Abstract
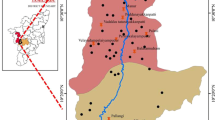
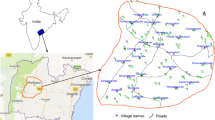
Hydrochemical studies were carried out in Mulugu-Venkatapur Mandals of Warangal district, Telangana state, India to find out the causes of high fluorides in groundwater and surface water causing a widespread incidence of fluorosis in local population. The fluoride concentration in groundwater ranges from 0.28 to 5.48 mg/l with a mean of 1.26 mg/l in pre-monsoon and 0.21 to 4.43 mg/l with a mean 1.45 mg/l in post-monsoon. About 32% and 34% of samples in pre and post-monsoon containing fluoride concentrations that exceed the permissible limit. The Modified Piper diagram reflects that, water belong to Ca+2-Mg+2-HCO3 - to Na+-HCO3 - facies. Negative chloroalkali indices in both the seasons prove that ion exchange took place between Na+ & K+ with Ca+2 and Mg+2 in aquatic solution in host rock. Different plots for major ions and molar ratios suggest that weathering of silicate rocks and water-rock interaction is responsible for major ion chemistry of water. High fluoride content in groundwater attributed to continuous water-rock interaction during the process of percolation with fluorite bearing country rocks under arid, low precipitation, and high evaporation conditions. The low calcium content in rocks and soils, and the presence of high content of sodium bicarbonate in soils and waters are important factors favouring high levels of fluoride in waters. The basement rocks provide abundant mineral sources of fluoride in the form of amphibole, biotite, fluorite, mica and apatite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrawal, V., Vaish, A. K. and Vaish, P. (1997) Groundwater quality-focus on fluoride and fluorosis in Rajasthan. Curr. Sci., v.73, pp.743–746.
Andezhath, S. K., Susheela, A. K. and Ghosh, G. (1999) Fluorosis management in India: The impact due to networking between health and rural drinking water supply agencies. IAHS-AISH Publication, v.260, pp.159–165.
Apambire, W. M., Boyle, D.R. and Michel, F.A. (1997) Genesis and health implications of fluori-ferrous groundwater in the upper regions of Ghana. Environ. Geol., v.35(1), pp.13–24.
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. American Public Health Association, Washington.
Ayoob, S. and Gupta, A.K. (2006) Fluoride in drinking water: a review on the status and stress effects. Critic Rev. Environ. Sci. Tech. v.36, pp.433–487.
Beck, B.F., Asmussen, L. and Leonard, R. (1985) Relationship of geology physiography, agriculture land use and groundwater quality in Southern Georgia. Groundwater, v.23(5), pp. 627–634.
BIS (1991) Specifications for drinking water IS: 1000:1991, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi. In the soils of Tallinn (Estonia). Environ. Geoche Health, v.22, pp.173–193.
Cerling, T.E., Pederson, B.L. and Damn, K.L.V. (1989) Sodium–calcium ion exchange in the weathering of shales implication for global weathering budgets. Geology, v.17, pp.552–554.
CGWB (2007) Central Ground Water Board. Ground Water Information, Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, pp.1–41.
CGWB (2013) Central Ground Water Board. Ground Water Information, Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, pp.1–25.
Chadha, D.K. (1999) A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrol. Jour., v.7, pp.431–439.
Chakraborti, D., Chanda, C.R., Samanta, G., Chowdhury, U.K., Mukherjee, S.C., Pal, A.B., Sharma, B., Mahanta, K.J., Ahmed, H.A. and Singh, B. (2000) Fluorosis in Assam, India. Curr. Sci., v.78, pp.1421–1423.
Datta, P.S., Deb, D.L. and Tyagi, S.K. (1996) Stable isotope (18O) investigations on the processes controlling fluoride contamination of groundwater. Jour. Contaminant Hydrol., v.24(1), pp.85–96.
Datta, P.S., Tyagi, S.K., Mookerjee, P., Bhattacharya, S.K., Gupta, N. and Bhatnagar, P.D. (1999) Groundwater NO3 and F contamination process in Pushkar Valley, Rajasthan as reflected from 18O isotopic signature and 3H recharge studies. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.56, pp.209–219.
Edmunds, W.M. and Smedley, P.L. (2005) Fluoride in natural waters. In: Selinus, O. (Ed.), Essentials of medical geology. Elsevier Academic Press, London, pp.301–329.
Elango, L. and Kannan, R. (2007) Rock–water interaction and its control on chemical composition of groundwater. In: Developments in Environmental Science, v.5, Chap 11. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp.22–243.
Fisher, R.S. and Mulican, W.F. (1997) Hydrogeochemical evolution of sodiumsulphate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the Northern Cnihvahvan desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas USA. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.10(4), pp.455–474.
