Abstract
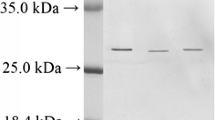
Two cystatins (cst-I and cst-II) were purified from crucian carp eggs by acidification and subsequent ion exchange and molecular sieve chromatography. The molecular masses of cst-I and cst-II analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis were 11.9 and 14.4 kDa, respectively, under reducing conditions and 13.5 and 12.7 kDa, respectively, under non-reducing conditions. The cst-I and cst-II molecules were stable after 30 min of incubation at 60 and 50°C, respectively. There was no significant loss in the inhibitory activity of either cst in the pH range 4–11. These two cystatins were able to affect the proteolysis of papain, cathepsin L, and bromelain, but they were unable to inhibit cathepsin B and trypsin. The partial N-terminal amino acid sequences of both cst inhibitors were homologous and that of cst-I was recognized as NH2-AGIPGGLVDADINDADVQ. This latter fragment shared 88.9% identity to common carp cystatin and 44.4–55.6% to cystatins of other aquatic animals. Based on these results, we conclude that the two cst inhibitors are members of family II cystatin.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett AJ, Fritz H, Grubb A, Isemura S, Jarvinen M, Katunuma N, Machleidt W, Muller-Esterl W, Sasaki M, Turk V (1986) Nomenclature and classification of the proteins homologous with the cysteine-proteinase inhibitor chicken cystatin. Biochem J 236:312
Barrett AJ (1987) The cystatins: a new class of peptidase inhibitors. Trends Biochem Sci 12:193–196
Turk V, Bode W (1991) The cystatins: protein inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. FEBS Lett 285:213–219
Lee JJ, Tzeng SS, Jiang ST (2000) Purification and characterization of low molecular weight kininogen from pig plasma. J Food Sci 65:81–86
Anastasi A, Brown MA, Kembhavi AA, Nicklin MJ, Sayers CA, Sunter DC, Barrett AJ (1983) Cystatin, a protein inhibitor of cysteine proteinases. Improved purification from egg white, characterization, and detection in chicken serum. Biochem J 211:129–138
Abrahamson M, Ritonja A, Brown MA, Grubb A, Machleidt W, Barrett AJ (1987) Identification of the probable inhibitory reactive sites of the cysteine proteinase inhibitors human cystatin C and chicken cystatin. J Biol Chem 262:9688–9694
Lindahl P, Abrahamson M, Bjork I (1992) Interaction of recombinant human cystatin C with the cysteine proteinases papain and actinidin. Biochem J 281:49–55
Bedi GS, Zhou T, Bedi SK (1998) Production of rat salivary cystatin S variant polypeptides in Escherichia coli. Arch Oral Biol 43:173–182
Abe K, Emori Y, Kondo H, Suzuki K, Arai S (1987) Molecular cloning of a cysteine proteinase inhibitor of rice (oryzacystatin). Homology with animal cystatins and transient expression in the ripening process of rice seeds. J Biol Chem 262:16793–16797
Abe M, Abe K, Kuroda M, Arai S (1992) Corn kernel cysteine proteinase inhibitor as a novel cystatin superfamily member of plant origin. Molecular cloning and expression studies. Eur J Biochem 209:933–937
Walsh TA, Strickland JA (1993) Proteolysis of the 85-kilodalton crystalline cysteine proteinase inhibitor from potato releases functional cystatin domains. Plant Physiol 103:1227–1234
Abe K, Kondo H, Watanabe H, Emori Y, Arai S (1991) Oryzacystatins as the first well-defined cystatins of plant origin and their target proteinases in rice seeds. Biomed Biochim Acta 50:637–641
Bjork I, Ylinenjarvi K (1990) Interaction between chicken cystatin and the cysteine proteinases actinidin, chymopapain A, and ficin. Biochemistry 29:1770–1776
Lindahl P, Alriksson E, Jornvall H, Bjork I (1988) Interaction of the cysteine proteinase inhibitor chicken cystatin with papain. Biochemistry 27:5074–5082
Lindahl P, Nycander M, Ylinenjarvi K, Pol E, Bjork I (1992) Characterization by rapid-kinetic and equilibrium methods of the interaction between N-terminally truncated forms of chicken cystatin and the cysteine proteinases papain and actinidin. Biochem J 286:165–171
Nicklin MJH, Barrett AJ (1984) Inhibition of cysteine proteinases and dipeptidyl peptidase I by egg-white cystatin. Biochem J 223:245–253
Machleidt W, Thiele U, Laber B, Assfalg-Machleidt I, Esterl A, Wiegand G, Kos J, Turk V, Bode W (1989) Mechanism of inhibition of papain by chicken egg white cystatin. Inhibition constants of N-terminally truncated forms and cyanogen bromide fragments of the inhibitor. FEBS Lett 243:234–238
Bode W, Engh RA, Musil D, Thiele U, Huber R, Karshikov A, Brzin J, Kos J, Turk V (1988) The 2.0 Å X-ray crystal structure of chicken egg white cystatin and its possible mode of interaction with cysteine proteinases. EMBO J 7:2593–2599
Stubbs MT, Laber B, Bode W, Huber R, Jerala R, Lenarcic B, Turk V (1990) The refined 2.4 Å X-ray crystal structure of recombinant human stefin B in complex with the cysteine proteinase papain: a novel type of proteinase inhibitor interaction. EMBO J 9:1939–1947
Arai S, Watanabe H, Kondo H, Emori Y, Abe K (1991) Papain-inhibitory activity of oryzacystatin, a rice seed cysteine proteinase inhibitor, depends on the central Gln-Val-Val-Ala-Gly region conserved among cystatin superfamily members. J Biochem 109:294–298
Koiwa H, Shade RE, Zhu-Salzman K, D’Urzo MP, Murdock LL, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2000) A plant defensive cystatin (soyacystatin) targets cathepsin L-like digestive cysteine proteinases (DvCALs) in the larval midgut of western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera). FEBS Lett 471:67–70
