Abstract
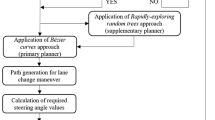
This study presents a novel planning approach of lane changing for autonomous vehicles to ensure multi-agent safety and comfortability in riding. First, a risk assessment model, Safety Field, combined with field theory and kinematics model was defined considering the passengers’ subjective feelings to identify the long-term safety trends. Based on the safety field, a new planning algorithm named S algorithm was developed, which was inspired by the A* algorithm. The special grid map, the lists, and the evaluation function designed in the S algorithm enabling its application to complex dynamic situations while considering riding safety and riding comfort. And the proposed path planning method has good scalability that we extend its application scenarios from straight roads to curved roads. Finally, the S algorithm was validated in virtual traffic environments on straight and curved roads, and the results from the test cases demonstrated the effectiveness and scalability of the algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Chen, X. Shi, and Y. D. Wong, “Key feature selection and risk prediction for lane-changing behaviors based on vehicles’ trajectory data,” Accident Analysis & Prevention, vol. 129, pp. 156–169, August 2019.
J. C. Kim, D. S. Pae, and M. T. Lim, “Obstacle avoidance path planning based on output constrained model predictive control,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 17, pp. 2850–2861, July 2019.
S. Dixit, U. Montanaro, M. Dianati, D. Oxtoby, T. Mizutani, A. Mouzakitis, and S. Fallah, “Trajectory planning for autonomous high-speed overtaking in structured environments using robust MPC,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 2310–2323, June 2020.
W. van Winsum, “The human element in car following models,” Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 207–211, December 1999.
S. Moon and K. Yi, “Human driving data-based design of a vehicle adaptive cruise control algorithm,” Vehicle System Dynamics, vol. 46, no. 8, pp. 661–690, August 2008.
J. Zhang, Y. Wang, and G. Lu, “Extended desired safety margin car-following model that considers variation of historical perceived risk and acceptable risk,” Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, vol. 2672, no. 20, pp. 86–97, June 2018.
S. Byrne, W. Naeem, and S. Ferguson, “Improved APF strategies for dual-arm local motion planning,” Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 73–90, July 2014.
D. Ni, “A unified perspective on traffic flow theory, part I: The field theory,” ICCTP 2011: Towards Sustainable Transportation Systems, pp. 4227–4243, 2013.
E. J. Rossetter and J. C. Gerdes, “Lyapunov based performance guarantees for the potential field lane-keeping assistance system,” Journal of Dynamics Systems, Measurement, and Control, vol. 128, no. 3, pp. 510–522, September 2006.
J. Wang, J. Wu, and Y. Li, “The driving safety field based on driver-vehicle-road interactions,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 2203–2214, February 2015.
Y. Rasekhipour, A. Khajepour, S. Chen, and B. Litkouhi, “A potential field-based model predictive path-planning controller for autonomous road vehicles,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 1255–1267, May 2017.
X. Song, X. Fan, Z. Cao, and H. Gao, “A TC-RRT-based path planning algorithm for the nonholonomic mobile robots,” Proc. of the 36th Chinese Control Conference, pp. 26–28, 2017.
E. W. Dijkstra, “A note on two problems in connexion with graphs,” Numerische Mathematik volume, vol. 1, pp. 269–271, December 1959.
R. Kala and K. Warwick, “Multi-level planning for semi-autonomous vehicles in traffic scenarios based on separation maximization,” Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, vol. 72, no. 3–4, pp. 559–590, March 2013.
P. E. Hart, N. J. Nilsson, and B. Raphael, “A formal basis for the heuristic determination of minimum cost paths,” IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and Cybernetics, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 100–107, July 1968.
S. Kammel, J. Ziegler, B. Pitzer, M. Werling, T. Gindele, D. Jagzent, J. Schröder, M. Thuy, M. Goebl, F. von Hundelshausen, O. Pink, C. Frese, and C. Stiller, “Team Annie WAY’s autonomous system for the DARPA urban challenge,” Journal of Field Robotics, vol. 25, no. 9, pp. 615–639, September 2018.
Y. Liu and Y. Jiang, “Robotic path planning based on a triangular mesh map,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 18, pp. 2658–2666, May 2020.
S. Suh and Y. Kang, “A robust lane recognition technique for vision-based navigation with a multiple clue-based filtration algorithm,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 348–357, April 2011.
M. Sualeh and G. W. Kim, “Simultaneous localization and mapping in the epoch of semantics: A survey,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 17, pp. 729–742, March 2019.
T. Kim, Y. Park, H. Kim, and D. Hong, “Cooperative superposed transmission in cellular-based V2V systems,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 68, no. 12, pp. 11888–11901, December 2019.
H. Xia, J. Chen, F. Lan, and Z. Liu, “Motion control of autonomous vehicles with guaranteed prescribed performance,” International Journal of Control, Automation, and Systems, vol. 18, pp. 1510–1517, June 2020.
Y. Lian, Y. Zhao, L. Hu, and Y. Tian, “Longitudinal collision avoidance control of electric vehicles based on a new safety distance model and constrained-regenerative-braking-strength-continuity braking force distribution strategy,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 65, no. 6, pp. 4079–4094, June 2016.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51705096), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M630348), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HIT.NSRIF.2019076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaoxing Lv received her B.E. degree in Vehicle Engineering from Harbin Institute of Technology in 2020. She is currently a master’s candidate at Jilin University, China. Her research interests include decision-making and safety evaluation of intelligent vehicles.
Weihua Li is an assistant professor at the School of Automotive Engineering in Harbin Institute of Technology (Weihai). He received his B.Sc., M.Sc., and Ph.D. degrees in manufacturing engineering of aerospace vehicle in Harbin Institute of Technology, in 2009, 2011, and 2016, respectively. His research interests include dynamics, simulation and teleoperation of wheeled mobile robots.
Jianfeng Wang is a professor at the School of Automotive Engineering in Harbin Institute of Technology (Weihai). He received his Ph.D. degree in mechanical engineering in Harbin Institute of Technology in 2018. His research interests include the design, simulation and control of automotive vehicles.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, X., Li, W. & Wang, J. Safety-field-based Path Planning Algorithm of Lane Changing for Autonomous Vehicles. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 20, 564–576 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-020-0942-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12555-020-0942-3