Abstract
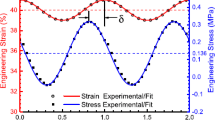
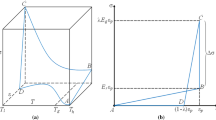
Shape memory polymers (SMPs) are soft active materials that have an ability to retain a temporary shape, and revert back to their original shape when triggered by a suitable stimulus, typically an increase in temperature. These materials are finding wide use in a variety of fields such as biomedical and aerospace engineering; hence it is important to model their mechanical behavior. Crystallizable shape memory polymers (CSMPs) is an important subclass of SMPs, and their temporary shape is fixed by a crystalline phase, while return to the original shape is due to the melting of this crystalline phase. In our earlier work, we have studied the mechanical behavior of CSMPs within a mechanical setting by considering the original amorphous network above the recovery temperature as a hyperelastic material. In this article, we extend our earlier work to incorporate the temperature-dependent viscoelasticity into the developed constitutive model to study the mechanical behavior of CSMPs. The viscoelastic behavior of the polymers at high temperature is simulated through a rate type model. Furthermore, the model of the semi-crystalline polymer after the onset of crystallization is developed based on the mixture theory and the theory of “multiple natural configurations”. In addition, we have applied the model to a specific boundary value problem, namely uniaxial extension. The shape memory cycles of the CSMPs under different stretch rates have been studied. The results are consistent with what has been observed in experiments.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lendlein, A., Kelch, S.: Shape-memory polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41(12), 2035–2057 (2002)
Tobushi, H., Hara, H., Yamada, E., Hayashi, S.: Thermomechanical properties in a thin film of shape memory polymer of polyurethane series. Smart Mater. Struct. 5(4), 483–491 (1996)
Lendlein, A., Jiang, H., Jünger, O., Langer, R.: Light-induced shape-memory polymers. Nature 434(7035), 879–882 (2005)
Jiang, H., Kelch, S., Lendlein, A.: Polymers move in response to light. Adv. Mater. 18(11), 1471–1475 (2006)
Lu, H.B., Huang, W.M., Yao, Y.T.: Review of chemo-responsive shape change/memory polymers. Pigm. Resin Technol. 42(4), 237–246 (2013). doi:10.1108/PRT-11-2012-0079
Liu, C., Qin, H., Mather, P.T.: Review of progress in shape-memory polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 17(16), 1543–1558 (2007)
Xue, L., Dai, S., Li, Z.: Biodegradable shape-memory block co-polymers for fast self-expandable stents. Biomaterials 31(32), 8132–8140 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.07.043
Eisenhaure, J.D., Rhee, S.I., Al-Okaily, A.M., Carlson, A., Ferreira, P.M., Kim, S.: The use of shape memory polymers for MEMS assembly. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 25(1), 69–77 (2016). doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2015.2482361
Yakacki, C.M., Shandas, R., Lanning, C., Rech, B., Eckstein, A., Gall, K.: Unconstrained recovery characterization of shape-memory polymer networks for cardiovascular applications. Biomaterials 28(14), 2255–2263 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.01.030
Ge, Q., Dunn, C.K., Qi, H.J., Dunn, M.L.: Active origami by 4D printing. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(9), 094007 (2014). doi:10.1088/0964-1726/23/9/094007
Reyntjens, W.G., Du Prez, F.E., Goethals, E.J.: Polymer networks containing crystallizable poly(octadecyl vinyl ether) segments for shape-memory materials. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 20(5), 251–255 (1999)
Barot, G., Rao, I.J.: Constitutive modeling of the mechanics associated with crystallizable shape memory polymers. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 57(4), 652–681 (2006)
Barot, G., Rao, I.J., Rajagopal, K.R.: A thermodynamic framework for the modeling of crystallizable shape memory polymers. IJES 46(4), 325–351 (2008)
Moon, S., Cui, F., Rao, I.J.: Constitutive modeling of the mechanics associated with triple shape memory polymers. IJES 96, 86–110 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.ijengsci.2015.06.003
Moon, S., Rao, I.J., Chester, S.A.: Triple shape memory polymers: constitutive modeling and numerical simulation. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 83(7), 071008 (2016). doi:10.1115/1.4033380
Michal, B.T., Jaye, C.A., Spencer, E.J., Rowan, S.J.: Inherently photohealable and thermal shape-memory polydisulfide networks. ACS Macro Lett. 2(8), 694–699 (2013). doi:10.1021/mz400318m
Atkin, R.J., Craine, R.E.: Continuum theory of mixtures: basic theory and historical development. Q J Mech Appl Math. 29(2), 209–244 (1976)
Rajagopal, K.R., Srinivasa, A.R.: Mechanics of the inelastic behavior of materials—part 1, theoretical underpinnings. Int. J. Plast 14(10–11), 945–967 (1998)
Rajagopal, K.R., Wineman, A.S.: A constitutive equation for nonlinear solids which undergo deformation induced microstructural changes. Int. J. Plast 8(4), 385–395 (1992). doi:10.1016/0749-6419(92)90056-I
Rajagopal, K.R., Srinivasa, A.R.: On the inelastic behavior of solids—part 1: twinning. Int. J. Plast 11(6), 653–678 (1995)
Rajagopal, K.R., Wineman, A.S.: A note on viscoelastic materials that can age. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 39(10), 1547–1554 (2004)
Cui, F., Moon, S., Rao, I.J.: Modeling the viscoelastic behavior of amorphous shape memory polymers at an elevated temperature. Fluids 1(2), 15 (2016)
Rao, I.J., Rajagopal, K.R.: A thermodynamic framework for the study of crystallization in polymers. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 53(3), 365–406 (2002)
Sodhi, J.S., Rao, I.J.: Modeling the mechanics of light activated shape memory polymers. IJES 48(11), 1576–1589 (2010)
Rajagopal, K.R., Srinivasa, A.R.: A thermodynamic frame work for rate type fluid models. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 88(3), 207–227 (2000)
Rao, I.J., Rajagopal, K.R.: Study of strain-induced crystallization of polymers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38(6–7), 1149–1167 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0020-7683(00)00079-2
Rao, I.J., Rajagopal, K.R.: Phenomenological modeling of polymer crystallization using the notion of multiple natural configurations. Interfaces Free Bound. 2(1), 73–94 (2000)
Rao, I.J., Rajagopal, K.R.: On the modeling of quiescent crystallization of polymer melts. Polym. Eng. Sci. 44(1), 123–130 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, F., Moon, S. & Joga Rao, I. Modeling the mechanical behavior of crystallizable shape memory polymers: incorporating temperature-dependent viscoelasticity. Int J Adv Eng Sci Appl Math 9, 21–29 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12572-016-0177-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12572-016-0177-y