Abstract
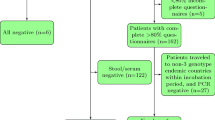
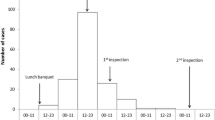
Hepatitis A (HAV) is a viral infection causing a range of symptoms, sudden onset of fever, malaise, diarrhea, and jaundice. It is mostly transmitted fecal-oral through contaminated food, with immediate household and sexual contacts having a higher risk of infection. Since 2016 an increased number of HAV infections, mostly affecting men who have sex with men (MSM) have been noticed worldwide, with three main genotypes circulating. We report here on the first spillover outbreak of the MSM-associated HAV genotype RIVM-HAV16-090 in the German general population in November 2017–February 2018. In total, twelve cases could be attributed to the outbreak with the index case and a coworker in a butchers shop being the most probable source of the outbreak. The identical HAV genotype was detected in two environmental samples in the premises of the butchers shop and in nine cases. Outbreak control measures included detailed contact tracing and stool examinations, several environmental investigations, thorough cleaning, and disinfection of the premises of the butchers shop. Post-exposure vaccination was recommended to all unprotected contacts during the investigation. Furthermore, although hand-washing facilities were in accordance with the required law, additional installment of soap and disinfectant dispensers and contactless faucets has been recommended.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bialek, S. R., George, P. A., Xia, G. L., Glatzer, M. B., Motes, M. L., Veazey, J. E., Hammond, R. M., Jones, T., Shieh, Y. C., Wamnes, J., Vaughan, G., Khudyakov, Y., & Fiore, A. E. (2007). Use of molecular epidemiology to confirm a multistate outbreak of hepatitis A caused by consumption of oysters. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 44, 838–840.
Bundesministerium für Arbeit (2018) Soziales, Gesundheit und Konsumentenschutz. Impfplan Österreich 2018.
Costafreda, M. I., Bosch, A., & Pinto, R. M. (2006). Development, evaluation, and standardization of a real-time TaqMan reverse transcription-PCR assay for quantification of hepatitis A virus in clinical and shellfish samples. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 72, 3846–3855.
Desenclos, J. C., Klontz, K. C., Wilder, M. H., Nainan, O. V., Margolis, H. S., & Gunn, R. A. (1991). A multistate outbreak of hepatitis A caused by the consumption of raw oysters. American Journal of Public Health, 81, 1268–1272.
Donnan, E. J., Fielding, J. E., Gregory, J. E., Lalor, K., Rowe, S., Goldsmith, P., Antoniou, M., Fullerton, K. E., Knope, K., Copland, J. G., Bowden, D. S., Tracy, S. L., Hogg, G. G., Tan, A., Adamopoulos, J., Gaston, J., & Vally, H. (2012). A multistate outbreak of hepatitis A associated with semidried tomatoes in Australia, 2009. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 54, 775–781.
ECDC (2018). ‘Epidemiological update: hepatitis A outbreak in the EU/EEA mostly affecting men who have sex with men’, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, Accessed 17.12.2018. https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/epidemiological-update-hepatitis-outbreak-eueea-mostly-affecting-men-who-have-sex-men-2.
Friesema, I. H. M., Sonder, G. J. B., Petrignani, M. W. F., Meiberg, A. E., van Rijckevorsel, G. G. C., Ruijs, W. L. M., & Vennema, H. 2018. Spillover of a hepatitis A outbreak among men who have sex with men (MSM) to the general population, the Netherlands, 2017. Eurosurveillance, 23, 23.
Harries, M., Monazahian, M., Wenzel, J., Jilg, W., Weber, M., Ehlers, J., Dreesman, J., & Mertens, E. (2014). Foodborne hepatitis A outbreak associated with bakery products in northern Germany, 2012. Eurosurveillance, 19, 20992.
Heymann, D. L. (2004). ‘Viral hepatitis A.’. In D. L. Heymann (Ed.), Control of communicable diseases manual. American Public Health Association: Washington, DC.
Houde, A., Guevremont, E., Poitras, E., Leblanc, D., Ward, P., Simard, C., & Trottier, Y. L. (2007). Comparative evaluation of new TaqMan real-time assays for the detection of hepatitis A virus. Journal of Virological Methods, 140, 80–89.
Hutin, Y. J., Pool, V., Cramer, E. H., Nainan, O. V., Weth, J., Williams, I. T., Goldstein, S. T., Gensheimer, K. F., Bell, B. P., Shapiro, C. N., & Alter, M. J., & Margolis, H. S. (1999). A multistate, foodborne outbreak of hepatitis A. National Hepatitis A investigation team’, New England Journal of Medicine, 340: 595–602.
Jeong, S. H., & Lee H. S. (2010) Hepatitis A: Clinical manifestations and management, Intervirology, 53: 15–19.
Niu, M. T., Polish, L. B., Robertson, B. H., Khanna, B. K., Woodruff, B. A., Shapiro, C. N., Miller, M. A., Smith, J. D., Gedrose, J. K., Alter, M. J., et al. (1992). Multistate outbreak of hepatitis A associated with frozen strawberries. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 166, 518–524.
Pinto, R. M., Costafreda, M. I., & Bosch, A. (2009). Risk assessment in shellfish-borne outbreaks of hepatitis A. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 75, 7350–7355.
