Abstract
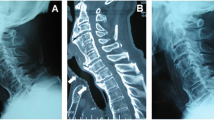
Osteoarthritis is a common complication in the elderly and is often associated with osteophyte growth on vertebral bodies. The clinical presentation of vertebral osteophytes is related to anatomical structures adjacent to the spinal column. For instance, cervical osteophytes potentially involve the pharynx and esophagus, leading to dysphagic symptoms that may be accompanied by food aspiration, vocal fold paralysis and obstructive sleep apnea. In addition to anterior cervical osteophytes, posterior and uncinate process osteophytes may form, compressing the spinal cord and vertebral artery blood supply, respectively. Cervical osteophytes have also been shown to form an accessory median atlanto-occipital joint when the relationship between the atlas, dens and basiocciput is involved. In the thorax, the esophagus is often affected by osteophytes and may result in dysphagia. Traumatic and non-traumatic thoracic aorta pseudoaneurysm formation has been attributed to sharp osteophytes lacerating the aorta, a direct complication of the relationship between the aorta anterior vertebral column. Additionally, aspiration pneumonia was reported in patients with compression of a main stem bronchus, due to mechanical compression by thoracic osteophytes. In the lumbar spinal region, the two major structures in close proximity to the spine are the inferior vena cava and abdominal aorta, both of which have been reported to be affected by osteophytes. Treatment of osteophytes is initially conservative with anti-inflammatory medications, followed by surgical removal. Increasing obesity and geriatric populations will continue to result in an array of osteoarthritic degenerative changes such as osteophyte formation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronowitz P, Cobarrubias F (2003) Anterior cervical osteophytes causing airway compromise. N Engl J Med 349:26
Aufdermauer M (1979) Bewegungsapparat. In: Buchner F, Grundmann E (eds) Lehrbuch der speziellen Pathologie, 6th edn. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München, pp 568–629
Barre JA (1924) Troubles pyramidaux et arthrite vertebrale chronique. Médecine 5:358
Bovim G, Schrader H, Sand T (1994) Neck pain in the general population. Spine 19:1307–1309
Brandenberg G, Leibrock LG (1986) Dysphagia and dysphonia secondary to anterior cervical osteophytes. Neurosurgery 18:90–93
Bridges PS (1994) Vertebral arthrits and physical activities in the prehistoric southeastern United States. Am J Phys Anthropol 92:83–93
Brown DE, Neumann RD (2004) Orthopedic secrets. In: Osteoarthritis, Chap I, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1–3
Cagnie B, Barbaix E, Vinck E, D’Herde K, Cambier D (2005) Extrinsic risk factors for compromised blood flow in the vertebral artery: anatomical observations of the transverse foramina from C3 to C7. Surg Radiol Anat 27:312–316
Cai FZJ, Rischmueller M, Pile K, Brady SJ (2003) Dysphagia associated with lower thoracic spondylosis. Rheumatology 42:1575–1576
Calisaneller T, Ozdemir O, Tosun E, Altinors N (2005) Dysphagia due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Acta Neurochir 147:1203–1206
Chanchairujira K, Chung CB, Kim JL, Papakonstantinou O, Lee MH, Clopton P, Resnick D (2004) Intervertebral disk calcification of the spine in an elderly population: radiographic prevalence, location, and distribution and correlation with spinal degeneration. Radiology 230:499–503
Chouret EE (1967) The greater occipital neuralgia headache. Headache 7:33–34
Chtata H, Koskas F, Cluzel P, Kieffer E (2005) Traumatic pseudoaneurysm of the descending thoracic aorta inflicted by a spinal osteophyte. Ann Vasc Surg 19:263–266
Cloward RB (1987) Spinal stenosis: treatment by posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 3:457–516
Crowther A, Ardran GM (1985) Dysphagia due to cervical spondylosis. J Laryngol Otol 99:1167–1169
Cvijetic S, McCloskey E, Korsic M (2000) Vertebral osteophytosis and vertebral deformities in an elderly population sample. Wien Klin Wochenschr 112:407–412
Davies R, Sage MR, Brophy B (1989) Cervical osteophyte-induced dysphagia. Australas Radiol 33:3
Deutsch E, Schild J, Mafee M (1985) Dysphagia and Foresteir’s disease. Arch Otolaryngol 111:400–403
Di Vito J (1998) Cervical osteophytic dysphagia: single and combined mechanisms. Dysphagia 13:58–61
Dregelid E, Jenssen G, Jonung T, Braaten A (2007) Pseudoaneurysm of the abdominal aorta due to a needle-like osteophyte on the first lumbar vertebra. J Vasc Surg 45:1059–1061
