Abstract
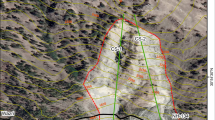
The Saptashrungi gad temple (SGT) situated on basaltic hills belongs to Deccan volcanic of Upper Cretaceous to Lower Eocene, is one among the 51 Shakti Peeths and most holy place for pilgrims. Rockfall is a major problem in the past and causing danger to the lives of the villagers settled at the toe of the SGT hill as well as the pilgrims who perform parikrama along the tracks. On the evening of 16 April 2011, an old woman died due to rockfall at SGT hill when she was performing parikrama, moreover, two persons got injured during the deliverance process of this old woman from the continuous rockfall activity. The problem of rockfall could be linked to rainfall, jointing, weathering, man-made or the compounding of all. In this research, the rockfall hazard analysis at SGT hill is assessed using both 2D and 3D rockfall programs along the two parikrama paths: Parikrama Path 1 (or the Badi Parikrama Path ‘BPP’), and Parikrama Path 2 (or the Chhoti Parikrama Path ‘CPP’). Also, the study area of the SGT hill has been divided into eight zones (Zone#01 to Zone#08), based on field observations, orientations of joint sets and hill slope faces and eighteen topographic profiles (AA' to RR') have been taken from these eight zones for rockfall analysis. A detailed topographic survey along with field investigation has been carried out along the temple for ascertaining the nature of rock, discontinuity orientations, and slope geometry. DEM has been generated using topographic profile in ArcGIS to facilitate the 3D rockfall analysis. Maximum rock block sizes are taken into the analysis and run-out distance, bounce height, kinetic energy and velocity of the basaltic blocks are evaluated separately. Based on the analyzed data, the rockfall hazard zone map has been prepared and site having potential rockfall risks have been identified. Finally, wire/net meshing has been proposed after removal of unstable blocks as a stabilization and protection measures.
It is worth mentioning here that for the first time rockfall hazard assessment was made in such detail for a site. Suggestions made are implemented by the State Government for the protection of the temple as well as the life of pilgrims performing the parikrama from the rockfall.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Umrao, R.K., Ansari, M.K., Singh, R., Singh, T.N. (2013), Assessment of Rockfall Hazard along the Road Cut Slopes of State Highway-72, Maharashtra, India. Geomaterials, v.3(1), pp.15–23.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, R., Singh, T.N. (2016a) Rockfall Slope Angle and its Effect on the Impact and Runout Distance of Falling Block: A Numerical Approach, Indorock-2016, Sixth Indian Rock Conference, IIT Bombay, Mumbai, pp.279–288.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Rajesh Singh, Singh, T.N. (2016b) Slope Stability Assessment of Saptashrungi Gad Temple, Vani, Nashik, Maharashtra, India–A Numerical Approach. Jour. Engg. Tech., v.4(1), pp.103–115.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, R., Singh, T.N. (2014a) Rockfall hazard assessment at Ajanta Cave, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. Arabian Jour. Geosci., v.7(5), pp.1773–1780.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, T.N. (2014b) Rockfall Hazard Analysis of Ellora Cave, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. Internat. Jour. Sci. Res., v.3(5), pp.427–431.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, T.N. (2014c) Rockfall risk assessment for pilgrims along the circumambulatory pathway, Saptashrungi Gad Temple, Vani, Nashik Maharashtra, India, Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, v.5(1), pp.81–92.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, R., Singh, T.N. (2014d) Laboratory Experiment for Coefficient of Restitution of Rocks and its Relation with Schmidt Rebound Number. Jour. African Earth Sci., v.104, pp.1–5.
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, R., Singh, T.N. (2012) Rockfall Assessment near Saptashrungi Gad Temple, Nashik, Maharashtra, India, Internat. Jour. Disaster Risk Reduction, v.22, pp.77–83.
Azzoni, A., La Barbera, G., Zaninetti, A., (1995) Analysis and prediction of rock falls using a mathematical model, International Jour. Rock Mech. Min. Sci., v.32(7), pp.709–724.