Soares-Costa A, Beltramini LM, Thiemann OH, Henrique-Silvaa F (2002) A sugarcane cystatin: recombinant expression, purification, and antifungal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296:1194–1199
Kang I, Lanier TC (2005) Inhibition of protease in intact fish fillets by soaking in or injection of recombinant soy cystatin or bovine plasma. J Agric Food Chem 53:9795–9799
Tzeng SS, Jiang ST (2004) Glycosylation modification improved the characteristics of recombinant chicken cystatin and its application on mackerel surimi. J Agric Food Chem 52:3612–3616
Yamashita M, Konagaya S (1991) Cysteine protease inhibitor in egg of chum salmon. J Biochem 110:762–766
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head bacteriophage T4. Nature 277:680–685
Neuhoff V, Arold N, Taube D, Ehrhardt W (1988) Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gel including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using coomassie brilliant blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis 9:255–262
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principal of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Machleidt W, Nagler DK, Assfalg-Machleidt I, Stubbs MT, Fritz H, Auerswald EA (1995) Distorted binding of the loops results in cleavage of the Gly9-Ala10 bond. FEBS Lett 361:185–190
Barrett AJ, Kirschke H (1981) Cathepsin B, cathepsin H, and cathepsin L. Methods Enzymol 80:535–561
Barrett AJ (1972) A new assay for cathepsin B1 and other thiol proteinases. Anal Biochem 47:280–293
Yamashita M, Konagaya S (1991) A comparison of cystatin activity in the various tissues of chum salmon Oncorhynchus keta between feeding and spawning migrations. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 100:749–751
Yamashita M, Konagaya S (1992) An enzyme−inhibitor complex of cathepsin L in the white muscle of chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) in spawning migration. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 103:1005–1010
Tsai YJ, Chang GD, Huang CJ, Chang YS, Huang FL (1996) Purification and molecular cloning of carp ovarian cystatin. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 113:573–580
Chen GH, Tang SJ, Chen CS, Jiang ST (2000) Overexpression of the soluble form of chicken cystatin in Escherichia coli and its purification. J Agric Food Chem 48:2602–2607
Tzeng SS, Chen GH, Chung YC, Jiang ST (2001) Expression of soluble form carp (Cyprinus carpio) ovarian cystatin in Escherichia coli and its purification. J Agric Food Chem 49:4224–4230
Koide Y, Noso T (1994) The complete amino acid sequence of pituitary cystatin from chum salmon. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:164–169
Li F, An H, Seymour TA, Bradford CS, Morrissey MT, Bailey GS, Helmrich A, Barnes DW (1998) Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and expression distribution of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) cystatin C. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 121:135–143
Bai J, Ma D, Lao H, Jian Q, Ye X, Luo J, Xong X, Li Y, Liang X (2006) Molecular cloning, sequencing, expression of Chinese sturgeon cystatin in yeast Pichia pastoris and its proteinase inhibitory activity. J Biotechnol 125:231–241
Wu J, Haard NF (2000) Purification and characterization of a cystatin from the leaves of methyl jasmonate treated tomato plants. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 127:209–220
Matsuishi M, Okitani A (2003) Purification and properties of cysteine proteinase inhibitors from rabbit skeletal muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B 136:309–316
Agarwala KL, Kawabata S, Hirata M, Miyagi M, Tsunasawa S, Iwanaga S (1996) A cysteine protease inhibitor stored in the large granules of horseshoe crab hemocytes: purification, characterization, cDNA cloning and tissue localization. J Biochem 119:85–94
Vihtelic TS, Fadool JM, Gao J, Thornton KA, Hyde DR, Wistow G (2005) Expressed sequence tag analysis of zebrafish eye tissues for NEIBank. Mol Vis 11:1083–1100
Colella R, Sakaguchi Y, Nagase H, Bird JW (1989) Chicken egg white cystatin. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem 264:17164–17169
Jiang ST, Lee BL, Tsao CY, Lee JJ (1997) Mackerel cathepsins B and L effects on thermal degradation of surimi. J Food Sci 62:310–315
Ho ML, Chen GH, Jiang ST (2000) Effects of mackerel cathepsins L, L-like and calpain on the degradation of mackerel surimi. Fish Sci 66:558–568
An H, Weerasinghe V, Seymour TA, Morrissey MT (1994) Cathepsin degradation of Pacific whiting surimi proteins. J Food Sci 59:1013–1017, 1033
Yamashita M, Henmi H, Ueda T, Obara M, Taro T, Nishioka F, Konagaya S (1996) Marked proteolysis occurring during thermal gel formation of the minced meat from matured chum salmon and restraining effect of protease inhibitor on gel-degradation. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 62:934–938
Siqueira-Júnior CL, Fernandes KVS, Machado OLT, da Cunha M, Gomes VM, Moura D, Jacinto T (2002) 87 kDa tomato cystatin exhibits properties of a defense protein and forms protein crystals in prosystemin overexpressing transgenic plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:247–254
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Council, ROC, under Grant Nr. NSC 94-2313-B-041-009, and Chia-Nan University of Pharmacy & Science, under Grant Nr. CN9731.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzeng, SS., Wu, HC., Sung, WC. et al. Purification and characterization of cysteine proteinase inhibitors from crucian carp Carassius auratus eggs. Fish Sci 75, 1453–1460 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-009-0170-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-009-0170-5