Genuxu, W and Guodong, C (2001) Fluoride distribution in water and the governing factors of environment in arid north-west China. Jour. Arid Environ., v.49, pp.601–614.
Gibbs, R.J. (1970) Mechanisms controlling World’s water chemistry. Science, v.170, pp.1088–1090
GSI (1995) Geological Survey of India’s geology and minerals map of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Handa, B.K. (1975) Geochemistry and genesis of fluoride containing groundwaters in India. Ground Water, v.13(3), pp.275–281.
Handa, B.K. (1988) Fluoride occurrence in natural waters in India and its significance. Bhu-Jal News, v.3(2), pp.31–37.
Hem, J.D. (1991) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water, 3rd edn. USGS Water Supply Paper-2254:264. Scientific Publ., Jodhpur.
Huh, Y., Tsoi, M.Y., Zaitiser, A. and Eeward, J.N. (1998) The fluvial geochemistry of the river of Eastern Siberia-1 tributaries of Lena river drainage the sedimentation platform of the Siberia Craton. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.62, pp.1657–1676.
ISI (1983) Indian Standard Specification for Drinking Water. IS: 10500.
IWACO (1992) Water resources study AP-III vol. II main report. Rural Water Supply, AP, India Director-General of International Co-op, The Netherlands, pp 29, 40.
Jacks, G., Bhattacharya, P., Choudhary, V. and Singh, K.P. (2005) Controls on the genesis of some high fluoride ground waters in India. Appld. Geochem., v.20, pp.221–228.
Johnson, C.C. (1979) Land application of water -an accident waiting to happen. Ground Water, v.17(1), pp.69–72.
Kim, K. and Jeong, G.Y. (2005) Factors influencing natural occurrence of fluoride-rich ground-waters: a case study in the southeastern part of the Korean Peninsula. Chemosphere, v.58, pp.1399–1408.
Kundu, N., Panigrahi, M.K., Triparthy, S., Munshi, S., Powell, M.A. and Hart, B.R. (2001) Geochemical appraisal of fluoride contamination of groundwater in the Nayagarh district of Orissa, India. Environ. Geol, v.41, pp.451–460.
Muralidharan, D., Nair, A.P., Satyanarayana, U. (2002) Fluoride in shallow aquifers in Rajgarh Tehsil of Churu District, Rajasthan: an arid environment. Curr. Sci., v.83(6), pp.699–702.
Machender, G., Dhakate, R., Reddy, M.N. and Panduranga Reddy, I. (2014) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of surface water (SW) and groundwater (GW) of the Chinnaeru river basin, northern part of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Earth Sci, v.71(6), pp.2885–2910.
Madhnure, P., Sirsikar, D.Y., Tiwari, A.N., Ranjan, B. and Malpe, D.B. (2007) Occurrence of fluoride in the groundwaters of Pandharkawada area, Yavatmal District, Maharashtra, India. Curr. Sci., v.92, pp.675–679.
Mandel, S. and Shiftan, Z.L. (1981) Groundwater resources investigation and development. Academic, New York May AL, Loucks
MD(1995) Solute and isotope geochemistry and groundwater flow in the Central Wasatch Range, Utah. Jour. Hydrobiology, v.170, pp.795–840.
McIntosh, J.C. and Walter, L.M. (2006) Paleowater in Silurian–Devonian carbonate aquifers: geochemical evolution of groundwater in the Great Lakes region since Late Pleistocene. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.70, pp.2454–2479.
Meybeck, M. (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river-dissolved leads. Amer. Jour. Sci., v.287, pp.401–428.
Mor, S., Singh, S., Yadav, P., Rani, V., Rani, P., Sheoran, M., Singh, G and Ravindra, K. (2009) Appraisal of salinity and fluoride in a semi-arid region of India using statistical and multivariate techniques. Environ. Geochem. Health, v.31, pp.643–655.
Natarajan, V. and Murthy, S.R.N. (1974) Fluorite bearing granites in Shivannagudem area, Nalgonda District, AP. In: Proceedings of National Symposium on Fluorosis, India: Indian Academy of Geoscience, Hyderabad.
Natarajan, V. and Rao, M.V.R. (1974) Hydrochemical investigation for fluoride bearing minerals in Kangal and Hallia river basin, Nalgonda District, AP.In: Proceedings of National Symposium on Fluorosis, India: Indian Academy of Geoscience, Hyderabad.
Nordstrom, D.K. and Jenne, E.A. (1977) Fluorite solubility equilibria in selected geothermal waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.41, pp.175–188.
Pandian, K. and Sankar, K. (2007) Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality in the Vaippar River Basin, Tamil Nadu. Jour. Geol Soc. India, v.69, pp.970–982.
