Abstract
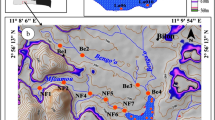
The Vellayani lake, located on the west coast, Kerala, South India, is a natural fresh water lake. In order to understand the source and nature of the sediments; thirteen lake floor sediment samples were collected from the Vellayani lake at different intervals along the S-N transects covering the entire surface area of the lake. Textural studies indicate that lake floor sediments are dominant in sand (55.39%) followed by clay (30.57%) and silt (14.04%) fractions. Coarse components are dominant at the inlet ofthe stream into the lake. The geochemical content of the sediments reveals low SiO2, MnO, CaO, MgO, Na2O, K2O, and P2O5 content while TiO2, Fe2O3 and Al2O3 are high when compared with Post Archean Australian Shale (PAAS) and Upper Continental Crust (UCC) values. SiO2 is high in coarse fractions while Al2O3 is strongly associated with fine sediments. Major oxide contents supported by Rare Earth Element (REE) data reveal a distinct negative Eu anomaly reflecting a dominant cratonic origin of the sediments. Detailed geochemical data indicate a mixed source, predominantly, the lateritic soils, sedimentary and metamorphic bedrocks exposed around the lake and in the catchment area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthakrishnan, R., Parthasarthy, B. and Pathan, J.M. (1979) Meteorology of Kerala. Contrib. Marine Sci., pp.123–125.
Anderson, S.P., Drever, J.I. and ·Humphrey, N.F. (1997) Chemical weathering in glacial environments. Geol., v. 25, pp.399–402.
Basu, A., Blanchard, D.P. and Brannon, J.C. (1982) Rare-earth elements in the sedimentary cycle: a pilot study of the first lag. Sediment., v.29, pp.737–742.
Bauluz, B., Mayayo, M. J., Fernandez-Nieto, C. and Lopez, J.M.G. (2000) Geochemistry of Precambrian and Paleozoic siliciclastic rocks from the Iberian range (NE Spain): implications for source-area weathering, sorting, provenance and tectonic setting. Chem. Geol., v.168, pp.135–150.
Bianchi, T.S., Mitra, S. and Mckee, B.A. (2002) Sources of terrestrially derived organic carbon in lower Mississippi River sediments: implications for differential sedimentation and transport at the coastal margin. Mar. Chem., v.77, pp.211–223.
Braun, J.J., Ngoupayou, J.R.N., Viers, J., Dupre, B., Bedimo, J.P.B., Boeglin, J.L., Robain, H., Nyeck, B., Freydier, R., Nkamdjou, L. S., Rouiller, J. and Muller, J.P. (2005) Present weathering rates in a humid tropical catchment: Nsimi, South Cameroon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., v.69, pp.357–387.
Carroll, D. (1970) Rock weathering. Plenum Press: New York, London, pp.203.
Condie, K.C. (1993) Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust: contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chemical Geol., v.104, pp.1–37.
Cullers, R.L. and Graf, J. (1983) Rare earth elements in igneous rocks of the continental crust: intermediate and silicic rocks, ore petrogenesis. In: P. Henderson (Ed.), Rare-Earth Geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp.275–312.
Cullers, R.L. (1994) The chemical signature of source rocks in size fractions of Holocene stream sediment derived from metamorphic rocks in the wet mountains region, Colorado, USA. Chem. Geol., v.113, pp.327–343.
Darmody, R.G., Thorn, C.E., Harder, R.L., Schlyter, J.P.L. and Dixon, J.C. (2000) Weathering implications of water chemistry in an arctic-alpine environment, northern Sweden. Geomorph., v.34, pp.89–100.
Das, B.K. (2002) Biogeochemistry as an indicator of organic matter sources, paleolimnological and paleoenvironmental change in lacustrine sediments: a study of two Himalayan lakes. Environ. Geosci., v.9, pp.115–126.
Das, B.K. and Haake, B. (2003) Geochemistry of Rewalsar Lake sediment, Lesser Himalaya, India: implications for source-area weathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Geosci. Jour., v.7, pp.299–312.
Das, B.K. and Singh, M. (1996) Water chemistry and control of weathering of Pichola Lake, Udaipur District, Rajasthan, India. Environ. Geol., v.27(3), pp.184–190.
Das, B.K., Al-Mikhlafi and Kaur, P. (2006) Geochemistry of Mansar lake sediments, Jammu, India: implication for source area weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.26, pp.649-668.
Fedo, C.M., Eriksson, K.A. and Krogstad, E.J. (1996) Geochemistry of shales from the Archean (~3.0 Ga) Buhwa Greenstone Belt, Zimbabwe: implications for provenance and source-area weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.60, pp.1751–1763.
