Abstract
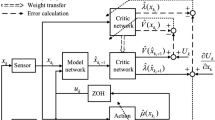
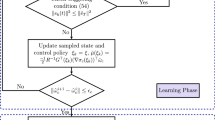
This paper considers the event-triggered optimal control (ETOC) strategy for constrained continuous-time nonlinear systems via adaptive dynamic programming (ADP). First, a novel event-triggering condition is proposed, which can guarantee the stability of the closed-loop system. Meanwhile, the existence of a lower bound for the execution time is proved, which can guarantee that the designed event-trigger scheme avoids Zeno behavior. Then, to solve the partial differential Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) equation, the critic Neural Network (NN) is designed to approximate the cost function. So that the ADP-based ETOC scheme is designed. Moreover, through Lyapunov stability analysis, the stability of the closed-loop system can be ensured. Also, the uniform ultimate boundedness of the states and the weight estimation error can also be guaranteed. Last, a numerical example is given to illustrate the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed control scheme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Z. Zhu, W. X. Zheng, and D. H. Zhou, “Quasi-synchronization of discrete-time Lur’e-type switched systems with parameter mismatches and relaxed PDT constraints,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 2026–2036, May 2020.
Y. Z. Zhu and W. X. Zheng, “Observer-based control for cyber-physical systems with periodic DoS attacks via a cyclic switching strategy,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 65, no. 8, pp. 3714–3721, August 2020.
Y. Z. Zhu and W. X. Zheng, “Multiple Lyapunov functions analysis approach for discrete-time-switched piecewise-affine systems under dwell-time constraints,” IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 65, no. 5, pp. 2177–2184, May 2020.
M. Lemmon, Networked Control Systems, Springer, London, 2010.
W. P. M. H. Heemels, K. H. Johansson, and P. Tabuada, “An introduction to event-triggered and self-triggered control,” Proc. of IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), December 2012.
X. F. Wang and M. Lemmon, “On event design in event-triggered feedback systems,” Automatica, vol. 47, no. 10, pp. 2319–2322, October 2011.
A. Sahoo, H. Xu, and S. Jagannathan, “Approximate optimal control of affine nonlinear continuous-time systems using event-sampled neurodynamic programming,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 639–652, March 2017.
X. H. Wang, Z. Wang, J. W. Xia, H. Shen, and Y. X. Li, “Adaptive event-trigger based sampled-data stabilization of complex-valued neural networks: A real and complex LMI approach” Science China Information Science, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3237-x.
B. Luo, Y. Yang, D. R. Liu, and H. N. Wu, “Event-triggered optimal control with performance guarantees using adaptive dynamic programming,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 76–88, January 2020.
M. Abu-Khalaf and F. L. Lewis, “Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach,” Automatica, vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 779–791, May 2005.
M. D. S. Aliyu, “An iterative relaxation approach to the solution of the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman-Isaacs equation in nonlinear optimal control,” IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 360–366, September 2017.
Y. W. Wang, Y. Lei, T. Bian, and Z. H. Guan, “Distributed control of nonlinear multiagent systems with unknown and nonidentical control directions via event-triggered communication,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 1820–1832, May 2020.
H. G. Zhang, Y. H. Luo, and D. R. Liu, “Neural-network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraints,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 20, no. 9, pp. 1490–1503, September 2009.
H. Modares, F. L. Lewis, and M. B. Naghibi-Sistani, “Integral reinforcement learning and experience replay for adaptive optimal control of partially-unknown constrained-input continuous-time systems,” Automatica, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 193–202, January 2014.
X. Yang, D. R. Liu, and Y. Z. Huang, “Neural-network-based online optimal control for uncertain non-linear continuous-time systems with control constraints,” IET Control Theory and Applications, vol. 7, no. 17, pp. 2037–2047, November 2013.
A. Sahoo and V. Narayanan, “Event-based near optimal sampling and tracking control of nonlinear systems,” Proc. of 2018 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), December 2018.
