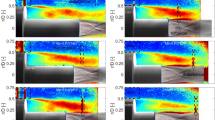
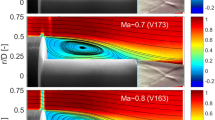
Abstract
Afterbody flow phenomena represent a significant source of uncertainties in the design of a launcher. Therefore, there is a demand for measuring such flows in wind tunnels. For propulsive jet simulation a new jet facility was integrated into a hypersonic/supersonic wind tunnel. The jet simulation resembles the generic model of a staged rocket launcher. The design and the qualification of the facility are reported. This includes measurements of pressure, temperature and Mach number distribution. Pressure and Schlieren measurements are conducted in the wake of the generic launcher. The unsteady pressure characteristics at the generic rocket base and fairing are analyzed for supersonic and hypersonic freestream. The influence of the under-expanded jet is reported and the jet temperatures are varied. On the base fluctuations at a Strouhal number around 0.25 dominates supersonic freestream flows. Additionally, a fluctuation level increase on the base is observed for Strouhal numbers above 0.75 in hypersonic flow regime, which is attributed to the interactions of wake flow and jet.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delery, J., Sirieix, M.: Base flows behind missiles. AGARD LS-98, vol. 6, pp. 1–78 (1979)
Shvets, A.: Base pressure fluctuations. Fluid Dyn. 14(3), 394–401 (1979)
Eldred, K.: Base pressure fluctuations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 33(1), 59–63 (1961)
Herrin, J.L., Dutton, J.C.: The turbulence structure of a reattaching axisymmetric compressible free shear layer. Phys. Fluids 9, 3502 (1997). doi:10.1063/1.869458
Mabey, D.G.: Some measurements of base pressure fluctuations at subsonic and supersonic speeds. Aeronautical Research Council, ARC-CP-1204, pp. 1–11 (1972)
Deck, S., Thorigny, P.: Unsteadiness of an axisymmetric separating-reattaching flow: numerical investigation. Phys. Fluids 19, 065103 (2007). doi:10.1063/1.2734996
Janssen, J.R., Dutton, J.C.: Time-series analysis of supersonic base-pressure fluctuations. AIAA J. 42(3), 605–613 (2004)
Herrin, J.L., Dutton, J.C.: Supersonic base flow experiments in the near wake of a cylindrical afterbody. AIAA J. 32(1), 77–83 (1994)
Xiao, Z., Fu, S.: Studies of the unsteady supersonic base flows around three afterbodies. Acta. Mech. Sin. 25, 471–479 (2009). doi:10.1007/s10409-009-0248-4
Weiss, P.-E., Deck, S., Robinet, J.-C., Sagaut, P.: On the dynamics of axisymmetric turbulent separating/reattaching flows. Phys. Fluids 21, 075103 (2009). doi:10.1063/1.3177352
Bitter, M., Scharnowski, S., Hain, R., Kaehler, C.J.: High-repetition-rate PIV investigations on a generic rocket model in sub- and supersonic flows. Exp. Fluids 50, 1019–1030 (2011). doi:10.1007/s00348-010-0988-8
Simon, F., Deck, S., Guillen, P., Sagaut, P.: Reynolds-averaged navier–stokes/large-eddy simulations of supersonic base flow. AIAA J. 44(11), 2578–2590 (2006)
Sahu, J.: Computations of supersonic flow over a missile afterbody containing an exhaust jet. J. Spacecr. 24(5), 403–410 (1987)
Kawai, S., Fujii, K.: Computational study of supersonic base flow using hybrid turbulence methodology. AIAA J. 43(6), 1265–1275 (2005)
Deprés, D., Reijasse, P.: Analysis of unsteadiness in afterbody transonic flows. AIAA J. 42(12), 2541–2550 (2004)
Sahu, J., Heavey, K.R.: Numerical investigation of supersonic base flow with base blees. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 34(1), 61–69 (1995)
Wong, H., Meijer, J., Schwane, R.: Theoretical and experimental investigations on Ariane 5 base-flow buffeting. In: Proceedings of the 5th European Symposium on Aerothermodynamics for Space Vehicles, ESA Publications Division ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands (ESA SP-563) (2005)
Bergman, D.: Effects of engine exhaust flow on boattail drag. J. Aircr. 8(6), 434–438 (1971)
Weiss, P.E., Deck, S., Sagaut, P.: Zonal-detached-eddy-simulation of a two-dimensional and axisymmetric separating/reattaching flow. In: 38th Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit, Seattle, Washington, AIAA 2008-4377, 23–26 June 2008
Venkatakrishnan, L., Suriyanarayanan, P., Mathur, N.B.: BOS density measurements in afterbody flows with shock and jet effects. In: 37th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit, Miami, FL, AIAA 2007-4223, 25–28 June 2007
Peters, W.L., Kennedy, T.L.: Jet simulation techniques—simulation of aerodynamic effects of jet temperature by altering gas compositions. In: Proceedings of the 17th Aerospace Sciences Meetings, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (1979)
Peters, W.L., Kennedy, T.L.: An evaluation of jet simulation parameters for nozzle/afterbody testing at transonic mach number. In: Proceedings of the 15th Aerospace Sciences Meetings, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (1977)
Kumar, R., Viswanah, P.R.: Mean and fluctuating pressure in boat-tail separated flows at transonic speeds. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 39(3), 430–438 (2002)