Dutton CB, Riley LH (1969) Cervical migraine. Am J Med 47:141–148
Ebraheim N, Lu J, Hao Y, Biyani A, Yeasting RA (1997) Anatomic considerations for uncovertebral involvement in cervical spondylosis. Clin Orthop 334:200–206
Edmeads J (1978) Headaches and head pains associated with diseases of the cervical spine. Med Clin North Am 62:533–544
Fournier AM, Rathelot J (1959) L’arthrose atlanto-odontoidienne: Sa frequence comme cause d’algies nucales. J Radiol d’Electrol Med Nucl 22:812–813
Fuerderer S, Eysel-Gosepath K, Schroder U, Delank KS, Eysel P (2004) Retro-pharyngeal obstruction in association with osteophytes of the cervical spine. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 86-B:837–840
Gilchrist RV, Slipman CW, Isaac Z, Lenrow DA, Chou LH (2002) Vascular supply to the lumbar spine: an intimate look at the lumbosacral nerve roots. Pain Phys 5:288–293
Goel R, Sampath P, Mikaelian DO (1999) Dysphagia caused by cervical osteophytes: three cases treated successfully by surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:92–96
Hanamura H, Higuchi Y, Nakagawa M, Iwata H, Urist MR (1980) Solubilized bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) from mouse osteosarcoma and rat demineralized bone matrix. Clin Orthop 148:281–290
Hasegawa H, Bitoh S, Ohtsuki H, Obashi J, Furukawa H, Yamamoto T (1984) A case of Forestier’s disease causing dysphagia. No Shinkei Geka 12:1379–1383
Hilding DA, Tachdjian MO (1960) Dysphagia and hypertrophic spurring of the cervical spine. N Engl J Med 263:11–14
Idem K (1906) Ein zweiter Fall von Abkinckung des Speiserohre durch vertebrale Ekchondrose. Munch Med Wochenschr 53:906–907
Iglauer S (1938) A case of dysphagia due to an osteochondroma of the cervical spine–osteotomy–recovery. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 47:799–803
Jackson R (1967) Headaches associated with disorders of the cervical spine. Headache 6:175–179
Kamieth H (1959) Ein nicht sicher einzuordnender Knochenkeil am Unterrand des Clivus. Fortshr Rontgenstr 91:334–339
Kanbay M, Selcuk H (2006) Dysphagia caused by cervical osteophytes: a rare case. J Am Geriatr 54:1147–1148
Karasik D, Kiel DP, Kiely DK, Cupples LA, Wilson PW, O’Donnell CJ, Felson DT (2006) Abdominal aortic calcification and exostoses at the hand and lumbar spine: the Framingham Study. Calcif Tissue Int 78:1–8
Knusel CJ, Goggel S, Lucy D (1997) Comparative degenerative joint disease of the vertebral column in the medieval monastic cemetery of the Gilbertine Priory of St. Andrew, Fishergate, York England. Am J Phys Anthropol 103:481–495
Kodama M, Sawada H, Udaka F, Kameyama M, Koyama T (1995) Dysphagia caused by an anterior cervical osteophyte: case report. Neuroradiology 37:58–59
Krogdahl T, Torgersen O (1940) Die “Unco-vertebral Gelenke” und die “Arthrosis Deformans Unco-vertebralis”. Acta Radiol 21:231
Lambert JR, Teppermann PS, Jimenez J, Newman A (1981) Cervical spine disease and dysphagia. Am J Gastroenterol 76:35–40
Leon JA, Calamia KT, Leventhal JP (2000) Chronic obstructive pneumonia caused by a vertebral body osteophyte. Mayo Clin Proc 75:185–188
Leroux JL, Legeron P, Moulinier L, Laroche M, Mazieres B, Blotman F, Arletet J (1992) Stenosis of the lumbar spinal cord in vertebral ankylosing hyperostosis. Spine 17:1213–1218
Matsumoto M, Chiba K, Nojiri K, Ishikawa M, Toyama Y, Nishikawa Y (2002) Extraforaminal entrapment of the fifth lumbar spinal nerve by osteophytes of the lumbosacral spine: anatomic study and a report of four cases. Spine 27:E169–E173
Meeks LW, Renshaw TS (1973) Vertebral osteophytosis and dysphagia. J Bone Joint Surg 55:197–201
Mosher HP (1926) Exostoses of the cervical osteophytes as a cause for difficulty in swallowing. Laryngoscope 36:181–182
Nathan H (1987) Osteophytes of the spine compressing the sympathetic trunk and splanchnic nerves in the thorax. Spine 12:527–532
Ng J, Gnanalingham KK, Stokes O, Singh A, Casey A (2005) Anterior cervico-thoracic osteophytes: an unusual cause of dysphagia. Br J Neurosurg 19:173–197
O’Neill TW, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Bhalla AK, Reeve J, Reid DM, Todd C, Woolf AD, Silman AJ (1999) The distribution, determinants, and clinical correlates of vertebral osteophytosis: a population based survey. J Rheumatol 26:842–848
Otake S, Takahashi M, Ishigaki T (2002) Focal pulmonary interstitial opacities adjacent to thoracic spine osteophytes. Am J Roentgenol 179:893–896
Pate D, Goobar J, Resnick D, Haghighi P, Sartoris DJ, Pathria MN (1988) Traction osteophytes of the lumbar spine: radiographic-pathologic correlation. Radiology 166:843–846
