Abstract
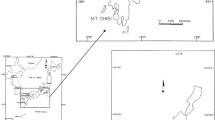
Pleistocene red soil horizons were exposed in different areas of the Barind Tract in north-west Bangladesh. X-ray diffractions of twenty seven samples from different depths of these soil horizons revealed that the soil horizons consisted of kaolinite, illite and chrysotile with significant amount of opal-CT. Samples from Maddhapara, Bogra, and Nachole contain kaolinite, illite, quartz and opal-CT, and the samples from Kantabari contain chrysotile instead of kaolinite.
Clay mineral compositions of different soil horizons indicated two different types of clay assemblages, viz. (a) illitekaolinite and (b) illite-chrysotile. In the village of Kantabari, illite-chrysotile clay mineral assemblage indicate that soil horizons were formed under low temperatures with alkaline and reducing conditions. However, other soil horizons of illite-kaolinite clay mineral assemblage indicate that soils were possibly formed under humid, temperate and welldrained conditions. These two soil horizons were formed under different geochemical, geomorphological and climatic conditions from different parent materials.
Scanning Electron Microscopy photographs showing the presence of glass shards and no opal-A were found using XRD, suggesting that the opal-A might not be a precursor to opal-CT in the red soil horizon of the study area. This opal-CT along with the general lack of fossils and presence of glass shards was indicative of a volcanogenic rather than biogenic origin for the Opal-CT in the study area, and X-ray fluorescence data reveals higher percentages of silica which is comparable to the Toba Ash of Toba Caldera, Indonesia of about 75,000 B.P.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya, S.K. and Basu, P.K. (1993) Toba Ash on the Indian Subcontinent and its implication for correlation on Late Pleistocene alluvium. Quaternary Res., v.40, pp.10–19.
Aftabuzzaman, M. (2011) Characteristics of Red Soil Horizon in Bangladesh: Unpubld. M.Sc. thesis, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi, Bangladesh, 114p.
Alam, Akmk, Coates, Da, Mannan, Kh, Ahmed, D. and Hossain, S. (2008) Geology of Parts of Tangail and Mymensingh districts. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, v.11, p.5.
Alam, M.K., Hossain, A.K.M.S., Khan, M.R. and Whitney, J.W., (1990) Geological map of Bangladesh. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, Dhaka, (Scale 1.1, 000,000).
Alam, M.S. and Paepe, R. (1996) Palaeosol in the Quaternary Stratigraphy in Northwestern Bangladesh: Bangladesh Geoscience Jour., v.2, pp.15–36.
Alam M.S., Hus, J. and Paepe, R. (1997) Magnetic Susceptibility Variation of Pleistocene Paleosol Sequence and its Significance in Paleoclimatic Studies in Bangladesh. Recent Progress in Geomagnetism, Rock Magnetism and Paleomagnetism, Islamabad, v.1, pp.113–127.
Biscaye, P.E. (1965) Mineralogy and sedimentation of Recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.76, pp.803–831.
Brown, G. and Brindley, G.W. (1980) X-ray Diffraction procedures for clay mineral identification. In: G.W. Brindley and G. Brown (Eds.), Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification: Mineralogical Society, London, Monograph No. 5, pp.305–359.
Cerling, T.E. (1984) The stable isotopic composition of modern soil carbonate and its relationships to climate. Earth Planet Sci. Lett., v.71, pp.229–240.
Eslinger, E. and Peaver, D. (1988) Clay minerals for Petroleum Geologists and Engineers. Soc. Econ. Paleont. and Mineral. short course no.22, 346 p.
Flörke, O.W., Graetch, H., Martin, B., RÖLLER, K. and Writh, R. (1991) Nomenclature of micro-and non-crystalline silica minerals based on structure and microstructure. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie Abh, v.163, pp.19–42.
Hein, J.R., Scholl, D.W., Barron, J.A., Jones, M.J. and Miller, J. (1978) Diagenesis of Late Cenozoic diatomaceous deposits and formation of the bottom simulating reflector in the southern Bering Sea. Sedimentology, v.25, pp.155–181.
Huq, M.A., Islam, M.K., Hasan, M. and Whitney, J.W. (2003) Geology of the Parts of Habiganj District, Bangladesh. Rec. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, v.10,part 2, 48p.
Huq, M.A., Whitney, J.W., Das, S.K. and Ali R.M.E. (1991) Geological Map and Report of the Western Part of Rajshahi District, Bangladesh. Rec. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, v.6, p.1.
Iijima, A. (1978) Geological occurrences of zeolite in marine environments. In: L.B. Sand and F. A. Mumpton (Eds.), Natural Zeolites: Permagon Press, Oxford, pp.314–371.
Iijima, A. and Tada, R. (1981) Silica diagenesis of Neogene diatomaceous and volcaniclastic sediments in northern Japan. Sedimentology, v.28, pp.185–200.
Jackson, M.L. (1969) Soil Chemical Analysis-Advanced Course. 2nd. Ed., Published by the author, Madison, Wisconsin, 895 p.
Jones, J.B. and Segnit, E.R. (1971) The nature of opal I. Nomenclature and Constituent Phases. Jour. Geol. Soc. Australia, v.18, no.1, pp.57–68.
Kabir, S. (2001) Investigation of volcanic ash in Tanor and Godagari Upazilas, Rajshahi District and its possible correlation with other areas. Rec. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, v.9,part 4, 20 p.
Kabir, S. and Panhorst, T.L. (2004) Origin of Gulf Coast Opal-CT: A Study of the Claystone-Rich Tallhatta Formation in Mississippi: Southern Geol., v.42, no.8, pp.151–163.
Kabir, S. (2008) Origin of opal-CT in Lower Eocene Tallhatta Formation, Mississippi, USA and Pleistocene Barind Clay Formation in Bangladesh: A comperative study. Pakistan Jour. of Scientific and Industrial Res., v.51, no.2, pp.61–64.
Khan, M.A.M., (1970) Gravel and Sand deposits of Panchagarh and Tetulia Thana, Dinajpur District, Rec. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, v-20, p-2.
Khan, S.I., Das, S.K., Hassan, K.Z. and Williams, V.S. (1990) Geology of Panchagarh District, Rajshahi Division, Bangladesh. Rec. Geol. Surv. Bangladesh, v.6, p.2.
Macewan, D.M.C. and Wilson, M.J. (1980) Interlayer and Intercalation Complexes of Clay Minerals. In: G.W. Brindley and G. Brown (Eds.), Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals and their X-Ray Identification. Mineral. Soc., London, 495p.
Monsur, M.H. (1990) Stratigraphical and Paleomagnetical Studies of some Quaternary Deposits of the Bengal Basin, Bangladesh: D.Sc. dissertation, Free university of Brussels, Pleinlann-2, 1050, Brussels, Belgium.
Monsur, M.H. (1995) An Introduction to the Quaternary Geology of Bangladesh. City Press and Publications, Dhaka, 70p.
Morgan, P. and Mcintire, W.G. (1959) Quaternary Geology of Bengal Basin. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., v.70, pp.319–342.
Reineck, H. E., and Singh, I. B. (1980) Depositional sedimentary environments (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag, New York, 784 p.
Yaalon, D.H. (1990) The relevance of soils and paleosols in interpreting past and on going climatic changes: Palaeogeo., Palaeoclimat., Palaeoeco., v.82, pp.63–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aftabuzzaman, M., Kabir, S., Islam, M.K. et al. Clay mineralogy of the pleistocene soil horizon in Barind Tract, Bangladesh. J Geol Soc India 81, 677–684 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0089-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-013-0089-4