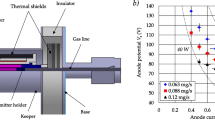
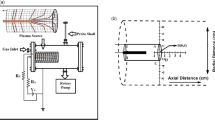
Abstract
When operated with a Hall effect thruster, either centrally or externally mounted, the hollow cathode discharge occurs in a magnetic field environment. Therefore, it is important to assess the influence of the magnetic field on the standalone operation of a hollow cathode to better predict device behavior when coupled with a Hall effect thruster. This study focuses on the influence of an applied axial magnetic field on the main oscillatory phenomena in the plume of a Kr-fed sub-ampere hollow cathode operated with an external disk anode. A probe array consisting of two cylindrical Langmuir probes and an emissive probe is used to assess changes in plasma parameters and collected ion saturation current as the magnetic field strength is varied up to 3 mT at the cathode’s location. The electron transport along the cathode–anode space is analyzed in terms of total electron collision frequency. It is shown that a higher magnetic field strength induces larger plasma densities and lower electron temperatures. Applying a magnetic field to the discharge of a cathode operating in plume mode causes a reduction in both the ionization instability and ion acoustic turbulence (IAT) energies. This suggests a dampening of the main oscillatory phenomena in the plume of the hollow cathode. Furthermore, the total electron collision frequency and its main contributor, the anomalous collision frequency due to high-frequency IAT, decrease at higher field strengths. The results included in this communication are, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, the first characterization of the response in low- and high-frequency wave content depending on a magnetic field in low-current hollow cathodes operating in standalone mode at \(<1\) A.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request from the authors.
Abbreviations
- \(A_p\) :
-
Probe collection area, m\(^{2}\)
- \(A_z\) :
-
Plume cross-sectional area, m\(^{2}\)
- B :
-
Magnetic field strength, T
- CEVAC:
-
Cathode Experiments Vacuum Chamber
- e :
-
Elementary charge, 1.602\(\times\)10\(^{-19}\) C
- E :
-
Electric field strength, V cm\(^{-1}\)
- f :
-
Frequency, Hz
- IAT:
-
Ion acoustic turbulence
- \(I_a\) :
-
Anode current, A
- \(I_{a,std}\) :
-
Standard deviation of the anode current, A
- \(I_k\) :
-
Keeper current, A
- \(I_{sat}\) :
-
ion saturation current, A
- \(J_e\) :
-
current density, A
- \(k_{B}\) :
-
Boltzmann’s constant, 1.38\(\times\)10\(^{-23}\) J K\(^{-1}\)
- KE:
-
Knife-edge
- \(L_{ca}\) :
-
Cathode–anode distance, m
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate, kg s\(^{-1}\)
- m :
-
Electron mass, 9.1\(\times\)10\(^{-31}\) kg
- M :
-
Ion mass, kg
- \(n_e\) :
-
Plasma (electron) density, m\(^{-3}\)
- \(n_n\) :
-
Neutral density, m\(^{-3}\)
- p :
-
Plasma pressure, N m\(^{-2}\)
- PSAC:
-
Plasma Sources and Applications Centre
- \(r_{ko}\) :
-
Keeper orifice radius, m
- \(T_e\) :
-
Electron temperature, eV
- \(T_i\) :
-
Ion temperature, eV
- \(T_g\) :
-
Neutral gas temperature, eV
- \(u_e\) :
-
Electron drift velocity, m s\(^{-1}\)
- \(U_{iz}\) :
-
Ionization reaction rate, m\(^{3}\) s\(^{-1}\)
- \(v_n\) :
-
Neutral thermal velocity, m s\(^{-1}\)
- z :
-
Axial distance, m
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Correction parameter
- \(\phi _{em}\) :
-
Floating potential of the hot emissive probe, V
- \(\phi _f\) :
-
Floating potential, V
- \(\phi _p\) :
-
Plasma potential, V
- \(\varphi\) :
-
Phase angle, degrees
- \(\eta\) :
-
Total plasma resistivity, \(\Omega \cdot {m}\)
- \(\nu _{an}^{IAT}\) :
-
Anomalous collision frequency due to IAT, Hz
- \(\nu _{e}\) :
-
Total electron collision frequency, Hz
- \(\nu _{ei}\) :
-
Electron–ion collision frequency, Hz
- \(\nu _{en}\) :
-
Electron–neutral collision frequency, Hz
- \(\nu _{iz}\) :
-
Ionization collision frequency, Hz
- \(\theta\) :
-
Plume half-angle, degrees
- \(\sigma _{en}\) :
-
Electron–neutral scattering cross section, m\(^{2}\)
- \(\sigma _{iz}\) :
-
Ionization cross section, m\(^{2}\)
- \(\omega\) :
-
Oscillation frequency, Hz
References
Frongello, B.R., Hoskins, W.A., Cassagy, R.J., Kalkowska, L., Maliga, R.K.: Spacecraft electric propulsion at an inflection point. In: Proceedings of the ASCEND Conference. AIAA paper 2021-4151, Las Vegas, NV (2021)
