Abstract
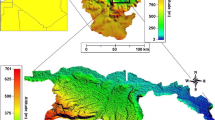
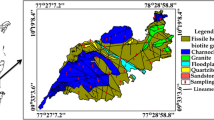
Isotopic and hydrochemical studies of groundwater were attempted in a part of central Ganga basin to gain knowledge on recharge conditions, to outline the processes responsible for isotopic fractionation, to determine the surface-water groundwater interaction and to locate the sources of groundwater contamination in the area. In the present study, conjunctive use of isotopic and silica data is employed to make an assessment of residence time of water underground and to decipher the role of rock water interaction in isotopic variations. Although the aquifer in the area is isotopically heterogeneous in its lateral extension, but oxygen and hydrogen isotopic compositions of most of the samples in premonsoon and post-monsoon exhibited very similar ranges which point to the single source of recharge in both the seasons. However, during post-monsoon, evaporation effects can be observed in some groundwater samples which can be attributed to the irrigation return flow in the area. Various sources of groundwater contamination have been narrowed down and it has been found that agriculture plays a dominant role in groundwater contamination in addition to other domestic and industrial sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-El-Samie, S.G. and Sadek, M.A. (2001) Groundwater recharge and flow in the Lower Cretaceous Nubian Sandstone aquifer in the Sinai Peninsula, using isotopic techniques and hydrochemistry. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.9, pp.378–389.
Burns, D.A., Plummer, L.N., Mcdonnell, J.J., Busenberg, E., Casile, C., Kendall, C., Hooper, R.P., Freer, J.E., Peters, N.E., Beven, K. and Schlosser, P. (2003) The geochemical evolution of riparian ground water in a forested piedmont catchment. Ground Water, v.41(7), pp.913–925.
Clark, I.D. and Fritz, P. (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton.
Datta, P.S., Deb, D.L. and Tyagi, S.K. (1996) Assessment of groundwater contamination from fertilizers in the delhi area based on 18O, NO3 — and K+ composition, Jour. Contaminant Hydrology, v.27, pp. 249–262.
Datta, P.S., Tyagi, S.K., Mookerjee, P., Bhattacharya, S.K., Gupta, N. and Bhatnagar, P.D. (1997) Groundwater NO3 and F contamination processes in Pushkar valley, Rajasthan as reflected from 18O isotopic signature and 3H recharge studies. Environ. Monitoring and assessment, v.56, pp.209–219.
Edmunds, W.M., Ma, J., Aeschbach-Hertig, W., Kipfer, R. and Darbyshire, D.P.F. (2006) Groundwater recharge history and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Minqin Basin, North West China. Appld. Geochem., v.21, pp.2148–2170.
Fernández-Chacón, F., Benavente, J., Rubio-Campos, J.C., Kohfahl, C., Jiménez, J., Meyer, H., Hubberten, H. and Pekdeger, A. (2010) Isotopic composition (d18O and dD) of precipitation and groundwater in a semi-arid, mountainous area (Guadiana Menor basin, Southeast Spain). Hydrol. Process., v.24, pp.1343–1356.
Final report of the committee on pollution caused by leather tanning industry to the water bodies/groundwater in Unnao district of Uttar Pradesh (2013) by NIH, CWC, CGWB, CPCB and UPPCB
Gat, J.R. (1970) Environmental isotope balance of Lake Tiberias. In: Isotope Hydrology. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp.109–127.
Gat, J.R. and Matsui, E. (1991) Atmospheric water balance in the Amazon basin: An isotopic evapotranspiration model. Jour. Geophys. Res., v.96, pp.13179–13188.
Gupta, S.K. and Deshpande, R.D. (2005) Groundwater isotopic investigation in India, what has been learnt. Curr. Sci., v.89, pp.825–835.
Hailemichael, D.W. (2008) Origin of geothermal waters and subsurface temperature estimates in the southern lowlands of Iceland. Geothermal training programme, Orkustofnun, Grensásvegur 9, IS-108 Reykjavík, Iceland, Report Number 28, pp.539–562.
Khanna, S.P. (1992) Hydrogeology of Central Ganga Plain, U. P. Gangetic Plain. Tera Incognita, pp.23–27.
Mahlknecht, J., Schneider, J.F., Merkel, B.J., de León, I.N. and Bernasconi, S.M. (2004) Groundwater recharge in a sedimentary basin in semi-arid Mexico. Hydrogeol. Jour., v.12, pp.511–530.
Mazor, E. (1997) Applied Chemical and Isotopic Groundwater Hydrology, second ed. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 413p.
Mcquillan, D. (2004) Groundwater quality impacts from on-site septic systems. Proceedings, National Onsite Wastewater Recycling Association, 13th Annual Conference Albuquerque, NM, November 7–10.
Misra, A.K. (2011) Impact of Urbanization on the Hydrology of Ganga Basin (India) Water Resour. Manage, v.25, pp.705–719 DOI 10.1007/s11269-010-9722-9.
Moravec, B.G., Keller, C.K., Smith, J.L., Allen-King, R.M., Goodwin, A.J., Fairley, J.P. and Larson, P.B. (2010) Oxygen-18 dynamics in precipitation and streamflow in a semi-arid agricultural watershed, Eastern Washington, USA. Hydrol. Process., v.24, pp.446–460.
Noseck, U., Rozanski, K., Dulinski, M., Havlová, V., Sracek, O., Brasser, T., Hercik, M. and Buckau, G. (2009) Carbon chemistry and groundwater dynamics at natural analogue site Ruprechtov, Czech Republic: Insights from environmental isotopes. Appld. Geochem., v.24, pp.1765–1776.
Oxtobee, J.P.A. and Novakowski, K. (2002) A field investigation of groundwater/surface water interaction in a fractured bedrock environment. Jour. Hydrol., v.269, pp.169–193.
Rosenthal, E. (1987) Chemical composition of rainfall and groundwater in recharge areas of the Bet shean-harod multiple aquifer system, Israel. Jour. Hydrology, v.89, pp.329–352.
Stewart, M.K., Mehlhorn, J. and Elliott, S. (2007) Hydrometric and natural tracer (oxygen-18, silica, tritium and sulphur hexafluoride) evidence for a dominant groundwater contribution to pukemanga stream, Newzealand, Hyrol. Process., v.21, pp.3340–3356.
Yu, J.Y. and Park, Y. (2004) Sulphur isotopic and chemical compositions of the natural waters in the Chuncheon area, Korea. Appld. Geochem., v.19, pp.843–853.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, Z.A., Umar, R. Stable isotopic and hydrochemical studies in a part of central Ganga basin. J Geol Soc India 85, 706–716 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0267-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0267-7