Abstract
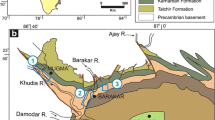
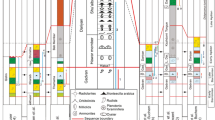
In Bengal basin the subcrop Gondwana sediments occur in N-S trending elongated grabens originated largely by the graben forming tectonisms of the Gondwanaland which overlie the crystalline basement in the sub-surface in an intra-cratonic setup. So far five wells in shelf part of Bengal Basin have penetrated Gondwana sediments, out of which three wells i.e.,G1, G3 and G2 have been drilled up to Precambrian basement. In subcrop Gondwana graben, glacial to glacio-fluvial Talchir Formation of Early Permian age was deposited above the basement. Early Permian Barakar Formation overlies Talchir Formaion. Flood basin model of deposition is postulated for this coal rich unit. In the absence of Barren Measure Formation, coal bearing Raniganj Formation overlies Barakar Formation. The fluvial set up changed over to arid environment during deposition of Panchet/Supra Panchet Formation (undifferentiated). The deposition of Panchet Formation is followed by eruption of doleritic rocks in both subcrop and outcrop Bengal Gondwana whereas lamprophyres are absent in subcrop of Bengal Gondwana. Rifting as well as pull-apart basin model due to transtensional movement is postulated for Gondwana basins. Detailed lithostratigraphic analysis of the core / cutting samples of the Gondwana sediments reveal that the sediments are mainly fine to coarse grained, poorly sorted sandstone. These sediments are characterized as poor reservoir and needs some treatment for permeability enhancement for hydrocarbon production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
das Sharma, S., Chakrabarti, M.K. and Bisht, S.S. (1993) Shallow Marine area, Bengal Basin-The site of an ancient Fan. In: S.K. Biswas (Ed.), Proc. Second Seminar on Petroliferous Basins of India, pp.61–82.
GSI (2003) Coal fields of India. Bull. GSI, Series A, No.45, Compiled byR.K. Dutta and A.B. Dutta.
Krishnan, M.S. (1982) Geology of India and Burma. CBS Publishers and Distributors, pp.239–291.
Mukherjea, A. and Neogi, B.B. (1993) Status of Exploration in Bengal Basin, West Bengal, India. In: S.K. Biswas, (ED.), Proc. Second Seminar on Petroliferous Basins of India, pp.93–119.
Roybarman, A (1983) Geology and Hydrocarbon Prospects of West Bengal. Petroleum Asia Journal, pp.53.
Vaidyanadhan, R. and Ramakrishnan, M. (2008) Geology of India, Geological Society of India, Bangalore, pp.615–661.
ONGC Reports (unpublished)
Well Completion Reports of G4, G5, G2 and G3.
Petrology, palaeontology and palynology reports of G2,G3,G4,G5.
Electrolog interpretation reports of G2,G3,G4,G5.
Lithostratigraphy of Bengal basin, 1993, Mahesh Chandra.
Bengal Basin Evaluation and Exploration Recommendations:John Kingston, 1996.
Sedimentological and Palynological. Studies of Gondwana Sediments of Bengal Basin and comparison with Purnea and Krishna-Godavari Basins by B.Prasad and B.S.Pundeer,1998.
Subsurface Geology of Bengal Basin with special reference to Stratigraphy, Facies, Geological history and Re appraisal of Hydrocarbon Plays. by B.B.Neogi et al.1987.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banerjee, B., Marak, I.A. & Biswas, A.K. Subcrop Gondwana of Bengal basin and their reservoir characteristics. J Geol Soc India 81, 741–754 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0099-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0099-2