Mazouffre, S.: Electric propulsion for satellites and spacecraft: Established technologies and novel approaches. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 25, 033002 (2016)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Mazouffre, S., Grimaud, L., Joussot, R.: Anode geometry influence on LaB\(_{6}\) cathode discharge characteristics. Phys. Plasmas 26, 113506 (2019)
Goebel, D.M., Katz, I.: Fundam. Electric Propuls. Ion Hall Thrusters. JPL Space Science and Technology Series. Wiley & Sons, NJ (2008)
Hall, S.J., Gray, T.G., Yim, J.T., Choi, M., Mooney, M.M., Sarver-Verhey, T.R., Kamhawi, H.: The Effect of a Hall Thruster-like Magnetic Field on Operation of a 25-A class Hollow Cathode. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Electric Propulsion Conference. IEPC paper 2019-300, Vienna, Austria (2019)
Tilley, D.L., de Grys, K.H., Myers, R.M.: Hall thruster - cathode coupling. In: Proceedings of the 35th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. AIAA paper 1999-2865, Los Angeles, CA (1999)
Hofer, R.R., Johnson, L.K., Goebel, D.M., Fitzgerald, D.J.: Effects of an internally-mounted cathode on Hall thruster plume properties. In: Proceedings of the 42nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. AIAA paper 2006-4482, Sacramento, CA (2007)
Sommerville, J.D., King, L.B.: Effect of cathode position on Hall-effect thruster performance and cathode coupling voltage. In: Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. AIAA paper 2007-5174, Cincinnati, OH (2007)
McDonald1, M.S., Gallimore, A.D.: Cathode Position and Orientation Effects on Cathode Coupling in a 6-kW Hall Thruster. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference. IEPC paper 2009-113, Ann Arbor, MI (2009)
Bechtel, R.T.: Discharge chamber optimization of the SERT II thruster. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 5, 795–800 (1968)
Knauer, W., Poeschel, R.L., Ward, J.W.: The radial field Kaufman thruster. In: Proceedings of the 7th Electric Propulsion Conference. AIAA paper 1969-259, Williamsburg, VA (2007)
Tsikata, S., Hara, K., Mazouffre, S.: Characterization of hollow cathode plasma turbulence using coherent Thomson scattering. J. Appl. Phys. 130, 243304 (2021)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Xu, L., Xu, S.: A low-current LaB\(_{6}\) open-end knife-edge emitter hollow cathode for low-power Hall thrusters. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 30, 085012 (2021)
Goebel, D.M., Jameson, K.K., Katz, I., Mikellides, I.G.: Potential fluctuations and energetic ion production in hollow cathode discharges. Phys. Plasmas 14, 103508 (2007)
Thomas, R.E., Kamhawi, H., Williams, G.J.: High current cathode plasma plume measurements. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Electric Propulsion Conference. IEPC paper 2013-076, Washington, D.C. (2013)
Becatti, G., Goebel, D.M., Zuin, M.: Observation of rotating magnetohydrodynamic modes in the plume of a high-current hollow cathode. J. Appl. Phys. 129, 033304 (2021)
Georgin, M.P.: Ionization instability of the hollow cathode plume. Ph.D. thesis, University of Michigan, MI, USA (2020)
Imaguchi, D., Watanabe, H., Imai, S., Funaki, I., Yamagiwa, Y.: Characterization of a hollow cathode plasma with magnetic fields. In: Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2021 Forum. AIAA 2021-3388, Virtual event (2021)
Becatti, G., Burgalassi, F., Paganucci, F., Zuin, M., Goebel, D.M.: Resistive MHD modes in hollow cathodes external plasma. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 31, 015016 (2022)
Tanaka, S., Akiba, M., Horiike, H., Okumura, Y., Ohara, Y.: Effect of magnetic field on the characteristics of a hollow cathode ion source. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 54, 1104 (1983)
Gabriel, S., Daykin-Iliopoulos, A., Praeger, M., Coletti, M.: Hollow cathode operation with different gases. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Electric Propulsion Conference. IEPC paper 2017-440, Hyogo-Kobe, Japan (2017)
Lev, D.R., Mikellides, I.G., Pedrini, D., Goebel, D.M., Jorns, B.A., McDonald, M.S.: Recent progress in research and development of hollow cathodes for electric propulsion. Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 3, 6 (2019)
