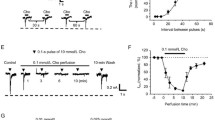
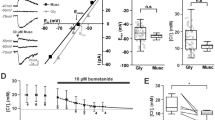
Abstract
This Commentary presents a brief discussion of the action of glutamate calcium permeable receptors present with neurons on the release of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In particular, Glutamate sensitive Kainic Acid Receptors (KARs) and α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-isoxazole Propionic Acid Receptor (AMPARs) are Na+ channels that typically cause neuronal cells to depolarize and release GABA. Some of these receptors are also permeable to Ca2+ and are hence involved in the calcium-dependent release of GABA neurotransmitters. Calcium-permeable kainate and AMPA receptors (CP-KARs and CP-AMPARs) are predominantly located in GABAergic neurons in the mature brain and their primary role is to regulate GABA release. AMPARs which do not contain the GluA2 subunit are mainly localized in the postsynaptic membrane. CP-KAR receptors are located mainly in the presynapse. GABAergic neurons expressing CP-KARs and CP-AMPARs respond to excitation earlier and faster, suppressing hyperexcitation of other neurons by the advanced GABA release due to an early rapid [Ca2+]i increase. CP-AMPARs have demonstrated a more pronounced impact on plasticity compared to NMDARs because of their capacity to elevate intracellular Ca2+ levels independently of voltage. GABAergic neurons that express CP-AMPARs contribute to the disinhibition of glutamatergic neurons by suppressing GABAergic neurons that express CP-KARs. Hence, the presence of glutamate CP-KARs and CP-AMPARs is crucial in governing hyperexcitation and synaptic plasticity in GABAergic neurons.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Azarnia Tehran D, Kochlamazashvili G, Pampaloni NP, Sposini S, Shergill JK, Lehmann M, Pashkova N, Schmidt C, Löwe D, Napieczynska H, Heuser A, Plested AJR, Perrais D, Piper RC, Haucke V, Maritzen T (2022) Selective endocytosis of Ca2+-permeable AMPARs by the Alzheimer’s disease risk factor CALM bidirectionally controls synaptic plasticity. Sci Adv. 8(21):eab15032. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abl5032
Banke TG, Bowie D, Lee H, Huganir RL, Schousboe A, Traynelis SF (2000) Control of GluR1 AMPA receptor function by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Neurosci 20:89–102. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci20-01-00089
Barbon A, Barlati S (2011) Glutamate receptor RNA editing in health and disease. Biochemistry (mosc) 76(8):882–889. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297911080037
Behm M, Wahlstedt H, Widmark A, Eriksson M, Öhman M (2017) Accumulation of nuclear ADAR2 regulates adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing during neuronal development. J Cell Sci. 130(4):745–753. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.200055
Bonnet C, Charpentier J, Retailleau N, Choquet D, Coussen F (2023) Regulation of different phases of AMPA receptor intracellular transport by 4.1N and SAP97. Elife 20(12):e85609. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife85609
Bowie D (2012) Redefining the classification of AMPA-selective ionotropic glutamate receptors. J Physiol 590(Pt1):49–61. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol221689
Burnashev N, Monyer H, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B (1992) Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron 8(1):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0896-6273(92)90120-3
Caffino L, Mottarlini F, Bilel S, Targa G, Tirri M, Maggi C, Marti M, Fumagalli F (2021) Single exposure to the cathinones MDPV and α-PVP alters molecular markers of neuroplasticity in the adult mouse brain. Int J Mol Sci 22(14):7397. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147397
Caroni P, Donato F, Muller D (2012) (2012) Structural plasticity upon learning: regulation and functions. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(7):478–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3258
Chater TE, Goda Y (2014) The role of AMPA receptors in postsynaptic mechanisms of synaptic plasticity. Front Cell Neurosci 27(8):401. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2014.00401
Chevaleyre V, Castillo PE (2002) Assessing the role of Ih channels in synaptic transmission and mossy fiber LTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(14):9538–9543. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.142213199
Choquet D, Triller A (2003) The role of receptor diffusion in the organization of the postsynaptic membrane. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(4):251–265. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1077
Contractor A, Swanson G, Heinemann SF (2001) Kainate receptors are involved in short- and long-term plasticity at mossy fiber synapses in the hippocampus. Neuron 29(1):209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00191-x
Contractor A, Mulle C, Swanson GT (2011) Kainate receptors coming of age: milestones of two decades of research. Trends Neurosci 34:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2010.12.002
Dasgupta D, Sikdar SK (2015) Calcium permeable AMPA receptor-dependent long lasting plasticity of intrinsic excitability in fast spiking interneurons of the dentate gyrus decreases inhibition in the granule cell layer. Hippocampus 25(3):269–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22371
Derkach V, Barria A, Soderling TR (1999) Ca2+/calmodulin-KII enhances channel conductance of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate type glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(6):3269–3274. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.6.3269
Dolgacheva LP, Tuleukhanov ST, Zinchenko VP (2020) Participation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity Biochemistry (Moscow). Suppl Ser: Membr Cell Biol 14(3):194–204. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747820030046
