Abstract
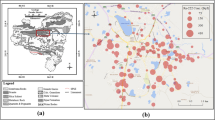
Radon is a naturally occurring colourless and odourless radioactive gas that is soluble in water and is the main source of radioactivity of groundwater. Use of radon contaminated groundwater increased the radon levels in the air, especially in poorly ventilated houses, which is hazardous to health. Ingestion of such water for quite long period may lead to stomach cancer. The drinking water standards proposed by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) exclude the permissible concentration of radon in drinking water. The US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) in 1991 proposed a Maximum Concentration Level (MCL) of 11.1 Bq/l for public water supply. The water samples from the bore wells in Tumkur district of Karnataka show radon concentrations in the range of 5 to 250 Bq/l. Ninety percentages of the samples show radon levels above the permissible limit as per USEPA. The spatial variation and geological control over radon concentration in groundwater in the area and sampling sensitivity are discussed here. The study was conducted during March 2012.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerblom, G. and Lindgren, J. (1997) Mapping of groundwater radon potential. European Geologist, v.5, pp.13–22.
Choubey, V.M., Sharma, K.K. and Ramola R.C. (1997) Preliminary investigations of geology and radon occurrence around Jari in Parvati valley, Himachal Pradesh, India. Jour Environ Radioactivity, v.34, pp.139–148.
Choubey, V.M. and Ramola, R.C. (1997) Correlation between geology and radon levels in groundwater, soil, and indoor air in Bhilangana Valley, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Envron. Geol., v.32(4), pp.258–262.
Choubey, V.M., Bartarya, S.K., Saini, N.K. and Ramola, R.C. (2001) impact of geohydrology and neotectonic activity on radon concentration in groundwater of intermontane Doon valley, India. Environ. Geol., v.40(3), pp.257–266.
Dunduli, W.P, Bell, W.J., Keene, B.E. and Dostie, P.J., (1984). Radon-222 in the gastrointestinal tract: A proposed modification of ICRP 30 model. Health Phys., v.47, pp.243–252.
Hunse, T.M., Najeeb K. Md., Rajarajan, K. and Muthukkannan (2010) Presence of Radon in Groundwater in Parts of Bangalore. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.75(5), pp.704–708.
ICRP (1993) Protection against Radon-222 at home and at work. ICRP publication 65. Ann. ICRP 23(2).
Ramola, R.C., Choubey, V.M., Saini, N.K. and Bartarya S.K. (1999) Occurrence of radon in the drinking water of dehradun city, India. Indoor Built Environ., v.8, pp.67–70.
Ramola R.C., Choubey, V.M., Negi, M.S., Yogesh Prasad and Ganesh Prasad (2008) Radon occurrence in soil-gas and groundwater around an active landslide. Radiation Measurements, v.43, pp.98–101.
Sonkawade, R.G., Rewa Ram, Knjilal, D.K. and Ramola, R.C. (2004) Radon in tube well drinking water and indoor air. Indoor Built Environ., v.13, pp.383–385.
US EPA (1991) National Primary drinking water regulations: Radionuclids: Proposed rules. Federal register. 56, pp.33050–33127.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Md, N.K., Vinayachandran, N., Jose, B. et al. Radon in groundwater in Tumkur district of Karnataka with special reference to sampling sensitivity. J Geol Soc India 83, 665–668 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0097-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0097-z