Abstract
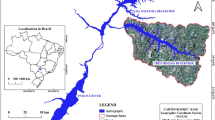
The construction of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River has extensive impact on the ecosystems and the population of the Three Gorges Area (TGA). Inundation and resettlement have induced far-reaching land use and land cover change (LUCC). The areas that are affected by measures of resettlement are in a tense situation between the implementation of various governmental tasks addressing sustainable land use and water retention and the fulfilment of the population’s economic needs, which primarily depend on agricultural production. Destabilization of slopes and soil erosion are immediate hazards induced by the impoundment. Farming is a very important source of income and has to persist on the one hand to assure the income of the rural population. On the other hand, the environment has to be protected from runoff, soil erosion and instabilities connected to relief, geology and hydraulic influences. In this study, supervised classifications are performed using Landsat-TM (1987 and 2007) and ASTER (2007) images. LUCC is assessed by post-classification change analysis. On the catchment scale, arable land has decreased significantly, while garden land (citrus orchards) and woodland have increased. LUCC mainly affects the area surrounding the reservoir (“backwater”) of the Xiangxi (香溪) River, driven by local resettlement, newly built infrastructure, relocation of land cultivation, and conversion of arable land to garden land. In the hinterland, LUCC occurs in form of abandonment of land cultivation as a consequence of the Grain-for-Green programme.
Similar content being viewed by others

References Cited
Chen, B. M., Zhou, X. P., 2007. Explanation of Current Land Use Condition Classification for National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Journal of Natural Resources, 22(6): 994–1003 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Congalton, R. G., 1991. A Review of Assessing the Accuracy of Classifications of Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 37(1): 35–46
Corbane, C., Raclot, D., Jacob, F., et al., 2008. Remote Sensing of Soil Surface Characteristics from a Multiscale Classification Approach. Catena, 75(3): 308–318
Couto, P., 2003. Assessing the Accuracy of Spatial Simulation Models. Ecological Modelling, 167(1–2): 181–198
Crippen, R. E., 1988. The Dangers of Underestimating the Importance of Data Adjustments in Band Ratioing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 9(4): 767–776
Dai, D. Z., Tan, Y., 1996. Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in the Upper Yangtze River Basin. AHS-AISH Publ., 236: 191–203
Fan, F. L., Wang, Y. P., Wang, Z. S., 2008. Temporal and Spatial Change Detecting (1998–2003) and Predicting of Land Use and Land Cover in Core Corridor of Pearl River Delta (China) by Using TM and ETM+ Images. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 137(1–3): 127–147
Fourniadis, I. G., Liu, J. G., Mason, P. J., 2006. Landslide Hazard Assessment in the Three Gorges Area, China, Using ASTER Imagery: Wushan-Badong. Geomorphology, 84(1–2): 126–144
Guo, Z. W., Gan, Y. L., 2002. Ecosystem Function for Water Retention and Forest Ecosystem Conservation in a Watershed of the Yangtze River. Biodiversity and Conservation, 11(4): 599–614
Guo, Z. W., Xiao, X. M., Gan, Y. L., et al., 2001. Ecosystem Functions, Services and Their Values—A Case Study in Xingshan County of China. Ecological Economics, 38(1): 141–154
Guo, Z. W., Xiao, X. M., Li, D., 2000. An Assessment of Ecosystem Services: Water Flow Regulation and Hydroelectric Power Production. Ecological Applications, 10: 925–936
Guo, Z. W., Xiao, X. M., Gan, Y. L., et al., 2003. Landscape Planning for a Rural Ecosystem: Case Study of a Resettlement Area for Residents from Land Submerged by the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landscape Ecology, 18(5): 503–512
He, L., King, L., Jiang, T., 2003. On the Land Use in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 13: 416–422
Heggelund, G., 2006. Resettlement Programmes and Environmental Capacity in the Three Gorges Dam Project. Development and Change, 37(1): 179–199
