Abstract
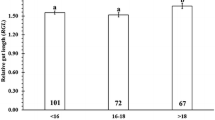
Spotted scat Scatophagus argus is a euryhaline species generally nursed in brackish water and shipped to freshwater ponds or sea cages of local farms in Thailand. To find the best practice for this process in terms of survival and cost, we conducted two culture experiments. In experiment 1, spotted scat fries (up to 6.72 ± 2.15 g) were divided into 5 size classes (S1–S5), and their survival rates were determined after 4 patterns of salinity changes [from 0 to 30 parts per thousand (ppt), from 0 to 15 ppt, and vice versa]. The survival rates were not significantly different between groups when fries were transferred from or to 15 ppt water. However, smaller fries (S1–S3) presented lower survival rates than larger fries (S4 and S5) when transferred from 0 to 30 ppt. In experiment 2, fries (0.21 ± 0.05 g) were nursed at three densities (125, 250, and 500 fish/m3) using underground water without water changes for 80 days. The 125 and 250 fish/m3 groups showed similar culture performance, suggesting that the nursing density can be up to 250 fish/m3 under these conditions. These results provide empirical data for establishing the best nursery practice of spotted scat, which will be particularly useful for small-scale farmers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen PJ, Cech JJ (2007) Age/size effects on juvenile green sturgeon, Acipenser medirostris, oxygen consumption, growth, and osmoregulation in saline environments. Environ Biol Fishes 79:211–229
Aryani N, Mardiah A, Syandri H (2017) Influence of different stocking densities on growth, feed efficiency and carcass composition of Bonylip barb (Osteochilus vittatus Cyprinidae) fingerlings. Pak J Biol Sci 20:489–497
Barry TP, Fast AW (1988) Natural history of the spotted scat (Scatophagus argus), pp 4–32. In: Arlo WF (ed) Spawning induction pond culture of the spotted scat (Scatophagus argus, Linnaeus) in The Philippines. Mariculture Research and Training Center, Iloilo
Barry TP, Fast AW (1992) Biology of the spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) in the Philippines. Asian Fish Sci 5:163–179
Chang SL, Hsieh CS, Cheng MJ (2005) Salinity adaptation of the spotted scat (Scatophagus argus). J Taiwan Fish Res 13:33–39 (in Chinese, English abstract)
Costa AAP, Roubach R, Dallago BSL, Bueno GW, McManus C, Bernal FEM (2017) Influence of stocking density on growth performance and welfare of juvenile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in cages. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 69:243–251
Ghazilou A, Morovvati H, Chenari F (2011) Time course of saltwater adaptation in spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) (Pisces): A histomorphometric approach. Ital J Zool 78:82–89
Gupta S (2016) An overview on morphology, biology, and culture of spotted scat Scatophagus argus (Linnaeus 1766). Rev Fish Sci Auac 24:203–212
Kim WS, Kong KH, Kim JO, Jung SJ, Kim JH, Oh MJ (2017) Amoebic gill disease outbreak in marine fish culture in Korea. J Vet Diagn Invest 29:357–361
Lupatsch I, Santos GA, Schrama JW, Verreth JAJ (2010) Effect of stocking density and feeding level on energy expenditure and stress responsiveness in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. Aquaculture 298:245–250
Manangkalangi E, Pertami IND, Asriansyah A, Aditriawan RM, Sala R, Rahardjo MF (2022) Estimation of population parameters and fishery status of spotted scat, Scatophagus argus (Scatophagidae) in Pabean Bay, Indramayu, West Java, Indonesia. Biodiversita 23:3480–3487
Mandal B, Kailasam M, Bera A, Sukumaran K, Hussain T, Biswas G, Vijayan KK (2021) Standardization of oocyte size during artificial fertilization and optimization of stocking density during indoor larval and outdoor nursery rearing of captive spotted scat (Scatophagus argus) for viable juvenile production system. Aquaculture 534:736262
Moghadam MS, Abtahi B, Mosafer KS, Bitaab MA (2013) Salinity tolerance and gill histopathological alterations in Liza aurata Risso, 1810 (Actinopterygii: Mugilidae) fry. Ital J Zool 80:503–509
Musikasang W, Donnadon Y, Songsangchinda P (2006) Composition of food in the stomach and ecological conditions of sediment fish in Songkhla Lake, p 30. In: Technical Paper No. 47/2006. Coastal Aquaculture Research Institute, Department of Fisheries [in Thai]
Musikasang W, Asavaaree A, Thongraksa V, Prasertsom S (2014) Eating of Scatophagus argus in Outer Songkhla Lake, pp 106–113. In: Proceedings of Kasetsart University Academic Conference 52: Fisheries, Kasetsart University, Bangkok [in Thai]
Puttipong T, Senarat S, Kettratad J, Chantangsi C, Kaneko G, Siriwong W (2021) Evaluation of health status of the striped catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus (Sauvage, 1878) from Khlong Saen Saep, Thailand: The use of integrated biomarkers. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 27:938–953
Rico SS (1965) Scatophacus argus. Aquarium J 36:282–284
Rodger HD, Henry L, Mitchell SO (2011) Non-infectious gill disorders of marine salmonid fish. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 21:423–440
Ruensirikul J, Chiayvareesajja S (2016) Effect of salinity on artificial insemination of spotted scat Scatophagus argus Linnaeus, 1766 and survival rate of the larvae. J Fish Technol Res 2:11–22 ([in Thai])
Ruensirikul J, Assawaaree M, Danayadol Y, Chusrirat L (2008) Success in artificial insemination of spotted scat, Scatophagus argus Linnaeus, 1766 `Using LHRHa, p 20. In: Technical Paper No.32/2008. Coastal Aquaculture Research Institute, Department of Fisheries [in Thai]
Ruensirikul J, Singhabun A, Kesuwan K (2012) Survival Rate of Spotted Scat, Scatophagus argus Linnaeus, 1766 Larvae Rearing by 4 Salinity Reduction Trials, p 20. In: Technical Paper No. 36/2012. Coastal Aquaculture Research Institute, Department of Fisheries [in Thai]
Singhabun A, Khammee W (2013) Effect of density feeding frequency and salinity on the growth and survival of marine fish larvae (Epinephelus lanceolatus Bloch, 1790) adolescents, p 18. In: Technical Paper No. 19/2013. Krabi Coastal Aquaculture Research and Development Center, Department of Fisheries [in Thai]
Strickland JDH, Parsons TR (1972) A practical hand book of seawater analysis. In: Fisheries Research Board of Canada Bulletin 157, 2nd Edition, p 310
Su M, Duan Z, Shi H, Zhang J (2019) The effects of salinity on reproductive development and egg and larvae survival in the spotted scat Scatophagus argus under controlled conditions. Aquac Res 50:1782–1794
Xu J, Shui C, Shi Y, Yuan X, Liu Y, Xie Y (2020) Effect of salinity on survival, growth, body composition, oxygen consumption, and ammonia excretion of juvenile spotted scat. N Am J Aquac 82:54–62
Acknowledgements
We thank the Coastal Aquaculture Technology and Innovation Research and Development Center, Songkhla, Thailand for providing fish rearing facilities. We would also like to thank Assoc. Prof. Dr. Sommai Chiayvareesajja for his advice and Mr. Saransiri Nuanmanee for his suggestion on histology part.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yangthong, M., Suratata, M., Nontaso, A. et al. Salinity tolerance and nursing performance under different densities in spotted scat Scatophagus argus Linnaeus, 1766. Fish Sci 89, 367–373 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-023-01681-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-023-01681-x