Abstract
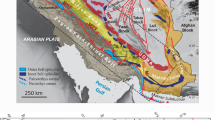
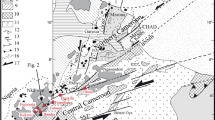
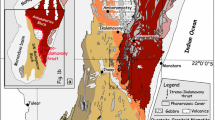
Inverted metamorphism in the Himalayas is closely associated with the Main Central Thrust (MCT). In the western Himalayas, the Main Central Thrust conventionally separates high grade metamorphic rocks of the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence (HHCS) from unmetamorphosed rocks of the Inner sedimentary Belt. In the eastern Himalayas, the Inner sedimentary Belt is absent, and the HHCS and meta-sedimentary Lesser Himalayan Sequence (LHS) apparently form a continuous Barrovian metamorphic sequence, leading to confusion about the precise location of the MCT. In this study, it is demonstrated that migmatitic gneisses of the sillimanite zone in the higher structural levels of the HHCS are multiply deformed, with two phases of penetrative fabric formation (S1HHCS and S2HHCS) followed by third folding event associated with a spaced, NW-SE trending, north-east dipping foliation (S3HHCS). The underlying LHS schists (kyanite zone and lower) are also multiply deformed, with the bedding S0 being isoclinally folded (F1LHS), and subsequently refolded (F2LHS and F3LHS). The contact zone between the HHCS and LHS is characterized by ductile, top-to-the southwest shearing and stabilization of a pervasive foliation that is consistently oriented NW-SE and dips northeast. This foliation is parallel to the S3HHCS foliation in the HHCS, and the S2LHS in the LHS. Early lineations in the HHCS and LHS also show different dispersions across the contact shear zone, implying that pre-thrusting orientations of the two units were distinct. The contact shear zone is therefore interpreted to be a plane of structural discordance, shows a shear sense consistent with thrust movement and is associated with mineral growth during Barrovian metamorphism. It may well be considered to represent the MCT in this region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya, S.K. (1975) Structure and stratigraphy of the Darjeeling frontal zone, Eastern Himalaya. Misc. Publ. Geol. Surv. India, v.24,I, pp.71–90.
Acharyya, S.K. (1976) On the nature of the Main Boundary Fault in the Darjeeling Sub-Himalaya. Misc. Publ. Geol. Surv. India, v.24, pt.II, pp.395–408.
Acharyya, S.K. (1980) Geochemistry and geotectonic implication of basic volcanic rocks in the Lower Gondwana sequence (Upper Palaeozoic) of the Sikkim Himalayas — Comments. Geol. Magz., v.117, pp.621–624.
Anbarasu, K., Gupta, S. and Sengupta, A. (2009) Site-specific geological and geotechnical studies at Lanta Khola landslide, North Sikkim Highway, India. Internat. Jour. Geotechnical Engg., v.3, pp.361–376.
Auden, J.B. (1935) Traverses in the Himalaya. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.69, pt.2, pp.123–167.
Bordet, P. (1961) Recherches géologiques dans l’Himalaya du Népal, région du Makalu Editions du CNRS, Paris, 275p.
Bose, P.N. (1891) Notes on the geology and mineral resources of Sikkim. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.24, pt.4, pp.217–230.
Caddick, M.J., Bickle, M.J., Harris, N.B.W., Holland, T.J.B., Horstwood, M.S.A., Parrish, R.R. and Ahmad, T. (2007) Burial and exhumation history of a Lesser Himalayan schist: Recording the formation of an inverted metamorphic sequence in NW India. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., v.264, pp.375–390.
Chambers, J., Argles, T., Horstwood, M., Harris, N., Parrish, R. and Ahmad, T. (2008) Tectonic implications of Palaeoproterozoic anatexis and Late Miocene metamorphism in the Lesser Himalayan Sequence, Sutlej Valley, NW India. Jour. Geol. Soc. London, v.165, pp.725–737.
Dasgupta, S., Ganguly, J. and Neogi, S. (2004) Inverted metamorphic sequence in the Sikkim Himalayas: crystallization history, P-T gradient and implications. Jour. Metamorphic Geol., v.22, pp.395–412.
Ganguly, J., Cheng, W. and Tirone, M. (1996) Thermodynamics of aluminosilicate garnet solid solution: new experimental data, an optimized model, and thermometric applications. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., v.126, pp.137–151.
Ghosh, A.M.N. (1956) Recent advances in the geology and structure of Eastern Himalaya. In: Indian Science Congress, pp.85–99.
