Abstract
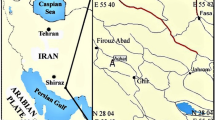
The first exploratory well Arani–A was drilled in the Palar basin to a depth of 2400m and terminated within the granitic basement.This well offered the first ever opportunity to understand biostratigraphy, sedimentation history and depositional environment of the entire sedimentary column based on arenaceous foraminifera, spores, pollen and dinoflagellate cyst assemblages. Previous studies on few scattered outcrops around Sriperumbudur, Chengalpattu and Sathyavedu areas have documented palynofossil assemblage of Neocomian–Aptian age. The present study reveals the presence of middle Jurassic (Bajocian-Callovian) sediments (2360-1725 m) resting on the granitic basement. The sediments are interpreted to have deposited under lacustrine/estuarine conditions with high tides providing occasional marine influence. The middle Jurassic sediments are conformably overlain by late Jurassic (Oxfordian–Tithonian) sediments (1725 - 950 m). The late Jurassic sediments have been inferred to have got deposited under fluctuating near shoremarginal marine conditions. There is a 55m thick boulder bed (950 - 895 m) separating the overlying Valanginian sediments. Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Early Albian) sediments are developed in the interval from 895-50m. The boulder bed possibly corresponds to the missing Berriasian stage of the earliest Cretaceous representing an unconformity of the order of ~5 Ma across Jurassic-Cretaceous boundary. These sediments are inferred to have deposited under shallow inner neritic conditions. The sediments from 50m to surface consist mainly of lateritic sandstone and alluvium. The sedimentary history of Palar basin began in Bajocian stage of middle Jurassic (170-168 Ma) and ended in early Albian stage of early Cretaceous (113-105 Ma). The late Albian marine transgression which facilitated huge sedimentation in Cauvery and Krishna-Godavari basins has bypassed the Palar basin thus adversely affecting the hydrocarbon potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basavaraju, M.H., Poovendan, A., Nagaraj, M., Rao, M.S., Malli Vijai, M. (2014) Palynostratigraphy and Sedimentological studies of sediments below G-1 Marker in Pallivaramangalam, Thiruvarur, Vijayapuram and Narimanam field, Nagapattinam Sub-basin, Cauvery Basin. Unpubld. Rept., RGL, ONGC, Chennai.
Basavaraju, M.H. and Poovendan, A. (2014) Palynostratigraphy and depositional environments of well Andimadam-3,Ariyalur -Pondicherry Sub Basin, Cauvery Basin. Unpublished Report, RGL, ONGC, Chennai.
Gradstein, F.M., Ogg, J.G., Schmitz, M.D. and Ogg, G.B (2012) The Geological Time Scale. Elsevier Publication, v.1, pp.1–435 and v.2, pp.437-1144.
Helby, R., Morgan, R. and Partridge, A.D. (1987a) A Palynological Zonation of the Australian Mesozoic. Mem. Assoc. Australasian Paleontologist, v.4, pp.1–94.
Helby, R., Morgan, R. and Partridge, A.D. (2004) Updated Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Dinocyst Zonation NWS Australia. Geoscience Australia Publication 1 920871 01 2.2 pp.
Mantle, D.J. and Riding, J.B. (2012) Palynology of the Middle Jurassic (Bajocian-Bathonian) Wanaea verrucosa dinoflagellate cyst zone of the North West Shelf of Australia. Review of Palaeobotony and Palynology, v.180, pp.41–78.
Mazumder, S., Blecy Tep., Pangtey, K.K.S., Mitra, D.S (2013) A morphotectonic based approach to derive tectonic framework and possible areas of hydrocarbon accumulation in onshore Palar Basin. ONGC Bull., v.48(5), December, pp.112–123.
Nagendra, A., Chidambaram,A., Ayyadurai, M (2011) Geological sampling in NELP VII Block-PR-ONN-2005/1 PALAR BASIN/Lab studies. ONGC, Unpublished report.
Rangaraju, M.K., Agarwal, A. and Prabhakar, K.N (1993) Tectanostratigraphy, structural styles, evolutionary model and hydrocarbon habitat of Cauvery and Palar Basins. In: Proc. Second Seminar on Petroliferous Basins of India (Eds. Biswas, S.K., Pandey, J., Dave, A., Maithani, A., Garg, P. and Thomas, N.J.) KDMIPE, ONGC, Dehradun, v.1, pp.371–338.
Riding, J.B., Mantle, D.J. and John Backhouse (2010) A review of chronostratigraphical ages of Middle Triassic to Late Jurassic dinoflagellate cyst biozones of the North West Shelf of Australia. Review of Paleobotony and Palynology, v.162, pp.543–575.
Sastri, V.V., Raju, A.T.R., Sinha, R.N., Venkatachala, B.S. and Banerjee, R.K. (1976b) Evolution of geosynclinals and platform basins. Stratigraphy and evolution of the Palar basin, India. Stratigraphic correlation between sedimentary basins of the ESCAP region, Mineral Resources Development Series 42, pp.212–215 (UN, New York)
Stover, L.E. and Williams, G.L. (1987) Analysis of Mesozoic and Cenozoic organic walled dinoflagellates In: Bolli, H.M., Saunders, J.B. and Perch–Nielsen, 16 (eds.). Plankton Stratigraphy. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, pp.847–864.
Tripathi, A. and Vijaya, A. (1997) Biostratigraphic age determination of Sriperumbudur Formation in borehole PBSD-1, Palar Basin, Tamil Nadu: a re-assessment. Jour. Palaeont. Soc. India, v.42, pp.101–116.
Vairavan, V. (1993) Tectonic history and hydrocarbon prospect of Palar and Pennar Basins. In: Biswas et al. (Eds.), Pre. Second seminar in Petroliferous Basins if India. pp.389–396.
Venkatachala, B.S. and Rajanikanth, A. (1988) Stratigraphic implication of Late Gondwana floras in the east coast. Paleobotonist, v.36, pp.183–196.
Wilson, G.J. and Clowes, C.D. (1980) A concise catalogue of OrganicWalled dinoflagellate genera, New Zealand Geological Survey, Report No.92, pp.1–199.
Williams, G.L. and Bujak, J.P. (1985) Mesozoic and Cenozoic Dinoflagellate, in Plankton Stratigraphy, Vol, 2. (eds.) H. M. Bolli, J. B. Saunders and K. Perch-Nielsen, Cambridge. pp.847–964, fig.1-43.
Williams, G. L., Stover, L.E. and Kidson, E.J. (1993) Morphology and Stratigraphic ranges of selected Mesozoic-Cenozoic dinoflagellate Taxa in the Northern Hemisphere, Geological Survey of Canada, and Paper 92-10, pp.1–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basavaraju, M.H., Jaiprakash, B.C., Chidambaram, L. et al. Biostratigraphy and depositional environments of subsurface sediments in well Arani-A, Palar basin, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 88, 407–420 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0504-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0504-8