Jorns, B.A., Hofer, R.R.: Low frequency plasma oscillations in a 6-kw magnetically shielded Hall thruster. In: Proceedings of the 49th AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. AIAA paper 2017-4119, San Jose, CA (2013)
Hepner, S.T., Tang, E., Dale, E.T., Jorns, B.A.: Rotational waves in the plume of an externally-mounted Hall thruster cathode. AIAA J. 8, 1–5 (2021)
Mikellides, I.G., Ortega, A.L., Goebel, D.M., Becatti, G.: Dynamics of a hollow cathode discharge in the frequency range of 1–500 kHz. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 29, 035003 (2020)
Mikellides, I..G., Guerrero, P., Ortega, A.L., Polk, J.E.: Spot-to-plume mode transition investigations in the HERMeS hollow cathode discharge using coupled 2-D axisymmetric plasma-thermal simulations. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Joint Propulsion Conference. AIAA paper 2018-4722, Cincinnati, OH (2018)
Jorns, B.A., Mikellides, I.G., Goebel, D.M.: Ion acoustic turbulence in a 100-A LaB\(_{6}\) hollow cathode. Phys. Rev. E 90, 063106 (2014)
Sary, G., Garrigues, L., Boeuf, J.-P.: Hollow cathode modeling: I A coupled plasma thermal two-dimensional model. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26, 055007 (2017)
Sary, G., Garrigues, L., Boeuf, J.-P.: Hollow cathode modeling: II Physical analysis and parametric study. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 26, 055008 (2017)
Georgin, M.P., Jorns, B.A., Gallimore, A.D.: Correlation of ion acoustic turbulence with self-organization in a low-temperature plasma. Phys. Plasmas 26, 082308 (2019)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Xu, S.: Evidence of the ionization instability and ion acoustic turbulence correlation in sub-ampere hollow cathodes. J. Electr. Propuls. 1, 6 (2022)
Georgin, M.P., Jorns, B.A., Gallimore, A.D.: Dependence of low frequency waves on magnetic field strength in hollow cathode plume. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Electric Propulsion Conference. IEPC paper 2019-249, Vienna, Austria (2019)
Pedrini, D., Ducci, C., Cesari, U., Misuri, T., Andrenucci, M.: SITAEL HC1 Low-Current Hollow Cathode. Aerospace 7, 96 (2020)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Xu, L., Levchenko, I., Huang, S., Sun, Y., Rohaizat, M.W.A..B., Lim, J.W.M., Bazaka, K., Xu, S.: Mode transition in a low-current LaB\(_{6}\) hollow cathode for electric propulsion systems for small satellites. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Electric Propulsion Conference. IEPC paper 2019-427, Vienna, Austria (2019)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Xu, L., Huang, S., Rohaizat, M.W.A.B., Xu, S.: Discharge mode transition in a krypton-fed 1 A-class LaB\(_{6}\) cathode for low-power Hall thrusters for small satellites. J. Appl. Phys. 127, 064501 (2019)
Georgin, M.P., Jorns, B.A., Gallimore, A.D.: Transient non-classical transport in the hollow cathode plume I: measurements of time-varying electron collision frequency. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 29, 105010 (2020)
Gurciullo, A., Fabris, A.L., Potterton, T.: Numerical study of a hollow cathode neutraliser by means of a zero-dimensional plasma model. Acta Astronaut. 174, 219–223 (2020)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Xu, S.: Phenomenological plasma model for open-end emitter with orificed keeper hollow cathodes. Acta Astronaut. 191, 293–316 (2022)
Jorns, B.A., Cusson, S.E., Brown, Z., Dale, E.: Non-classical electron transport in the cathode plume of a Hall effect thruster. Phys. Plasmas 27, 022311 (2020)
Georgin, M.P., McDonald, M.S.: Experimental evaluation of the 2D nonclassical ohmic transport model for electrons in the hollow cathode plume. J. Appl. Phys. 130, 203301 (2021)
Domonkos, M.T.: Evaluation of low-current orificed hollow cathodes. Ph.D. thesis, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA (1999)
Sheehan, J.P., Hershkowitz, N.: Emissive probes. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 20, 063001 (2011)
Sheehan, J.P., Raitses, Y., Hershkowitz, N., Kaganovich, I., Fisch, N.J.: A comparison of emissive probe techniques for electric potential measurements in a complex plasma. Phys. Plasmas 18, 073501 (2011)