Gaudette, H.E., Flight, W.R., Toner, L. and Folger D.W. (1974) An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. Jour. Sediment. Petrol., v.44, pp.249–253.
Hedges, J.I. and Keil, R.G. (1995) Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis. Mar. Chem., v.49, pp.81–115.
Herron, M.M. (1988). Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data: Jour Sediment. Petrol., v.58, pp.820–829.
Hoffman, S. (1988) Lake sediment geochemistry, General Geology, Encyclopedia of Earth Science., pp.373–379.
Jin, Z.D., Wang, S., Shen, J. and Wang, Y. (2003) Carbonate versus silicate Sr isotope in lake sediments and its response to the Little Ice Age. Chinese Sci. Bull., v.48, pp.95–100.
Johnsson, M.J., Stallard, R.F. and Meade, R.H. (1988) First-cycle quartz arenites in the Orinoco River Basin, Venezuela and Colombia. Jour. Geol., v.96, pp.263–277.
Krumbein, W.C. and Pettijohn, F.J. (1938) Manual of Sedimentary Petrography. Appleton-Century-Crofts: New York.
Loring, D.H. and Rantala, R.T.T. (1992) Manual for the geochemical analyses of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth Sci. Rev., v.32, pp. 235–283.
Mclennan, S.M. (1993) Weathering and global denudation. Jour. Geol., v.101, pp.295–303.
Mclennan, S.M. (1989) Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev. Miner., v.21, pp.170–199.
Mclennan, S.M., Hemming, S., Mcdaniel, D.K. and Hanson, G.N. (1993) Geochemical approach to sedimentation, provenance and tectonics. Geol. Soc. Amer. Spec. Paper 285, pp.21–40.
Nesbitt, H. W. and Young, G. M. (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature, v.299, pp.715–717.
Nesbitt, H. W., Markovics, G. and Price, R. C. (1980) Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., v.44, pp.1659–1666.
Oliva, P., Viers, J., Dupré, B., Fortuné, J.P., Martin, F., Braun, J.J., Nahon, D. and Robain, H. (1999) The effect of organic matter on chemical weathering: study of a small tropical catchment: NsimiZoétélé site, Cameroon. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., v.63, pp.4013–4035.
Pettijohn, F.J., Potter, P.E. and Siever, R. (1972) Sand and Sandstones: New York, Springer-Verlag, pp.618.
Rose, N.L., Boyle, J.F., Du, Y., Yi, C., Dai, X., Appleby, P.G., Bennion, H., Cai, S. and Yu, L. (2004) Sedimentary evidence for changes in the pollution status of Taihu in the Jiangsu region of eastern China. Jour. Paleolimnol., v.32, pp.41–51.
Sinha, S., Islam, R., Ghosh, S.K., Kumar, R. and Sangode, S.J. (2007) Geochemistry of Neogene Siwalik mudstones along Punjab re-entrant, India: Implications for source area weathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Curr. Sci., v.92(8), pp.1103–1113.
Taylor, S.R and Mclennan, S. (1985) The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Blackwell, Oxford, pp.312.
Veena, M.P., Achyuthan, H., Eastoe, E. and Farooqui, A. (2014) A multiproxy reconstruction of monsoon variability in the late Holocene, South India. Quaternary Internat., v.325, pp.63–73.
Viers, J., Dupré, B., Braun, J.J., Deberdt, S., Angeletti, B., Ngoupayou, J.N. and Michard, A. (2000). Major and trace element abundances, and strontium isotopes in the Nyong basin rivers (Cameroon): constraints on chemical weathering processes and elements transport mechanisms in humid tropical environments. Chem. Geol., v.169, pp.211–241.
Vital, H. and Stattegger, K. (2000) Lowermost Amazon River: evidence of late Quaternary sea-level fluctuations in a complex hydrodynamic system. Quaternary Internat., v.72, pp.53–60.
Wedepohl, K.H. (1995) The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, v.59, pp.1217–1239.
Wronkiewicz, D.J. and Condie, K.C. (1987) Geochemistry of Archean Shales from the Witwatersrand supergroup, South Africa: source area weathering and provenance. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., v.51, pp.2401–5416.
Young, E.D., Fogel, M.L., Rumble, D. III and Hoering, T.C. (1998) Isotoperatio-monitoring of O2 for microanalysis of 18O/16O and 17O/16O in geological materials. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., v.62, pp.3087–3094.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, V., Achyuthan, H. Geochemistry of Vellayani lake sediments: Indicators of weathering and provenance. J Geol Soc India 89, 21–26 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0554-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0554-6