Pillai, K.S. and Stanley, V.A. (2002) Implications of fluoride-an endless uncertainty. Jour. Environ. Biology, v.23, pp.81–97.
Pophare, M.A. and Dewalkar, S.M. (2007) Groundwater quality in eastern and south eastern parts of Rajura Tehsil, Chendrapur district, Maharashtra. Gondwana Geol. Mag. Spec., v.11, pp.119–129.
RGNDWM (1993). Prevention & Control of fluorosis in India. Water Quality and Defluoridation Techniques, Volume II, Published by Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission, Ministry of Rural Development, New Delhi.
Ramesam, V. and Rajagopalan, K. (1985) Fluoride ingestion into the natural waters of hard-rock areas, peninsular India. Jour Geol. Soc. India, v.26, pp.125–132.
Ram Mohan Rao, N.V., Surya Prakasa Rao, K. and Schviling, R.D. (1993) Fluorine distribution in waters of Nalgonda district, AndhraPradesh, India. Environ Geol., v.21, pp.84–89.
Rao, S. (1997) The occurrence and behaviour of fluoride in groundwater of the Lower Vamsadhara River Basin, India Hg. Sci Jour., v.42(6), pp.877–892.
Rayamahashay, B.C. (1996) Geochemistry for hydrologists. Allied Publishers, New Delhi.
Reddy, A.G.S. and Rao, P.N. (2006) Occurrence, behaviour and genesis of fluoride in groundwater of Wailpalli watershed in Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Jour. Appld. Geochem., v.8(2A), pp.618–630.
Sahu, N.K. and Karim, M.A. (1989) Fluoride incidence in groundwaters in Amreli District, Gujarat. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.33, pp.450–456.
Sami, K. (1992) Recharge mechanism and geochemical processes in a semi arid sedimentary basin, South Africa. Jour. Hydrol., v.139, pp.27–48.
Shaji, E., Bindu Viju, J. and Thambi, D.S. (2007) High fluoride in groundwater of Palghat District, Kerala. Curr. Sci., v.92, pp.240–245
Sarin, M.M., Krishnaswamy, S., Dilli, K., Somayajula, B.L.K. and Moore, W.S. (1989) Major ion chemistry of the Ganga–Brahmaputra river system: weathering processes and fluxes to the Bay of Bengal. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.53, pp.997–1009.
Sastry, J.C.V. (1994) Groundwater chemical quality in river basins, hydrogeochemical facies and hydrogeochemical modeling. Lecture notesrefresher course conducted by school of Earth Sciences. Bharathidasan University, Thiruchirapalli.
Saxena, V.K. and Ahmed, S. (2001) Dissolution of fluoride in groundwater: a water-rock interaction study. Environ. Geol., v.40, pp.1084–1087.
Schoeller, H. (1967) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development, water research, series-33. UNESCO, pp. 44–52.
Singh, B. and Dass, J. (1993) Occurrence of high fluoride in groundwater of Haryana. Bhujal News, v.8(1), pp.28–31.
Soltan, M.E. (1999) Evaluation of groundwater quality in Dakhla Oasis (Egyptian Western Desert). Environ. Monit. Assess., v.57, pp.157–168.
Stallard, R.F. and Edmond, J.M. (1983) Geochemistry of the Amazon, the influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. Jour. Geophys. Res, v.88, pp.9671–9688.
Subba Rao, N. (2003) Groundwater quality: focus on fluoride concentration in rural parts of Guntur district, AP, India, Hg. Sci. Jour., v.48(5), pp.835–847.
Subba Rao, N. and Rao, A.T. (2003) Fluoride in groundwaters in a developing area of Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Jour. Appld. Geochem., v.5, pp.99–100.
Subba Rao, N. (2011) High-fluoride groundwater. Environ. Monit. Assess., v.176, pp.637–645.
Sujatha, D. (2003) Fluoride levels in the groundwater of the southeastern part of Ranga Reddy District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ. Geol., v.44, pp.587–591.
Sumalatha, S., Ambika, S.R., Prasad, S.J. (1999) Fluoride contamination status of groundwater in Karnataka. Current Science, v.76(6), pp.730–734.
Susheela, A. K. (1999) Fluorosis management programme in India. Curr. Sci., v.77, pp.1250–1256.
WHO (1994) Fluorides and oral health, (Technical report series no.846). World Health Organisation, Geneva.
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, Geneva, 212p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satyanarayana, E., Dhakate, R., Kumar, D.L. et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater quality with special reference to fluoride concentration in parts of Mulugu-Venkatapur Mandals, Warangal district, Telangana. J Geol Soc India 89, 247–258 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0597-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0597-8