Hagen, T. (1969) Report on the geological survey of Nepal. Preliminary reconnaissance. Denkschr. Schwiz. Naturforsch. Ges., v.86, 185p.
Harris, N.B.W., Caddick, M., Kosler, J., Goswami, S., Vance, D. and Tindle, A.G. (2004)) The pressure-temperature-time path of migmatites from the Sikkim Himalaya. Jour. Metamorphic Geol., v.22, 3, pp.249–264.
Heim, A. and Gansser, A. (1939) Central Himalaya: Geologic observations of the Swiss expedition, 1936. Société Helvetique des Sciences Naturelles, Zurich, v.36, 245p.
Mallet, F.R. (1875) On the geology and mineral resources of the Darjiling district and the Western Duars. Mem. Geol. Surv. India, v.11, pp.1–50.
Mohan, A., Windley, B.F. and Searle, M.P. (1989) Geothermobarometry and development of inverted metamorphism in the Darjeeling-Sikkim region of the Eastern Himalaya. Jour. Metamorphic Geol., v.7, pp.95–110.
Mukhopadhyay, M.K. and Gangopadhyay, P.K. (1971) Structural characteristics of rocks around Kalimpong, West Bengal. Himalayan Geol., v.1, pp.213–230.
Mukul, M. (2000) The geometry and kinematics of the Main Boundary Thrust and related neotectonics in the Darjiling Himalayan fold-and-thrust belt, West Bengal, India. Jour. Struct. Geol., v.22, pp.1261–1283.
Neogi, S., Dasgupta, S. and Fukuoka, M. (1998) High P-T polymetamorphism, dehydration melting, and generation of migmatites and granites in the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Complex, Sikkim, India. Jour. Petrology, v.39,1, pp.61–99.
Raina, V. K. and Bhattacharya, U. (1975) Sedimentaries of North Sikkim. Rec. Geol. Surv. India, v.106, pp.75–85.
Ray, C. (1949) Regional metamorphism in Eastern Sikkim. Quart. Jour. Geol., Mineral. Metall. Soc. India, v.214(4), pp.155–170.
Ray, S. (1947) Zonal metamorphism in the Eastern Himalaya and some aspects of local geology. Quart. Jour. Geol. Mineral. Metall. Soc. India, v.19, pp.117–140.
Richards, A., Parrish, R., Harris, N., Argles, T. and Zhang, L. (2006) Correlation of lithotectonic units across the eastern Himalaya, Bhutan. Geology, v.34, pp.341–344.
Roy, K.K. (1976) Some problems of tectonics and stratigraphy of the Darjeeling and Sikkim Himalayas. Misc. Publ. Geol. Surv. India, v.24, pp.379–394.
Searle, M.P. and Szulc, A.G. (2005) Channel flow and ductile extrusion of the high Himalayan slab — the Kangchenjunga-Darjeeling profile, Sikkim Himalaya. Jour. Asian Earth Sci., v.25, pp.173–185.
Sinha-Roy, S. (1973) Structure and metamorphism of the Daling-Darjeeling Group of rocks in the northeastern parts of Kalimpong, hills, Eastern Himalayas. Quarterly Jour. Geol., Min. Metall. Soc. India, v.45, pp.9–21.
Sinha-Roy, S. (1977) Relation between coplanar folds of variable orientation, stretching lineation and thrust in the Daling and associated rocks from the Inner tectonic belt of Sikkim Himalayas. Jour. Geol. Soc. India, v.18, pp.153–169.
Sinha-Roy, S. (1979) Deformation sequence and strain estimate of the Himalayan nappes: example from Sikkim, Eastern Himalayas. In: P.S. Saklani (Ed.) Structural Geology of the Himalayas. Today and Tomorrow Publ., New Delhi, pp.285–306.
Sinha-Roy, S. (1981) Comments on ‘Initiation of intracontinental subduction in the Himalaya’ by Peter Bird Jour. Geophys. Res., v.86, B10, pp.9320–9322.
Sinha-Roy, S. (1982) Himalayan Main Central Thrust and its implications for Himalayan inverted metamorphism. Tectonophysics, v.84, pp.197–224.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Das, A., Goswami, S. et al. Evidence for structural discordance in the inverted metamorphic sequence of Sikkim Himalaya: Towards resolving the Main Central Thrust controversy. J Geol Soc India 75, 313–322 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0018-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-010-0018-8