Hobbs, G.D., Wesson, J.A.: Heat flow through a Langmuir sheath in the presence of electron emission. Plasma Phys. 9, 85 (1967)
Chen, F.F.: Langmuir probe diagnostics. In: IEEE-ICOPS Meeting. Mini-Course on Plasma Diagnostics, Jeju, Korea (2003)
Nobata, K.: Characteristics of Langmuir probe in a strong magnetic field. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2, 719–727 (1963)
Grimaud, L., Pétin, A., Vaudolon, J., Mazouffre, S.: Perturbations induced by electrostatic probe in the discharge of Hall thrusters. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 87, 043506 (2016)
Ito, T., Cappelli, M.A.: Electrostatic probe disruption of drift waves in magnetized microdischarges. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 211501 (2009)
Herman, D.A., Gallimore, A.D.: Discharge cathode electron energy distribution functions in a 40-cm next-type ion engine. In: Proceedings of the 2005 Joint Propulsion Conference. AIAA paper 2005-4252, Tucson, AZ (2005)
Reid, B.M., Gallimore, A.D.: Langmuir probe measurements in the discharge channel of a 6-kW Hall thruster. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Joint Propulsion Conference. AIAA paper 2008-4920, Hartford, CT (2008)
Popov, T.K., Dimitrova, M., Ivanova, P., Hasan, E., Horáček, J., Dejarac, R., Stöckel, J., Weinzettl, V., Kovačič, J.: Langmuir probe evaluation of the plasma potential in tokamak edge plasma for non-maxwellian EEDF. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 54(3), 267–272 (2014)
Potrivitu, G.-C., Joussot, R., Mazouffre, S.: Anode position influence on discharge modes of a LaB\(_{6}\) cathode in diode configuration. Vacuum 151, 122–132 (2018)
Abernethy, R.B., Benedict, R.P., Dowdell, R.B.: ASME measurement uncertainty. J. Fluids Eng. 107, 161–164 (1985)
Kline, S.J., McClintock, F.A.: Describing uncertainties in single sample experiments. Mech. Eng. 75, 3–8 (1953)
Joussot, R., Grimaud, L., Mazouffre, S.: Examination of a 5 A-class cathode with a LaB\(_{6}\) flat disk emitter in the 2 A-20 A current range. Vacuum 146, 52–62 (2017)
Lev, D.R., Alon, G., Appel, L.: Low current heaterless hollow cathode neutralizer for plasma propulsion-development overview. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90, 113303 (2019)
Nikrant, A.: Development and modelling of a low current LaB\(_{6}\) heaterless hollow cathode. M.Sc. thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University Blacksburg, VA, USA (2019)
Kaufman, H.R.: Technology of Electron-Bombardment Ion Thrusters. Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics, vol. 36, pp. 265–373. Academic Press, New-York, NY (1974)
Jack, T.M., Patterson, S.W., Fearn, D.G.: The effect of the keeper electrode on hollow cathode characteristics. In: Proceedings of the 36th Joint Propulsion Conference. AIAA paper 2000-3533, Huntsville, AL (2000)
Hall, S.J., Gray, T.G., Sarver-Verhey, T.R., Kamhawi, H.: The Effect of Anode Configuration on the Plasma Plume of a 25-A class Hollow Cathode. In: Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2021 Forum. AIAA 2021-3376, Virtual event (2021)
Mikellides, I.G., Katz, I., Goebel, D.M., Jameson, K.K.: Evidence of nonclassical plasma transport in hollow cathodes for electric propulsion. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 063301, 055008 (2007)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Sedina Tsikata for her valuable insights into plasma instabilities and turbulence.
Funding
This work was supported by OSTIn-SRP/EDB through the National Research Foundation and in part by the Ministry of Education Singapore through MOE AcRF (RP6/16XS). George-Cristian Potrivitu acknowledges the support from the National Institute of Education Singapore through the NIE PhD Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests as defined by Springer, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Consent for publication
The authors give their consent for publication.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Potrivitu, GC., Xu, S. Ionization instability and turbulence in the plume of sub-ampere hollow cathodes depending on an applied magnetic field. CEAS Space J 15, 729–749 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-022-00478-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-022-00478-5