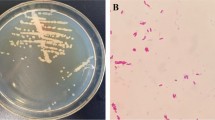
Abstract
We analyzed the bacterial flora and chemical properties of the Japanese traditional anchovy product called salted Etari, which is distributed in Nagasaki Prefecture in the western part of Japan. The pH and NaCl concentrations ranged from 6.4 to 6.6 and from 9.6% to 13.9%, respectively. The lactic acid and total free amino acid concentrations were determined to be between 122 and 344 mg/100 g of sample and between 2850 and 4783 mg/100 g of sample. The bacterial cell counts were determined to be 103–108 and 104–108 cells/g under aerobic and anaerobic conditions using a plate medium containing 10% NaCl, respectively. The isolates were classified into six groups on the basis of the results of PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis targeting the 16S rRNA gene. According to the results of 16S rRNA gene sequencing, the predominant PCR–RFLP group was identified as the halophilic lactic acid bacterium Tetragenococcus halophilus, and the remaining groups were identified as bacteria belonging to the genera Chromohalobacter, Halomonas, and Staphylococcus. The results of culture-independent analysis, namely, terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis targeting the 16S rRNA gene, indicated that T. halophilus is the bacterium commonly found in salted Etari.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arahal DR, García MT, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH, Ventosa A (2001) Transfer of Halomonas canadensis and Halomonas israelensis to the genus Chromohalobacter as Chromohalobacter canadensis comb. nov. and Chromohalobacter israelensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1443–1448
Bertuzzi AS, Guinane CM, Crispie F, Kilcawley KN, McSweeney PL, Rea MC (2017) Genome sequence of Staphylococcus saprophyticus DPC5671, a strain isolated from cheddar cheese. Genome Announc 5:e00193–e217
Cocconcelli PS, Fontana C (2010) Starter cultures for meat fermentation. In: Toldrá F (ed) Handbook of meat processing. Wiley, Iowa, pp 199–218
Hayashi A, Zhang K, Saruwatari T, Kawamura T, Watanabe Y (2016) Distribution of eggs and larvae of Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus in the Pacific waters off northern Japan in summer. Fish Sci 82:311–319
Irlinger F, Loux V, Bento P, Gibrat JF, Straub C, Bonnarme P, Landaud S, Monnet C (2012) Genome sequence of Staphylococcus equorum subsp. equorum Mu2, isolated from a French smear-ripened cheese. J Bacteriol 194:5141–5142
Jung WY, Lee HJ, Jeon CO (2016) Halomonas garicola sp. nov., isolated from saeu-jeot, a Korean salted and fermented shrimp sauce. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:731–737
Kobayashi T, Kajiwara M, Wahyuni M, Hamada-Sato N, Imada C, Watanabe E (2004) Effect of culture conditions on lactic acid production of Tetragenococcus species. J Appl Microbiol 96:1215–1221
Kobayashi T, Wang X, Shigeta N, Taguchi C, Ishii K, Shozen KI, Harada Y, Imada C, Terahara T, Shinagawa A (2016) Distribution of histamine-producing lactic acid bacteria in canned salted anchovies and their histamine production behavior. Ann Microbiol 66:1277–1284
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Laranjo M, Elias M, Fraqueza MJ (2017) The use of starter cultures in traditional meat products. J Food Qual 2017:9546026
Lee SH, Jung JY, Jeon CO (2015) Bacterial community dynamics and metabolite changes in myeolchi-aekjeot, a Korean traditional fermented fish sauce, during fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 203:15–22
Sanchez-Porro C, Tokunaga H, Tokunaga M, Ventosa A (2007) Chromohalobacter japonicus sp. nov., a moderately halophilic bacterium isolated from a Japanese salty food. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2262–2266
Song EJ, Lee ES, Park SL, Choi HJ, Roh SW, Nam YD (2018) Bacterial community analysis in three types of the fermented seafood, jeotgal, produced in South Korea. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82:1444–1454
Tanasupawat S, Visessanguan W (2014) Fish fermentation. In: Boziaris IS (ed) Seafood processing: technology, quality and safety. Wiley, West Sussex, pp 177–207
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thwe SM, Kobayashi T, Luan T, Shirai T, Onodera M, Hamada-Sato N, Imada C (2011) Isolation, characterization, and utilization of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing lactic acid bacteria from Myanmar fishery products fermented with boiled rice. Fish Sci 77:279–288
Villar M, de Ruiz Holgado AP, Sanchez JJ, Trucco RE, Oliver G (1985) Isolation and characterization of Pediococcus halophilus from salted anchovies (Engraulis anchoita). Appl Environ Microbiol 49:664–666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, T., Nishitake, M., Saito, M. et al. Bacterial and chemical properties of Japanese traditional anchovy product, salted Etari. Fish Sci 86, 721–728 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-020-01437-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-020-01437-x