Hill, R. D., Peart, M. R., 1998. Land Use, Runoff, Erosion and Their Control: A Review for Southern China. Hydrological Processes, 12(13–14): 2029–2042
Jim, C. Y., Yang, F. Y., 2006. Local Responses to Inundation and De-farming in the Reservoir Region of the Three Gorges Project (China). Environmental Management, 38(4): 618–637
Kahya, O., Bayram, B., Reis, S., 2010. Land Cover Classification with an Expert System Approach Using Landsat ETM Imagery—A Case Study of Trabzon. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1–4): 431–438
Kallen, D., Xiang, W., Ehret, D., et al., 2006. Landslides at Qingjiang River in the Downstream Area of Shuibuya Dam Site, China. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 17(2): 158–162
King, L., Gemmer, M., Metzler, M., 2002. Das Drei-Schluchten-Projekt am Yangtze-Gießener Forschergruppe untersucht Auswirkungen des Weltgrößten Staudammprojektes. Spiegel der Forschung, 19(1): 38–45 (in German)
King, L., Hartmann, H., Gemmer, M., et al., 2004. Der Drei-Schluchten-Staudamm am Yangtze-Ein Großbauprojekt und Seine Bedeutung für den Hochwasserschutz. Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen, 148: 26–33 (in German)
Liu, A. X., Wang, J., Liu, Z. J., 2008. Assessing the Effects of Land Use Changes on Soil Erosion in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region of China. 2008 International Workshop on Earth Observation and Remote Sensing Applications, NYC. 163–167
Long, H. L., Heilig, G. K., Wang, J., et al., 2006. Land Use and Soil Erosion in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River: Some Socio-Economic Considerations on China’s Grain-for-Green Programme. Land Degradation & Development, 17(6): 589–603
Long, H. L., Heilig, G. K., Li, X. B., et al., 2007. Socio-Economic Development and Land-Use Change: Analysis of Rural Housing Land Transition in the Transect of the Yangtze River, China. Land Use Policy, 24(1): 141–153
Meng, Q. H., Fu, B. J., Yang, L. Z., 2001. Effects of Land Use on Soil Erosion and Nutrient Loss in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Soil Use and Management, 17(4): 288–291
Ng, S. L., Cai, Q. G., Ding, S. W., et al., 2008. Effects of Contour Hedgerows on Water and Soil Conservation, Crop Productivity and Nutrient Budget for Slope Farmland in the Three Gorges Region (TGR) of China. Agroforestry Systems, 74(3): 279–291
Rocchini, D., Marignani, M., Bacaro, G., et al., 2009. Multi-scale Sampling and Statistical Linear Estimators to Assess Land Use Status and Change. Applied Vegetation Science, 12(2): 225–236
Schönbrodt, S., Ehret, D., Seeber, C., et al.. Geo-risks in the Highly Dynamic Three Gorges Reservoir Ecosystem: Interactions of Soil Erosion, Mass Movements, and Land Use. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms (Submitted)
Sun, Z. Y., Ma, R., Wang, Y. X., 2009. Using Landsat Data to Determine Land Use Changes in Datong Basin, China. Environmental Geology, 57(8): 1825–1837
Tan, Y., Yao, F. J., 2006. Three Gorges Project: Effects of Resettlement on the Environment in the Reservoir Area and Countermeasures. Population and Environment, 27(4): 351–371
Thomson, A. G., Fuller, R. M., Eastwood, J. A., 1998. Supervised versus Unsupervised Methods for Classification of Coasts and River Corridors from Airborne Remote Sensing. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(17): 3423–3431
Venkateswarlu, N. B., Raju, P. S. V. S. K., 1992. Fast ISODATA Clustering Algorithms. Pattern Recognition, 25(3): 335–342
Ye, L., Cai, Q. H., Liu, R. Q., et al., 2009. The Influence of Topography and Land Use on Water Quality of Xiangxi River in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Environmental Geology, 58(5): 937–942
Zhang, S., Xu, L., 2008. The Comparative Study of Three Methods of Remote Sensing Image Change Detection. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Services, 37: 1595–1598
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, No. 03 G 0669).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seeber, C., Hartmann, H., Xiang, W. et al. Land use change and causes in the Xiangxi catchment, Three Gorges Area derived from multispectral data. J. Earth Sci. 21, 846–855 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-010-0136-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-010-0136-7