Reijasse, P., Delery, J.: Experimental analysis of the flow past the afterbody of the Ariane 5 European launcher. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 31(2), 208–214 (1994). doi:10.2514/3.26424
Statnikov, V., Saile, D., Meiß, J.H., Henckels, A., Meinke, M., Guelhan, A., Schroeder W.: Experimental and numerical investigation of the turbulent wake flow of a generic space launcher configuration. In: Proceedings of the 5th European Conference for Aerospace Sciences, EUCASS (2013)
Statnikov, V., Sayadi, T., Meinke, M., Schmid, P., Schröder, W.: Analysis of pressure perturbation sources on a generic space launcher afterbody in supersonic flow using zonal turbulence modeling and dynamic mode decomposition. Phys. Fluids 27(1) (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4906219
Saile, D., Guelhan, A., Henckels, A., Glatzer, C., Statnikov, V., Meinke, M.: Investigations on the turbulent wake of a generic space launcher geometry in the hypersonic flow regime. EUCASS Prog. Flight Phys. 5, 209–234 (2013). doi:10.1051/eucass/201305209
Saile, D., Guelhan, A.: Plume-induced effects on the near-wake region of a generic space launcher geometry. In: Proceedings of the 32nd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, AIAA 2014–3137 (2014)
Koppenwallner, G., Mueller-Eigner, R., Friehmelt, H.: HHK Hochschul-Hyperschall-Kanal: Ein “Low cost” Windkanal für Forschung und Ausbildung. DGLR Jahrbuch, Band 2, 887–896 (1993)
Pindzola, M.: Jet simulation in ground test facilities. AGARDograph 79(11), 1–56 (1963)
Hannemann, K., Luedeke, H., Pallegoix, J.F., Ollivier, A., Lambare, H. Maseland, J.E.J., Geurts, E.G.M., Frey, M., Deck, S., Schrijer, F.F.J., Scarano, F., Schwane, R.: Launch vehicle base buffeting—Recent experimental and numerical investigations. In: Proceedings of 7th European Symposium on Aerothermodynamics, ESA Communications ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands (ESA SP-692) (2011)
Estorf, M., Wolf, T., Radespiel, R.: Experimental and numerical investigations on the operation of the hypersonic Ludwieg tube Braunschweig. In: Proceedings of the 5th European Symposium on Aoerothermo-dynamics for Space Vehicles, ESA SP-563, 579–586 (2005)
Wu, J., Radespiel, R.: Tandem nozzle supersonic wind tunnel design. Int. J. Eng. Syst. Model. Simul. Proc. 5(1), 8–18 (2013). doi:10.1504/IJESMS.2013.052369
Wu, J., Radespiel, R., Zamre, P.: Disturbance characterization and flow quality improvement in a Tandem Nozzle Mach 3 Wind Tunnel. Exp. Fluids (2015). doi:10.1007/s00348-014-1887-1
Saile, D., Henckels, A., Guelhan, A.: Design of the TIC-nozzle and Definition of the Instrumentation. In: ADAMS, N.A. et al. (eds) DFG Sonderforschungsbereich/Transregio 40—Annual Report 2009, TU München, Garching (2009)
Gruemmer, K.: Ein Rechenprogramm für den Entwurf ebener und rotationssymmetrischer Überschallwindkanaldüsen. DFVLR-FB 76–59, Deutsches Zentrum für Luft, Und Raumfahrt, Cologne (1976)
Launch Kit Flight 202 Ariane 5.http://www.astrium.eads.net/en/launch-kits/launch-kit-flight-202-ariane-5-st2-gsat-8-insat-4g.html (2013). Accessed 11 March 2013
Ali, S.R.C., Wu, J., Radespiel, R., Schilden, T., Schroeder, W.: High-frequency measurements of acoustic and entropy disturbances in a hypersonic wind tunnel. In: Proceedings of the 44th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference (2014). doi:10.2514/6.2014-2644
Morkovin, M.V.: Fluctuations and hot-wire anemometry in compressible flows. AGARD-AG-24 (1956)
Kovasznay, L.S.: Turbulence in supersonic flow. J. Aeronaut. Sci. 20, 657–674 (1953)
Laufer, J.: Some statistical properties of the pressure field radiated by a turbulent boundary layer. Phys. Fluids (1958–1988) 7(8), 1191–1197 (1964)
Stainback, P.C., Wagner, R.D.: A comparison of disturbance levels measured in hypersonic tunnels using a hot-wire anemometer and a pitot pressure probe. In: Proceedings of the 7th Aerodynamic Testing Conference. AIAA paper no. 72–1003. Palo Alto, California, Sep. 13–15 (1972)
Pain, R., Weiss, P.E., Deck S.: Zonal detached eddy simulation of the flow around a simplified launcher afterbody. AIAA J. 52(9), 1967–1979 (2014). doi:10.2514/1.J052743
Schwane, R.: Numerical prediction and experimental validation of unsteady loads on Ariane 5 and VEGA. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 52(1), 54–62 (2015). doi:10.2514/1.A32793
Acknowledgments
The work was funded by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) within the framework Sonderforschungsbereich Transregio 40 (Technological foundations for the design of thermally and mechanically highly loaded components of future space transporting systems). The authors thank R. Müller-Eigner (Hyperschall Technologie Goettingen GmbH, HTG, Katlenburg-Lindau) for the efforts in designing and manufacturing the jet simulation facility and D. Saile (German Aerospace Center, DLR, Cologne) and V. Statnikov (RWTH Aachen) for supporting the PSD analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stephan, S., Wu, J. & Radespiel, R. Propulsive jet influence on generic launcher base flow. CEAS Space J 7, 453–473 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-015-0098-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-015-0098-9