Beane, J.E., Turner, C.A., Hooper, P.R., Subbarao, K.V., Walsh, J.N. (1986) Stratigraphy, composition and form of the Deccan Basalts, Western Ghats, India. Bull. Volcanol., v.48, pp.61–83.
Chris, M., Ivan, H., David, P. (2006) A rockfall simulation study for housing development in Gibraltar. IAEG paper number 377.
Crosta, G.B., Agliardi, F. (2004) Parametric evaluation of 3D dispersion of rockfall trajectories, Natural Hazards Earth System Sciences, v.4(4), pp.583–598.
Dorren, L.K.A. (2003) A review of rockfall mechanics and modelling approaches. Progress in Physical Geography, v.27, pp.69–87.
Evans, S.G., Hungr, O. (1993) The assessment of rockfall hazard at a base of talus slopes. Canadian Geotech. Jour., v.30, pp.620–636.
Guzzetti, F., Crosta, G., Detti, R., Agliardi, F. (2002) STONE: a computer program for the three dimensional simulation of rock-falls. Computers and Geosciences, v.28, pp.1079–1093.
Hoek, E. (1987) Rockfall-A program in Basic for the analysis of rockfalls from slopes. Master Thesis, Department of Civil engineering, University of Toronto, Canada.
Lan, H., Martin, C.D., Lim, C.H. (2007) Rockfall Analyst: A GIS extension for three-dimensional and spatially distrubted rockfall hazard modeling, Computers and Geosciences, v.33, pp.262–279.
Maharshtra Times, 2011. Retrieved 05 March 2012, from http://maharashtra times.indiatimes.com/maharashtra/nashik/-/articleshow/8011123.cms
Mahoney, J., Macdougall, J.D., Lugmair, G.W., Murali, A.V., Das, M.S., Gopalan, K. (1982) Origin of the Deccan Trap flows at Mahabaleshwar inferred from Nd and Sr isotopic and chemical evidence. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.60, pp.47–60.
Pfeiffer, T.J., Bowen, T.B. (1989) Computer simulation of rock falls. Bull. Assoc. Engg. Geol., v.26(1), pp.135–146.
Rocscience (2004) RocFall software for risk analysis of falling rock on steep slope. Rocscience User’s Guide (/http: //www. rocscience. com/products/12/RocFall).
Ritchie, A.M. (1963) Evaluation of rockfalls and its control. Highways Research Record, v.17, pp.14–28.
Scioldo, G. (1991) ISOMAP and ROTOMAP, 3D surface modelling and rockfall analysis, Geo and Soft, Torino, Italy.
Sharma, L.K., Umrao, R.K., Singh, R., Ahmad, M. and Singh T.N. (2017) Stability Investigation of Hill Cut Soil Slopes along National Highway 222 at Malshej Ghat, Maharashtra. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.89, pp.65–174
Singh, P.K., Wasnik, A.B., Kainthola, A., Sazid, M. and Singh, T.N. (2013) The stability of road cut cliff face along SH-121: a case study. Natural Hazards, v.68(2), pp.497–507.
Singh, R., Umrao, R.K. and Singh, T.N. (2017) Hill Slope Stability Analysis using Two and Three Dimensions Analysis: A Comparative Study. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.89, pp.295–302.
Stevens, W. (1996) Rock fall 2.0, software for the analysis of falling rocks on a steep slope. BASc. Thesis. Department of Civil Engineering, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Topal, T., Akin, M., Ozden, A.U. (2007) Assessment of rockfall hazard around Afyon Castle. Environ. Geol., v.53(1), pp.191–200.
Varnes, D.J. (1978) Slope movement types and processes. Schuster, RL. And Krizek, RJ. Landslides-Analysis and Control, Transportation Research Board Special Report 176, National Academy of Sciences, Washington D.C., pp.11–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, M.K., Ahmad, M., Singh, R. et al. 2D and 3D rockfall hazard analysis and protection measures for Saptashrungi Gad Temple, Vani, Nashik, Maharashtra – A case study. J Geol Soc India 91, 47–56 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0819-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0819-8