Abstract
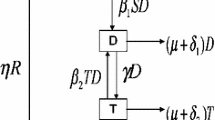
In the present work, we have proposed a new mathematical model of alcohol abuse with delay, saturated incidence function and logistic recruitment. The model is made up of the following four population classes: occasional drinkers, heavy drinkers, drinkers during treatment and drinkers who are temporarily recovered. In particular, we incorporate time delay because the non consumer population will take a period of time to become an alcohol consumer. We have studied the optimal control problem by considering a saturated control function and an objective function of type \(L^{1}\). The delay is incorporated in our model to make it more realistic and to describe the latency period. The existence of the optimal control is also proved. Pontryagin’s maximum principle with delay is used to characterize these optimal controls. The optimality system is derived and then solved numerically using an algorithm based on the forward and backward difference approximation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Addiction Centers (AAC): Alcoholism Treatment: What Is Alcohol Abuse and How To Treat Alcoholism (2020)
Benedict, B.: Modeling alcoholism as a contagious disease: how infected drinking buddies spread problem drinking. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. News 40, 226–239 (2007)
Bonyah, E., Khan, M.A., Okosun, K.O., Gomez-Aguilar, J.F.: Modelling the effects of heavy alcohol consumption on the transmission dynamics of gonorrhea with optimal control. Math. Biosci. 309, 1–11 (2019)
Brezis, H., Ciarlet, P.G. , Lions, J.L.: Analyse fonctionnelle: théorie et applications, vol. 91. Dunod Paris, Malakoff (1999)
Buonomo, B., Lacitignola, D.: Modelling peer influence effects on the spread of high-risk alcohol consumption behaviour. Ricer. Matemat. 63, 101–117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11587-013-0167-3
Galbicsek, C.: What is Alcoholism? (2019)
Ghosh, S., Guria, S., Das, M.: Alcohol as a risk factor for cancer burden: a review. Proc. Zool. Soc. 69, 32–37 (2016)
Göllmann, L., Kern, D., Maurer, H.: Optimal control problems with delays in state and control variables subject to mixed control-state constraints. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 30(4), 341–365 (2009)
Hattaf, K., Yousfi, N.: Optimal control of a delayed HIV infection model with immune response using an efficient numerical method. ISRN Biomath. (2012). https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/215124
Huo, H.F., Song, N.N.: Global stability for a binge drinking model with two stages. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc, 829386 (2012)
Huo, H.F., Wang, Q.: Modelling the influence of awareness programs by media on the drinking dynamics. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 1–8 (2014)
Khajji, B., Labzai, A., Balatif, O., Rachik, M.: Mathematical modeling and analysis of an alcohol drinking model with the influence of alcohol treatment centers. Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 2020, Article ID 4903168, 12 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4903168
Laarabi, H., Abta, A., Hattaf, K.: Optimal control of a delayed SIRS epidemic model with vaccination and treatment. Acta Biother. 63(2), 87–97 (2015)
Lechner, W., Day, A.M., Metrik, J., Leventhal, A.M., Kahler, C.W.: Effects of alcohol-induced working memory decline on alcohol consumption and adverse consequences of use. Psychopharmacology 233, 83–88 (2016)
Lenhart, S., Workman, J.T.: Optimal Control Applied to Biological Models. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL, USA (2007)
Manthey, J.L., Aidoob, A.Y., Ward, K.Y.: Campus drinking: an epidemiological model. J. Biol. Dyn. 2, 346–356 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1080/17513750801911169
Mulone, G., Straughan, B.: Modeling binge drinking. Int. J. Biomath. 5, 57–70 (2012)
Mushayabasa Steady: The role of optimal intervention strategies on controlling excessive alcohol drinking and its adverse health effects. J. Appl. Math. Article ID 238784, 11 (2015). http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/238784
Pérez, E.: Mathematical modeling of the spread of alcoholism among Colombian College Students. Ing. Cien. 16(32), 195–223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.17230/ingciencia.16.32.9
Sánchez, F., Wang, X., Castillo-Cahvez, C., Gorman, D.M., Gruenwald, P.J.: Drinking as an epidemic, a simple mathematical model with recovery and relapse. In: Therapists Guide to Evidence-based Relapse Prevention, p 353 (2015)
Sanchez, F.J., Sanchez, E., Rubio, M., Morera, J.L.: Alcohol consumption in Spain and its economic cost: a mathematical modeling approach. Math. Comput. Model. 52, 999–1003 (2010)
Rehn, J., Mathers, C., Popova, S., Thavorncharoensap, M., Teerawattananon, Y., Patra, J.: Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 373, 2223–2233 (2009)
Sharma, S., Samanta, G.P.: Analysis of a drinking epidemic model. Int. J. Dyn. Control 3(3), 288–305 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-015-0151-8
Wang, X.Y., Huo, H.F., Kong, Q.K., Shi, W.X.: Optimal control strategies in an alcoholism model. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2014, 1–18 (2014)
Zhaofeng, A., Zhang, S., Xu, J.: Stability analysis of an alcoholism model with public health education and NSFD scheme. Discr. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2020, Article ID 4272914, 15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4272914
Zhou, L., Fan, M.: Dynamics of an SIR epidemic model with limited medical resources revisited. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 13, 312–324 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the editor and the anonymous referees for very helpful suggestions and comments that helped us to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouajaji, R., Abta, A., Laarabi, H. et al. Optimal Control of a Delayed Alcoholism Model with Saturated Treatment. Differ Equ Dyn Syst 32, 277–292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12591-021-00570-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12591-021-00570-y