Abstract
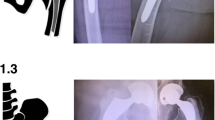
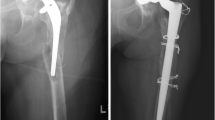
Vancouver type B 2 fractures occur at the tip or just around the stem with the stem being loose but the proximal bone stock is usually well preserved. Their management can be challenging. Fracture and patient-related factors can influence in decision-making process. Both cemented and uncemented revision stems have been usually used with variable success. However, robust recommendations with regard to which treatment might be superior to other cannot be made. Until prospective randomized control trials provide some sound recommendations, the type of treatment used should be individualized.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G (2005) Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplast 20(7):857–865
Bhattacharyya T, Chang D, Meigs JB, Estok DM 2, Malchau H (2007) Mortality after periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89(12):2658–2662
Lindahl H, Garellick G, Regnér H, Herberts P, Malchau H (2006) Three hundred and twenty-one periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88(6):1215–1222
Della Valle CJ, Paprosky WG (2004) The femur in revision total hip arthroplasty evaluation and classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:55–62
Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (2000) The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of the femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplast 15(1):59–62
Naqvi GA, Baig SA, Awan N (2012) Interobserver and Intraobserver reliability and validity of the Vancouver Classification System of periprosthetic femoral fractures after hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 27(6):1047–1050, Epub 2012 Mar 14
Rayan F, Dodd M, Haddad FS (2008) European validation of the Vancouver classification of periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(12):1576–1579
Van Houwelingen AP, Duncan CP (2011) The pseudo A(LT) periprosthetic fracture: it’s really a B2. Orthopedics 34(9):e479–e481
Duwelius PJ, Schmidt AH, Kyle RF, Talbott V, Ellis TJ, Butler JBV (2004) A prospective, modernized treatment protocol for periprosthetic femur fractures. Orthop Clin North Am 35(4):485–492
Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (1998) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur: principles of prevention and management. Instr Course Lect 47:237–242
Neumann D, Thaler C, Dorn U (2012) Management of Vancouver B2 and B3 femoral periprosthetic fractures using a modular cementless stem without allografting. Int Orthop 36(5):1045–1050
Parvizi J, Rapuri VR, Purtill JJ, Sharkey PF, Rothman RH, Hozack WJ (2004) Treatment protocol for proximal femoral periprosthetic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(Suppl 2):8–16
Sledge JB 3, Abiri A (2002) An algorithm for the treatment of Vancouver type B2 periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures. J Arthroplast 17(7):887–892
Chevillotte CJ, Ali MH, Trousdale RT, Larson DR, Gullerud RE, Berry DJ (2009) Inflammatory laboratory markers in periprosthetic hip fractures. J Arthroplast 24(5):722–727
Beals RK, Tower SS (1996) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 327:238–246
Corten K, Macdonald SJ, McCalden RW, Bourne RB, Naudie DD (2012) Results of cemented femoral revisions for periprosthetic femoral fractures in the elderly. J Arthroplast 27(2):220–225, Epub 2011 Jul 12
Katzer A, Ince A, Wodtke J, Loehr JF (2006) Component exchange in the treatment of periprosthetic femoal fractures. J Arthroplast 21(4):572–579
McLauchlan GJ, Robinson CM, Singer BR, Christie J (1997) Results of an operative policy in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fracture. J Orthop Trauma 11(3):170–179
Mont MA, Maar DC (1994) Fractures of the ipsilateral femur after hip arthroplasty. A statistical analysis of outcome based on 487 patients. J Arthroplast 9(5):511–519
Springer BD, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG (2003) Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty with femoral component revision. J Bone Jt Surg Am 85-A(11):2156–2162
Tsiridis E, Narvani AA, Haddad FS, Timperley JA, Gie GA (2004) Impaction femoral allografting and cemented revision for periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(8):1124–3
Briant-Evans TW, Veeramootoo D, Tsiridis E, Hubble MJ (2009) Cement-in-cement stem revision for Vancouver type B periprosthetic femoral fractures after total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 80(5):548–552
