Abstract
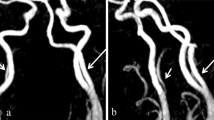
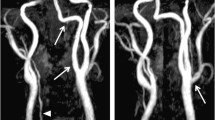
We observed a rare case of the right persistent hypoglossal artery (PHA) in the posterior cranial fossa of a deceased 74-year-old Japanese man who did not have any clinical manifestations related to this anomaly when alive. The large-sized PHA originating from the cervical internal carotid artery passed through the hypoglossal canal together with the hypoglossal nerve and reached the posterior cranial fossa to anastomose the basilar artery. In addition, the ipsilateral vertebral artery and bilateral posterior communicating arteries were hypoplastic. Here, we discuss the developmental mechanisms underlying the formation of the PHA and the spectrum of diseases related to its presence.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- XII:
-
Hypoglossal nerve
- AICA:
-
Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- BA:
-
Basilar artery
- HC:
-
Hypoglossal canal
- ICA:
-
Cervical internal carotid artery
- PCoA:
-
Posterior communicating artery
- PHA:
-
Persistent hypoglossal artery
- PICA:
-
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- SA:
-
Subclavian artery
- SIA:
-
Supreme intercostal artery
- VA:
-
Vertebral arteries
References
Agnoli AL (1982) Vascular anomalies and subarachnoid haemorrhage associated with persisting embryonic vessels. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 60:183–199
Brismar J (1976) Persistent hypoglossal artery, diagnostic criteria. Report of a case. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 17:160–166
De Caro R, Parenti A, Munari PF (1995) The persistent primitive hypoglossal artery: a rare anatomic variation with frequent clinical implications. Ann Anat 177:193–198
Fantini GA, Reilly LM, Stoney RJ (1994) Persistent hypoglossal artery: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations concerning carotid thromboendarterectomy. J Vasc Surg 20:995–999
Huynh-Le P, Matsushima T, Muratani H, Hikita T, Hirokawa E (2004) Persistent primitive hypoglossal artery associated with proximal posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm. Surg Neurol 62:546–551
Kamisasa A, Inaba Y, Fukushima Y, Hiratsuka H (1970) Persistent primitive hypoglossal artery: 2 cases and its angiographic features in axial projection. No To Shinkei 22:1009–1016
Kanai H, Nagai H, Wakabayashi S, Hashimoto N (1992) A large aneurysm of the persistent primitive hypoglossal artery. Neurosurgery 30:794–797
Katayama W, Enomoto T, Yanaka K, Nose T (2001) Moyamoya disease associated with persistent primitive hypoglossal artery: report of a case. Pediatr Neurosurg 35:262–265
Kobayashi M, Akaji K, Tanizaki Y, Mihara B, Ohira T, Kawase T (2008) Posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysm associated with persistent primitive hypoglossal artery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 48:259–261
Komiyama M, Nakajima H, Nishikawa M, Yasui T, Kitano S, Sakamoto H, Fu Y (1999) High incidence of persistent primitive arteries in moyamoya and quasi-moyamoya diseases. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 39:416–422
Lie TA (1968) Persistent carotid-basilar carotid-vertebral anastomosis, in congenital anomalies of the carotid arteries. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 76–84
Vasovic L, Milenkovic Z, Jovanovic I, Cukuranovic R, Jovanovic P, Stefanovic I (2008) Hypoglossal artery: a review of normal and pathological features. Neurosurg Rev 31:385–396
Vasovic L, Mojsilovic M, Andelkovic Z, Jovanovic I, Arsic S, Vlajkovic S, Milenkovic Z (2009) Proatlantal intersegmental artery: a review of normal and pathological features. Childs Nerv Syst 25:411–421
Vlychou M, Georganas M, Spanomichos G, Kanavaros P, Artinopoulos C, Zavras GM (2003) Angiographic findings and clinical implications of persistent primitive hypoglossal artery. BMC Med Imaging 3:2
Wagner AL (2001) Isolated stenosis of a persistent hypoglossal artery visualized at 3D CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1613–1614
Yamamoto S, Sunada I, Matsuoka Y, Hakuba A, Nishimura S (1991) Persistent primitive hypoglossal artery aneurysms—report of two cases. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 31:199–202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terayama, R., Toyokuni, Y., Nakagawa, S. et al. Persistent hypoglossal artery with hypoplasia of the vertebral and posterior communicating arteries. Anat Sci Int 86, 58–61 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-009-0062-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-009-0062-x