Evans AJ, Gurung S, Henley JM, Nakamura Y, Wilkinson KA (2019) Exciting times: new advances towards understanding the regulation and roles of kainate receptors. Neurochem Res 44(3):572–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2450-2
Filippini M, Ardu E, Stefanelli S, Boni A, Gobbi G, Benso F (2016) Neuropsychological profile in new-onset benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): focusing on executive functions. Epilepsy Behav 54:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.11.010
Gaidin SG, Maiorov SA, Laryushkin DP, Zinchenko VP, Kosenkov AM (2023) A novel approach for vital visualization and studying of neurons containing Ca2+ -permeable AMPA receptors. J Neurochem 164(5):583–597. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15729
Graham L, Collingridge R, Olsen W, Peters J, Spedding M (2009) A nomenclature for ligand-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology 56(1):2–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.06.063
Gurung S, Evans AJ, Wilkinson KA, Henley JM (2018) ADAR2-mediated Q/R editing of GluK2 regulates kainate receptor upscaling in response to suppression of synaptic activity. J Cell Sci 131(24):jcs222273. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.222273
Hollmann M, Hartley M, Heinemann S (1991) Ca2+permeability of KA-AMPA – gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science 252(5007):851–853. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1709304
Huang CC, Lin HJ, Hsu KS (2007) Repeated cocaine administration promotes long-term potentiation induction in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 17(8):1877–1888. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhl096
Hume RI, Dingledine R, Heinemann SF (1991) Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science 253(5023):1028–1031. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1653450
Isaac JT, Ashby MC, Mcbain CJ (2007) The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 54(6):859–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.001
Jane DE, Lodge D, Collingridge GL (2009) Kainate receptors: pharmacology, function and therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 56:90–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.023
Kieval JZ, Hubert GW, Charara A, Paré JF, Smith Y (2001) Subcellular and subsynaptic localization of presynaptic and postsynaptic kainate receptor subunits in the monkey striatum. J Neurosci 21(22):8746–8757. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-22-08746.2001
Lalanne T, Oyrer J, Mancino A, Gregor E, Chung A, Huynh L (2016) Synapse-specific expression of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in neocortical layer. J Physiol 594(4):837–861. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP271394
Lee HK, Takamiya K, He K, Song L, Huganir RL (2010) Specific roles of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 (GluA1) phosphorylation sites in regulating synaptic plasticity in the CA1 region of hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 103:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00835.2009
Lerma J (2003) Roles and rules of kainate receptors in synaptic transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci 4(6):481–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1118
Lippman-Bell JJ, Zhou C, Sun H, Feske JS, Jensen FE (2016) Early-life seizures alter synaptic calcium-permeable AMPA receptor function and plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci 76:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2016.08.002
Liu SJ, Zukin RS (2007) Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and neuronal death. Trends Neurosci 30(3):126–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2007.01.006
Liu P, Zheng Y, Smith PF, Bilkey DK (2003) Changes in NOS protein expression and activity in the rat hippocampus, entorhinal and postrhinal cortices after unilateral electrolytic perirhinal cortex lesions. Hippocampus 13(5):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.10112
Lüscher C, Malenka RC (2011) Drug-evoked synaptic plasticity in addiction: from molecular changes to circuit remodeling. Neuron 69(4):650–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.017
Maiorov SA, ZinchenkoVP GSG, Kosenkov AM (2021) Potential mechanism of GABA secretion in response to the activation of GluK1-containing kainate receptors. Neurosci Res 171:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2021.03.009
Mameli M, Halbout B, Creton C, Engblom D, Parkitna JR, Spanagel R, Lüscher C (2009) Cocaine-evoked synaptic plasticity: persistence in the VTA triggers adaptations in the NAc. Nat Neurosci 12(8):1036–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2367
Man HY (2011) GluA2-lacking, calcium-permeable AMPA receptors—inducers of plasticity? Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:291–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2011.01.001
Mayer ML, Westbrook GL, Guthrie PB (1984) Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature 309(5965):261–263. https://doi.org/10.1038/309261a0
Nicoll RA, Schmitz D (2005) Synaptic plasticity at hippocampal mossy fibre synapses. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(11):863–876. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1786
Nishikura K (2016) A-to-I editing of coding and non-coding RNAs by ADARs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2015.4
Park P, Kang H, Georgiou J, Zhuo M, Kaang BK, Collingridge GL (2021) Further evidence that CP-AMPARs are critically involved in synaptic tag and capture at hippocampal CA1 synapses. Mol Brain 14(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-021-00737-2
Park P, Kang H, Sanderson TM, Bortolotto ZA, Georgiou J, Zhuo M, Kaang BK and Collingridge GL (2018) The role of calcium-permeable AMPARs in long-term potentiation at principal neurons in the rodent hippocampus. Front Synaptic Neurosci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2018.00042