K. G. Vamvoudakis, “Event-triggered optimal adaptive control algorithm for continuous-time nonlinear systems,” IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 282–293, July 2014.
A. Sahoo, H. Xu, and S. Jagannathan, “Neural network-based event-triggered state feedback control of nonlinear continuous-time systems,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 497–509, March 2016.
Q. C. Zhang, D. B. Zhao, and D. Wang, “Event-based robust control for uncertain nonlinear systems using adaptive dynamic programming,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 37–50, Jauary 2018.
K. G. Vamvoudakis and H. Ferraz, “Model-free event-triggered control algorithm for continuous-time linear systems with optimal performance,” Automatica, vol. 87, pp. 412–420, January 2018.
W. Zhao, W. Yu, and H. Zhang, “Event-triggered optimal consensus tracking control for multi-agent systems with unknown internal states and disturbances,” Nonlinear Analysis Hybrid Systems, vol. 33, pp. 227–248, August 2019.
X. Yang and H. B. He, “Adaptive critic designs for event-triggered robust control of nonlinear systems with unknown dynamics,” IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 49, no. 6, pp. 2255–2267, June 2019.
L. L. Cui, X. P. Xie, X. W. Wang, Y. H. Luo, and J. B. Liu, “Event-triggered single-network ADP method for constrained optimal tracking control of continuous-time nonlinear systems,” Applied Mathematics and Computation, vol. 352, pp. 220–234, July 2019.
L. Dong, X. N. Zhong, C. Y. Sun, and H. B. He, “Event-triggered adaptive dynamic programming for continuous-time systems with control constraints,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 28, no. 8, pp. 1941–1952, August 2016.
F. L. Lewis, D. L. Vrabie, and V. L. Syrmos, Optimal Control, 3rd ed., Wiley, 2012.
P. Tabuada, “Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks,” IEEE Transaction on Automatic Control, vol. 52, no. 9, pp. 1680–1685, September 2007.
S. L. Hu, D. Yue, X. X. Yin, and X. P. Xie, “Neural network-based event-triggered control design of nonlinear continuous-time systems with variable sampling,” Proc. of 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), July 2016.
D. L. Vrabie and F. L. Lewis, “Neural network approach to continuous-time direct adaptive optimal control for partially unknown nonlinear systems,” Neural Networks, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 237–246, April 2009.
R. W. Beard, G. N. Saridis, and J. Wen, “Approximate solutions to the time-invariant Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation,” Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, vol. 96, no. 3, pp. 589–626, March 1998.
S. Bhasin, R. Kamalapurkar, M. Johnson, K. G. Vamvoudakis, F. L. Lewis, and W. E. Dixon, “A novel actor-critic-identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems,” Automatica, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 82–92, January 2013.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation of China under Grant 61973199, 61573008, 61773207; in part by the Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20190020; in part by Shandong University of Science and Technology Research Fund 2018 TDJH101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ping Wang received her B.S. degree in mathematics from Shandong Normal University, Jinan, China in 2003. She is currently pursuing a Ph.D. degree with the College of Mathematics and Systems Science, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China. Her current research interests include neural networks, optimal control, and event-triggered control.
Zhen Wang received his B.S. degree in mathematics from Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China in 2004 and a Ph.D. degree in the School of Automation, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China in 2014. Since 2004, he has been with Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China, where he is currently a Professor and a Doctoral Supervisor. His current research interests include nonlinear control, neural networks, fractional order systems, and multi-agent systems.
Qian Ma received her B.Sc. degree in computational mathematics from Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, in 2005, an M.Sc. degree in fluid dynamics from Nanjing University of Science and Technology, in 2007 and a Ph.D. degree in control theory from Nanjing University of Science and Technology, in 2013. Since June 2013, she has joined the School of Automation at Nanjing University of Science and Technology, where she is currently a Professor. Her current research interests include time-delay systems, stability theory, and multi-agent systems.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Wang, Z. & Ma, Q. Adaptive Event Triggered Optimal Control for Constrained Continuous-time Nonlinear Systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 20, 857–868 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-021-0210-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-021-0210-1