Pye SR, Reid DM, Lunt M, Adams JE, Silman AJ, O’Neill TW (2007) Lumbar disc degeneration: association between osteophytes, end-plate sclerosis and disc space narrowing. Ann Rheum Dis 66:330–333
Resnick DE, Shapiro RF, Wiesner KB, Niwayama G, Utsinger PD, Shaul SR (1978) Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). Semin Arthritis Rheum 17:153–187
Robinson RA, Walker AE, Ferlic DC, Wiecking DK (1962) The results of anterior interbody fusion of the cervical spine. J Bone Joint Surg A 44:1569–1587
Rosen HJ (1985) Dysphagia due to cervical spine osteophytes. Can Med Assoc J 133:15
Scapinelli R (1997) Compression of the inferior vena cava due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 64:198–201
Schmidek HH (1986) Cervical spondylosis. Am Fam Phys 33:89–99
Schmitt H, Dubljanin E, Schneider S, Schiltenwolf M (2004) Radiographic changes in the lumbar spine in former elite athletes. Spine 29:2554–2559
Schmorl G, Junghanns H (1971) The human spine in health and disease, 2nd edn. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 158–198
Seawright AA, English PB, Gartner RJW (1965) Hypervitaminosis A and hyperostosis of the cat. Nature (Lond) 206:1171–1172
Sheehan S, Bauer R, Meyer J (1960) Vertebral artery compression in cervical spondylosis. Arteriographic demonstration during life of vertebral artery insufficiency due to rotation and extension of the neck. Neurology 10:386–396
Snodgrass JJ (2004) Sex differences and aging of the vertebral column. J Forensic Sci 49:458–463
Sobol SM, Rigual NR (1984) Anterolateral extrapharyngeal approach for cervical osteophyte-induced dysphagia: literature review. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 93:498–504
Sofaer-Derevenski JR (2000) Sex differences in activity-related osseous change in the spine and the gendered division of labor at Ensay and Wharram Percy, UK. Am J Phys Anthropol 111:333–354
Srinivas P, George J (1999) Cervical osteoarthropathy: an unusual cause of dysphagia. Age Aging 28:321–322
Stancampiano FF, Zavelta EG, Astor FC (2002) Anterior cervical osteophytes: a rare cause of dysphagia and upper airway obstruction in older patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 50:1910
Stevens JM, Clifton AG, Whitear P (1993) Appearances of posterior osteophytes after sound anterior interbody fusion in the cervical spine: a high definition computed myelographic study. Neuroradiology 35:227–228
Strasser G, Schima W, Schober E, Pokieser P, Kaider A, Denk DM (2000) Cervical osteophytes impinging on the pharynx: importance of size and concurrent disorders for development of aspiration. Am J Roentgenol 174:449–453
Stuart D (1989) Dysphagia due to cervical osteophytes. Int Orthop 13:95–99
Uppal S, Wheatley AH (1999) Transpharyngeal approach for the treatment of dysphagia due to Forestier’s disease. J Laryngol Otol 113:366–368
Urist MR, Mikulski A, Lietze A (1979) Solubilized and insolubilized bone morphogenetic protein (BMP). Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:1828–1832
von Ludinghausen M, Fahr M, Prescher A, Schindler G, Kenn W, Weiglein A, Yoshimura K, Kageyama I, Kobayashi K, Tsuchimochi M (2005) Accessory joints between basiocciput and atlas/axis in the median plane. Clin Anat 18:558–571
von Ludinghausen M, Prescher A, Kageya I, Yoshimura K (2006) The median atlanto-occipital joint in advanced age. Spine 31:E430–E436
Willing S, El Gammal T (1983) Thoracic osteophyte producing dysphagia in a case of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hypertrophy. Am J Gastroenterol 78:381–383
Yee C, Wong HY, Fewer HD, Rogers AG (1985) Two cases of dysphagia due to cervical spine osteophytes successfully treated surgically. Can Med Assoc J 132:810–812
Yoskovitch A, Kantor S (2001) Cervical osteophytes presenting as unilateral vocal fold paralysis and dysphagia. J Laryngol Otol 115:422–424
Yutan E, Daras M, Koppel BS (2001) Dysphagia due to cervical osteophytes. J Clin Imag 25:262–264
Zahn H (1905) Ein Fall von Abknickung der Speiserohre durch vertebrale Ekchondrose. Munch Med Wochenschr 52:1680–1682
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Miss Kate Kryger for obtaining the pictures from the anatomy laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klaassen, Z., Tubbs, R.S., Apaydin, N. et al. Vertebral spinal osteophytes. Anat Sci Int 86, 1–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-010-0080-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-010-0080-8