Paschen W, Schmitt J, Gissel C, Dux E (1997) Developmental changes of RNA editing of glutamate receptor subunits GluR5 and GluR6: in vivo versus in vitro. Dev Brain Res 98(2):271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-3806(96)00193-9
Peerboom C, Wierenga CJ (2021) (2021) The postnatal GABA shift: A developmental perspective. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 124:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.01.024
Pelkey KA, Barksdale E, Craig MT, Yuan X, Sukumaran M, Vargish GA, Mitchell RM, Wyeth MS, Petralia RS, Chittajallu R, Karlsson RM, Cameron HA, Murata Y, Colonnese MT, Worley PF, McBain CJ (2015) Pentraxins coordinate excitatory synapse maturation and circuit integration of parvalbumin interneurons. Neuron 85(6):1257–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2015.02.020
Postnikova TY, Griflyuk AV, Zhigulin AS, Soboleva EB, Barygin OI, Amakhin DV, Zaitsev AV (2018) Febrile seizures cause a decrease in calcium-permeable AMPA receptors at synapses of rat cortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Genes Cells 18(4):532–535. https://doi.org/10.17816/gc623255
Purkey AM, Dell’Acqua ML (2020) Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors during hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Front Synaptic Neurosci 27(12):8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsyn.2020.00008
Purkey AM, Woolfrey KM, Crosby KC, Stich DG, Chick WS, Aoto J, Dell’Acqua ML (2018) AKAP150 Palmitoylation regulates synaptic incorporation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors to control LTP. Cell Rep 25(4):974-987.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.085
Sanderson JL, Scott JD, Dell’Acqua ML (2018) Control of homeostatic synaptic plasticity by AKAP-anchored kinase and phosphatase regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors. J Neurosci 38(11):2863–2876. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-17.2018
Shepherd JD (2012) Memory, plasticity and sleep - a role for calcium permeable AMPA receptors? Front Mol Neurosci 5:49. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2012.00049
Soares C, Lee KF, Nassrallah W, Béïque JC (2013) Differential subcellular targeting of glutamate receptor subtypes during homeostatic synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 33(33):13547–13559. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1873-13.2013
Sommer B, Köhler M, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH (1991) RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell 67(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(91)90568-j
Sun HY, Bartley AF, Dobrunz LE (2009) Calcium-permeable presynaptic kainate receptors involved in excitatory short-term facilitation onto somatostatin interneurons during natural stimulus patterns. J Neurophysiol 101(2):1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.90286.2008
Swanson GT, Feldmeyer D, Kaneda M, Cull-Candy SG (1996) Effect of RNA editing and subunit co-assembly single-channel properties of recombinant kainate receptors. J Physiol 492(Pt 1):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021295
Szczurowska E, Ergang P, Kubova H, Druga R, Salaj M, Mares P (2016) Influence of early life status epilepticus on the developmental expression profile of the GluA2 subunit of AMPA receptors. Exp Neurol 283(Pt A):97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.05.039
van der Sluijs P, Hoogenraad CC (2011) New insights in endosomal dynamics and AMPA receptor trafficking. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22(5):499–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.06.008
Verdoorn TA, Burnashev N, Monyer H, Seeburg PH, Sakmann B (1991) Structural determinants of ion flow through recombinant glutamate receptor channels. Science 252(5013):1715–1718. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1710829
Wang HX, Gao WJ (2010) Development of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors and their correlation with NMDA receptors in fast-spiking interneurons of rat prefrontal cortex. J Physiol 588(Pt 15):2823–2838. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2010.187591
Wang AL, Carroll RC, Nawy S (2014) Down-regulation of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR2 contributes to RGC death in a mouse model of glaucoma. PLoS ONE 9(3):e91288. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091288
Wang C, Xu R, Wang X, Li Q, Li Y, Jiao Y, Zhao Q, Guo S, Su L, Yu Y, Yu Y (2020) Spinal CCL1/CCR8 regulates phosphorylation of GluA1-containing AMPA receptor in postoperative pain after tibial fracture and orthopedic surgery in mice. Neurosci Res 154:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2019.05.003
Zinchenko VP, Gaidin SG, Teplov IYu, Kosenkov AM, Sergeev AI, Dolgacheva LP, Tuleuhanov ST (2020) Visualization, properties, and functions of GABAergic hippocampal neurons containing calcium-permeable kainate and AMPA receptors. Biochemistry (Moscow). Suppl Ser: Membr Cell Biol 14(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990747820010109
Zinchenko VP, Kosenkov AM, Gaidin SG, Sergeev AI, Dolgacheva LP, Tuleukhanov ST (2021) Properties of GABAergic neurons containing calcium-permeable kainate and AMPA-receptors. Life 11(12):1309. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11121309
Funding
This research has been funded by the Science Committee of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Grant No. AP19680470 “Involvement of phosphoinositol diphosphate (PIP2) and Kv7 potassium channels in the regulation of hyperexcitation in an epileptic model”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.Z. conceptualized and outlined the review. L.D. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. S.T. review & editing and all three authors finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zinchenko, V.P., Dolgacheva, L.P. & Tuleukhanov, S.T. Calcium-permeable AMPA and kainate receptors of GABAergic neurons. Biophys Rev (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-024-01184-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-024-01184-8