Abstract
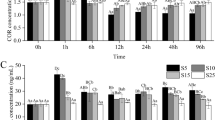
We evaluated whether bearing tetrodotoxin (TTX) affects salinity stress in the juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes. Juveniles of hatchery-reared non-toxic T. rubripes [body weight (BW): 1.7 ± 0.2 g, n = 120] were divided into six tanks and acclimatized to salinity (8.5 ppt) that is equivalent to blood osmolality. Fish in three tanks were fed non-toxic diet, and those in the other three tanks were fed a TTX-containing diet (356 ng/g diet) three times a day until satiation. In each diet treatment, salinity of one tank was kept at 8.5 ppt, and the other two tanks were adjusted to either 1.7 or 34.0 ppt, and fish were reared for another 33 days. Then, we compared survival, growth, TTX accumulation, plasma osmolality, plasma cortisol, and glucose levels among treatments. We detected TTX only in the fish in the TTX-diet groups. Survival was highest at 8.5 ppt (70%) and lowest at 1.7 ppt in the TTX-diet group (20%). The BW was greater at 8.5 ppt, and plasma osmolality was significantly higher at 34.0 ppt than at any other salinities. Plasma cortisol level was significantly higher but glucose level was lower at 1.7 ppt. Possessing TTX at a low salinity may be lethal to tiger puffer juveniles.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-022-01662-6
References
Amano M, Amiya N, Takaoka M, Sato H, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Sakakura Y (2019) Tetrodotoxin functions as a stress relieving substance in juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes. Toxicon 171:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.09.024
Bœuf G, Payan P (2001) How should salinity influence fish growth? Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 130:411–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(01)00268-X
Gao W, Kanahara Y, Yamada M, Tatsuno R, Yoshikawa H, Doi H, Takatani T, Arakawa O (2019) Contrasting toxin selectivity between the marine pufferfish Takifugu pardalis and the freshwater pufferfish Pao suvattii. Toxins 11:470. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11080470
Han K, Chuang H, Matsui S, Furuichi M, Kitajima C (1995) Effect of ambient salinity on growth, survival rate, and feed efficiency in the early stages of puffer fish Takifugu rubripes. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 61:21–26. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.61.21
Hosoya S, Kaneko T, Suzuki Y, Hino A (2008) Individual variations in behavior and free cortisol responses to acute stress in tiger pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Fish Sci 74:755–763. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2008.01586.x
Itoi S, Yoshikawa S, Asahina K, Suzuki M, Ishizuka K, Takimoto N, Mitsuoka R, Yokoyama N, Detake A, Takayanagi C, Eguchi M, Tatsuno R, Kawane M, Kokubo S, Takanashi S, Miura A, Suitoh K, Takatani T, Arakawa O, Sakakura Y, Sugita H (2014) Larval pufferfish protected by maternal tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 78:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.11.003
Lee KM, Kaneko T, Aida K (2005) Low-salinity tolerance of juvenile fugu Takifugu rubripes. Fish Sci 71:1324–1331. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1444-2906.2005.01098.x
Lee KM, Kaneko T, Aida K (2006a) Prolactin and prolactin receptor expressions in a marine teleost, pufferfish Takifugu rubripes. Gen Comp Endocrinol 146:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.12.003
Lee KM, Kaneko T, Katoh F, Aida K (2006b) Prolactin gene expression and gill chloride cell activity in fugu Takifugu rubripes exposed to a hypoosmotic environment. Gen Comp Endocrinol 149:285–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2006.06.009
Matsui T, Hamada S, Konosu S (1981) Difference in accumulation of puffer fish toxin and crystalline tetrodotoxin in the puffer fish, Fugu rubripes rubripes. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 47:535–537. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.47.535
Matsumoto T, Nagashima Y, Kusuhara H, Ishizaki S, Shimakura K, Shiomi K (2008) Pharmacokinetics of tetrodotoxin in puffer fish Takifugu rubripes by a single administration technique. Toxicon 51:1051–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.01.007
Nakashima K, Arakawa O, Taniyama S, Nonaka M, Takatani T, Yamamori K, Fuchi Y, Noguchi T (2004) Occurrence of saxitoxins as a major toxin in the ovary of a marine puffer Arothron firmamentum. Toxicon 43:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2003.05.001
Noguchi T, Arakawa O (2008) Tetrodotoxin–distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar Drugs 6:220–242. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080011
Noguchi T, Arakawa O, Takatani T (2006) Toxicity of pufferfish Takifugu rubripes cultured in netcages at sea or aquaria on land. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D Genomics Proteomics 1:153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbd.2005.11.003
Okita K, Takatani T, Nakayasu J, Yamazaki H, Sakiyama K, Ikeda K, Arakawa O, Sakakura Y (2013) Comparison of the localization of tetrodotoxin between wild pufferfish Takifugu rubripes juveniles and hatchery-reared juveniles with tetrodotoxin administration. Toxicon 71:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.05.018
Pankhurst NW (2011) The endocrinology of stress in fish: an environmental perspective. Gen Comp Endocrinol 170:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.07.017
Saito T, Maruyama J, Kanoh S, Jeon J-K, Noguchi T, Harada T, Murata O, Hashimoto K (1984) Toxicity of the cultured pufferfish Fugu rubripes rubripes along with their resistibility against tetrodotoxin. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 50:1573–1575. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.50.1573
Sakakura Y, Takatani T, Nakayasu J, Yamazaki H, Sakiyama K (2017) Administration of tetrodotoxin protects artificially raised juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes from predators. Fish Sci 83:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-016-1046-0
Shimizu D, Sakiyama K, Sakakura Y, Takatani T, Takahashi Y (2008) Quantitative evaluation of post-release mortality using salt pond mesocosms: case studies of hatchery and wild juvenile tiger puffer. Rev Fish Sci 16:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641260701681755
Taga M, Yamashita Y (2011) Effectiveness and relating factors of low salinity on growth of larval and juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes. Aquac Sci 59:225–233
Takita T, Intong S (1991) Ecological studies on young puffers Takifugu rubripes and T. xanthopterus in Ariake Sound. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 57:1883–1889. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.57.1883
Taniguchi K, Takao H, Abe K, Tatsuno R, Nishihara GN, Sakakura Y, Takatani T, Arakawa O (2020) Simplification of extraction procedure and evaluation of extraction ratio in pufferfish toxin examination method. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 86:410–417. https://doi.org/10.2331/suisan.20-00023
Yamaguchi A, Kume G (2008) Evidence for up-estuary transport of puffer Takifugu larvae (Tetraodontidae) in Ariake Bay, Japan. J Appl Ichthyol 24:60–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0426.2007.00868.x
Yamane H, Yoshida A, Yamazaki H, Sakiyama K, Kawabata Y, Sakakura Y (2015) Changes in behavior and feeding habits of hatchery-reared tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes juveniles. Aquac Sci 63:141–149
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (19K06225 and 22K05822). We thank Ryo Uzawa and Keisuke Fukushima for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: To insert the text “, Saint Louis, MO, USA” after Sigma-Aldrich in page 2.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sakakura, Y., Takeshige, R., Takatani, T. et al. Tetrodotoxin accumulation conflicts with low salinity tolerance in juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes. Fish Sci 89, 21–28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-022-01644-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-022-01644-8