Abstract
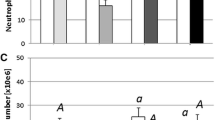
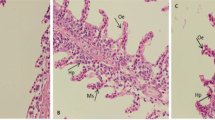
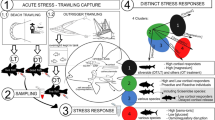
We studied the link between high zinc levels and the extreme stress tolerance of common carp. Fish under stress showed much higher plasma cortisol levels than controls. Stress or cortisol injection induced large changes in zinc levels in the common carp but not in grass carp, silver carp or tilapia. The effect of 5 days of anoxia and 4 subsequent days of recovery on cortisol and zinc contents in the common carp was investigated. Elevated plasma cortisol resulting from anoxia was correlated with decreased zinc in digestive tract tissue and increased zinc in the head kidney. Zinc was mobilized in the common carp while under stress. Changes in cortisol and zinc contents were reversible during the subsequent recovery from anoxia. Under stress, protein-bound zinc levels increased in the head kidney cell nuclei of common carp as cortisol increased. Zinc and cortisol were bound to the same protein, which was bound to DNA. The protein is likely a glucocorticoid receptor. An increase in immature red blood cells in stressed common carp was observed. Zinc was involved in the stress erythropoiesis response. Zinc may play an important role in stress defense in the common carp via the glucocorticoid receptor.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hambidge KM, Casey CE, Krebs NF (1986) Zinc. In: Mertz W (ed) Trace elements in human and animal nutrition, 4th edn. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 3–28
Hogstrand C, Wood CM (1996) The physiology and toxicology of zinc in fish. In: Taylor EW (ed) Toxicology of aquatic pollution: physiological, cellular and molecular approaches. Cambridge university press, Cambridge, pp 61–84
Sun LT, Jeng SS (1998) Comparative zinc concentrations in tissues of common carp and other aquatic organisms. Zool Stud 37:184–190
Jeng SS, Lin TY, Wang MS, Chang YY, Chen CY, Chang CC (2008) Anoxia survival in common carp and crucian carp is related to high zinc concentration in tissues. Fish Sci 74:627–634
Donaldson EM (1981) The pituitary-interrenal axis as an indicator of stress in fish. In: Pickering AD (ed) Stress and fish. Academic Press, London, pp 11–47
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1997) The stress response in fish. Physiol Rev 77:591–625
Balm PHM, Pepels P, Helfrich S, Hovens MLM, Bonga SEW (1994) Adrenocorticotropic hormone in relation to interrenal function during stress in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 96:347–360
Barton BA, Iwama GK (1991) Physiological changes in fish from stress in aquaculture with emphasis on the response and effects of corticosteroids. Annu Rev Fish Dis 1:3–26
Ruane NM, Huisman EA, Komen J (2001) Plasma cortisol and metabolite level profiles in two isogenic strains of common carp during confinement. J Fish Biol 59:1–12
Van Raaij MTM, Van den Thillart GEEJM, Vianen GJ, Pit DSS, Balm PHM, Steffens AB (1996) Substrate mobilization and hormonal changes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, L.) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio, L.) during deep hypoxia and subsequent recovery. J Comp Physiol B 166:443–452
Chen GR, Sun LT, Lee YH, Chang CF (1996) Characteristics of blood in common carp, Cyprinus carpio, exposed to low temperatures. J Appl Aquac 5:21–31
Tanck MWT, Booms GHR, Eding EH, Bonga SEW, Komen J (2000) Cold shocks: a stressor for common carp. J Fish Biol 57:881–894
Ogino C, Takeuchi L, Takeda H, Watanabe T (1979) Availability of dietary phosphorous in carp and rainbow trout. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 45:1527–1532
Jeng SS, Yau JY, Chen YH, Lin TY, Chung YY (2007) High zinc in the erythrocyte plasma membranes of common carp Cyprinus carpio. Fish Sci 73:421–428
Freshney RI (2000) Culture of animal cells: a manual of basic technique, 4th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York, p 235
Liao HJ, Chen YH, Jeng SS (2006) Association of zinc with connective tissue in the digestive tract of common carp. Fish Sci 72:893–902
Chen YH, Liao HJ, Jeng SS (2008) Separation and characterization of connective tissue cells expressing 43-kDa zinc-binding protein from common carp. Fish Sci 74:1322–1329
Speckner W, Schindler J, Albers C (1989) Age-dependent changes in volume and haemoglobin content of erythrocytes in the carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J Exp Biol 141:133–149
Rothmann C, Levinshal T, Timan B, Avtalion RR, Malik Z (2000) Spectral imaging of red blood cells in experimental anemia of Cyprinus carpio. Comp Biochem Physiol A 125:75–83
Tripathi NK, Latimer KS, Burnley VV (2004) Hematologic reference intervals for koi (Cyprinus carpio), including blood cell morphology, cytochemistry, and ultrastructure. Vet Clin Pathol 33:74–83
Kito H, Ose Y, Mizuhira V, Sato T, Ishikawa T, Tazawa T (1982) Separation and purification of (Cd, Cu, Zn)-metallothionein in carp hepato-pancreas. Comp Biochem Physiol C 73:121–127
Roesijadi G (1992) Metallothioneins in metal regulation and toxicity in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 22:81–113
Hyllner SJ, Andersson T, Haux C, Olsson PE (1989) Cortisol induction of metallothionein in primary culture of rainbow trout hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol 139:24–28