Richards CJ, Duncan CP, Crawford RW (2011) Cement-in-cement femoral revision for the treatment of highly selected vancouver B2 periprosthetic fractures. J Arthroplast 26(2):335–337
Mulay S, Hassan T, Birtwistle S, Power R (2005) Management of types B2 and B3 femoral periprosthetic fractures by a tapered, fluted, and distally fixed stem. J Arthroplast 20(6):751–756
Berry DJ (2003) Treatment of Vancouver B3 periprosthetic femur fractures with a fluted tapered stem. Clin Orthop Relat Res 417:224–231
Fink B, Grossmann A, Schubring S, Schulz MS, Fuerst M (2007) A modified transfemoral approach using modular cementless revision stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res 462:105–114
Moran MC (1996) Treatment of periprosthetic fractures around total hip arthroplasty with an extensively coated femoral component. J Arthroplast 11(8):981–988
Parvizi J, Vegari DN (2011) Periprosthetic proximal femur fractures: current concepts. J Orthop Trauma 25(Suppl 2):S77–S81
Sporer SM, Paprosky WG (2004) Femoral fixation in the face of considerable bone loss: the use of modular stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res 429:227–231
Mertl P, Philippot R, Rosset P, Migaud H, Tabutin J, Van de Velde D (2011) Distal locking stem for revision femoral loosening and peri-prosthetic fractures. Int Orthop 35(2):275–282
Eingartner C, Ochs U, Egetemeyer D, Volkmann R (2007) Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures with the Bicontact revision stem. Z Orthop Unfall 145(Suppl 1):S29–S33
Incavo SJ, Beard DM, Pupparo F, Ries M, Wiedel J (1998) One-stage revision of periprosthetic fractures around loose cemented total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop 27(1):35–41
Ko PS, Lam JJ, Tio MK, Lee OB, Ip FK (2003) Distal fixation with Wagner revision stem in treating Vancouver type B2 periprosthetic femur fractures in geriatric patients. J Arthroplast 18(4):446–452
Levine BR, Della Valle CJ, Lewis P, Berger RA, Sporer SM, Paprosky W (2008) Extended trochanteric osteotomy for the treatment of vancouver B2/B3 periprosthetic fractures of the femur. J Arthroplast 23(4):527–533
Macdonald SJ, Paprosky WG, Jablonsky WS, Magnus RG (2001) Periprosthetic femoral fractures treated with a long-stem cementless component. J Arthroplast 16(3):379–383
O’Shea K, Quinlan JF, Kutty S, Mulcahy D, Brady OH (2005) The use of uncemented extensively porous-coated femoral components in the management of Vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(12):1617–1621
Park M-S, Lim Y-J, Chung W-C, Ham D-H, Lee S-H (2009) Management of periprosthetic femur fractures treated with distal fixation using a modular femoral stem using an anterolateral approach. J Arthroplast 24(8):1270–1276
Rayan F, Haddad F (2010) Periprosthetic femoral fractures in total hip arthroplasty—a review. Hip Int 20(4):418–426
Corten K, Vanrykel F, Bellemans J, et al. Long cementless stems used to treat periprosthetic fractures of the femur in the elderly. A cautionary note. Presented at EFORT meeting, Madrid, June 2–5, poster 587. www.efort.org/madrid2010/finalprogramme/PosterContent.asp
Weiss RJ, André S, Kärrholm J (2011) A modular cementless stem vs cemented long-stem prostheses in revision surgery of the hip. A population-based study from the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 82(2):136–142
Richards CJ, Duncan CP, Masri BA, Garbuz DS (2010) Femoral revision hip arthroplasty: a comparison of two stem designs. Clin Orthop Relat Res 46(2):491–496
Harris B, Owen JR, Wayne JS, Jiranek WA (2010) Does femoral component loosening predispose to femoral fracture?: an in vitro comparison of cemented hips. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(2):497–503
Giannoudis PV, Kanakaris NK, Tsiridis E (2007) Principles of internal fixation and selection of implants for periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury 38(6):669–687
Tsiridis E, Spence G, Gamie Z, El Masry MA, Giannoudis PV (2007) Grafting for periprosthetic femoral fractures: strut, impaction or femoral replacement. Injury 38(6):688–697
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special Issue: Periprosthetic fracture treatment
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra-Farfán, E., Carrera, L., Muñetón, D. et al. Vancouver type B 2 fractures: best choice of treatment. Eur Orthop Traumatol 4, 81–88 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12570-012-0119-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12570-012-0119-5