity Method to detect deep cracks in unsaturated residual soil slope. Unsaturated Soils: Theory and Practice 2011. Jotisankasa, Sawangsuriya, Soralump and Mairaing (Eds.), Kasetsart University, Thailand. pp.901–906.
Wang Z.F. Li, J.H. and Zhang, L.M. (2011) Influence of Cracks on the Stability of a Cracked Soil Slope, Unsaturated Soils: Theory and Practice 2011. Jotisankasa, Sawangsuriya, Soralump and Mairaing (Eds.) Kasetsart University, Thailand, pp.721–727.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhlisin, M., Khiyon, K.N. The Effects of Cracking on Slope Stability. J Geol Soc India 91, 704–710 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0927-5