Robert Koch Institut, R. K. I. (1998). Hepatitis-A-Ausbruch in Nordbayern Importierte Erkrankung löste Streuung über kontaminierte Fleischwaren aus. In Epidemiologisches Bulletin. Berlin: Robert Koch Institut.
Robert Koch Institut, R. K. I. 2017. ‘Hepatitis A RKI-Ratgeber’, Robert Koch Institute, Accessed 25.02.2019. https://www.rki.de/DE/Content/Infekt/EpidBull/Merkblaetter/Ratgeber_HepatitisA.html;jsessionid=EA58EB1BE8C0284E5EE19C5017270DD9.1_cid372#doc2374552bodyText12.
Sabria, A., Gregori, J., Garcia-Cehic, D., Guix, S., Pumarola, T., Manzanares-Laya, S., Cayla, J. A., Bosch, A., Quer, J., & Pinto, R. M. (2019). Evidence for positive selection of hepatitis A virus antigenic variants in vaccinated men-having-sex-with men patients: Implications for immunization policies. EBioMedicine, 39: 348–357.
Sanchez, G., Pinto, R. M., Vanaclocha, H., & Bosch, A. (2002). Molecular characterization of hepatitis a virus isolates from a transcontinental shellfish-borne outbreak. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 40, 4148–4155.
Sane, J., MacDonald, E., Vold, L., Gossner, C., & Severi, E. and Team Outbreak Investigation. (2015). Multistate foodborne hepatitis A outbreak among European tourists returning from Egypt–need for reinforced vaccination recommendations, November 2012 to April 2013, Eurosurveillance, 20(4), 21018
Sattar, S. A., Jason, T., Bidawid, S., & Farber, J. (2000). ‘Foodborne spread of hepatitis A: Recent studies on virus survival, transfer and inactivation’. Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases, 11, 159–163.
Schenkel, K., Bremer, V., Grabe, C., Van Treeck, U., Schreier, E., Hohne, M., Ammon, A., & Alpers, K. (2006). Outbreak of hepatitis A in two federal states of Germany: Bakery products as vehicle of infection. Epidemiology & Infection, 134, 1292–1298.
Schmid, D., Fretz, R., Buchner, G., Konig, C., Perner, H., Sollak, R., Tratter, A., Hell, M., Maass, M., Strasser, M., & Allerberger, F. (2009). Foodborne outbreak of hepatitis A, November 2007-January 2008, Austria. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases, 28, 385–391.
Severi, E., Verhoef, L., Thornton, L., Guzman-Herrador, B. R., Faber, M., Sundqvist, L., Rimhanen-Finne, R., Roque-Afonso, A. M., Ngui, S. L., Allerberger, F., Baumann-Popczyk, A., Muller, L., Parmakova, K., Alfonsi, V., Tavoschi, L., Vennema, H., Fitzgerald, M., Myrmel, M., Gertler, M., Ederth, J., Kontio, M., Vanbockstael, C., Mandal, S., Sadkowska-Todys, M., Tosti, M. E., Schimmer, B., Gorman, O., Stene-Johansen, J. K., Wenzel, J. J., Jones, G., Balogun, K., Ciccaglione, A. R., Connor, O., Vold, L. L., Takkinen, J., & Rizzo, C. (2015). Large and prolonged food-borne multistate hepatitis A outbreak in Europe associated with consumption of frozen berries, 2013 to 2014, Eurosurveillance, 20: 21192.
Shieh, Y. C., Khudyakov, Y. E., Xia, G., Ganova-Raeva, L. M., Khambaty, F. M., Woods, J. W., Veazey, J. E., Motes, M. L., Glatzer, M. B., Bialek, S. R., & Fiore, A. E. (2007). Molecular confirmation of oysters as the vector for hepatitis A in a 2005 multistate outbreak. Journal of Food Protection, 70, 145–150.
Nordic, C.O. I. T. (2013). Joint analysis by the Nordic countries of a hepatitis A outbreak, October 2012 to June 2013: frozen strawberries suspected, Eurosurveillance, 18.
Victor, J. C., Monto, A. S., Surdina, T. Y., Suleimenova, S. Z., Vaughan, G., Nainan, O. V., Favorov, M. O., Margolis, H. S., & Bell B. P. (2007). Hepatitis A vaccine versus immune globulin for postexposure prophylaxis, New England Journal of Medicine, 357: 1685–94.
Wenzel, J. J., & Allerberger, F. (2014). Hepatitis A as a foodborne infection. Lancet Infectious Diseases, 14, 907–908.
Whelan, J., Sonder, G. J., Bovee, L., Speksnijder, A., & van den Hoek, A. (2013). Evaluation of hepatitis A vaccine in post-exposure prophylaxis, The Netherlands, 2004–2012. PLoS ONE, 8, e78914.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Robert Koch Institute and the German Federal Ministry of Health [Grant Number 1369–386 to J. Wenzel].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marosevic, D., Belting, A., Schönberger, K. et al. Hepatitis A Outbreak in the General Population due to a MSM-Associated HAV Genotype Linked to a Food Handler, November 2017–February 2018, Germany. Food Environ Virol 11, 149–156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-019-09375-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-019-09375-3