Wu SM, Chou YY, Deng AN (2002) Effects of exogenous cortisol and progesterone on metallothionein expression and tolerance to waterborne cadmium in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Zool Stud 41:111–118
Jeng SS, Wang JT, Sun LT (1999) Zinc and zinc binding substances in the tissues of common carp. Comp Biochem Physiol B 122:461–468
Sun LT, Jeng SS (1999) Accumulation of zinc from diet and its release in common carp. Fish Physiol Biochem 20:313–324
Stickney RR (2000) Tilapia culture. In: Stickney RR (ed) Encyclopedia of aquaculture. Wiley, New York, pp 934–941
Favier AA, Faure H, Arnaud J (1985) Determination of ultrafilterable zinc, transferrin bound and albumin bound zinc using ultrafiltration and flameless AAS. In: Mills CF, Bremner I, Chesters JK (eds) Trace elements in man and animals. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau, Slough, pp 666–670
Tapiero H, Tew KD (2003) Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed Pharmacother 57:399–411
Hardy RW, Sullivan CV, Koziol AM (1987) Absorption, body distribution, and excretion of dietary zinc by rainbow trout. Fish Physiol Biochem 3:133–143
Spry DJ, Hodson PV, Wood CM (1988) Relative contributions of dietary and waterborne zinc in Salmo gairdneri. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:32–41
Jeng SS, Lian JL (1994) Comparison of zinc absorption between common carp and other fresh water fishes. Zool Stud 37:78–85
Jeng SS, Wang MS (2003) Isolation of a Zn-binding protein mediating cell adhesion from common carp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:733–742
Wang MS, Jeng SS (2006) Binding characteristics of the Zn-binding membrane protein from common carp. Fish Sci 72:437–445
Jeng SS, Sun LT (1981) Effects of dietary zinc levels on zinc concentrations in tissues of common carp. J Nutr 111:134–140
Brown ED, Chan W, Smith JC (1978) Bone mineralization during a developing zinc deficiency. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 157:211–214
Wu FYH, Wu CW (1987) Zinc in DNA replication and transcription. Annu Rev Nutr 7:251–272
Beato M, Herrlich P, Schütz G (1995) Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search of a plot. Cell 83:851–857
Iwama GK, Afonso LOB, Vijayan MM (2006) Stress in fishes. In: Evans DH, Claiborne JB (eds) The physiology of fishes. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 319–342
Stolte EH, de Mazon AF, Leon-Koosterziel KM, Jesiak M, Bury NR, Sturm A, Savelkoul HFJ, van Kemenade BMLV, Flik G (2008) Corticosteroid receptors involved in stress regulation in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. J Endocrinol 198:403–417
Stolte EH, Chadzinska M, Przybylska D, Flik G, Savelkoul HFJ, Verburg-van Kemenade BML (2009) The immune response differentially regulates Hsp70 and glucocorticoid receptor expression in vitro and in vivo in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 27:9–16
Mommsen TP, Vijayan MM, Moon TW (1999) Cortisol in teleosts: dynamics, mechanisms of action, and metabolic regulation. Rev Fish Biol Fish 9:211–268
Vijayan MM, Prunet P, Boone AN (2005) Xenobiotic impact on corticosteroid signaling. In: Moon TW, Mommsen TP (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of fishes, vol 6. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 365–394
Murad A, Houston AH, Samson L (1990) Haematological response to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity, increased temperature and hypoxia in goldfish, Carassius auratus L. J Fish Biol 36:289–305
Houston AH, Murad A (1995) Erythrodynamics in fish: recovery of the goldfish Carassius auratus from acute anemia. Can J Zool 74:411–418
Bauer A, Tronche F, Wessely O, Kellendonk C, Reichardt HM, Steinlein P, Schütz G, Beug H (1999) The glucocorticoid receptor is required for stress erythropoiesis. Genes Dev 13:2996–3002
Hrubec TC, Smith AS (2000) Hematology of fish. In: Feldman BF, Zinkl JG, Jain NC (eds) Schalm’s veterinary hematology, 5th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1120–1125
Jelkmann W (1992) Erythropoietin: structure, control of production, and function. Physiol Rev 72:449–489
Semenza GL (1999) Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:551–578
Kodama T, Shimizu N, Yoshikawa N, Makino Y, Ouchida R, Okamoto K, Hisada T, Nakamura H, Morimoto C, Tanaka H (2003) Role of the glucocorticoid receptor for regulation of hypoxia-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem 278:33384–33391
Kassahn KS, Crozier RH, Pörtner HO, Caley MJ (2009) Animal performance and stress: responses and tolerance limits at different levels of biological organisation. Biol Rev 84:277–292
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Mr. Chin-Tsung Chen, Mr. Jung-Yu Lo, Miss Yi-Chun Hsieh and Miss Szu-Wei Fang for their technical assistance. This research was supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan, project no. NSC 97-2313-B-019-008-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, TY., Chen, YH., Liu, CL. et al. Role of high zinc levels in the stress defense of common carp. Fish Sci 77, 557–574 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-011-0374-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-011-0374-3