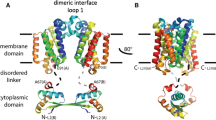
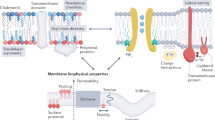
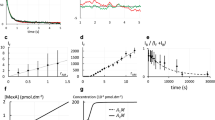
Abstract
Interaction between membrane proteins and ligands plays a key role in governing a wide spectrum of cellular processes. These interactions can provide a cooperative-type regulation of protein function. A wide variety of proteins, including enzymes, channels, transporters, and receptors, displays cooperative behavior in their interactions with ligands. Moreover, the ligands involved encompass a vast diversity and include specific molecules or ions that bind to specific binding sites. In this review, our particular focus is on the interaction between integral membrane proteins and ligands that can present multiple “binding sites”, such as protons or membrane phospholipids. The study of the interaction that protons or lipids have with membrane proteins often presents challenges for classical mechanistic modeling approaches. In this regard, we show that, like Hill’s pioneering work on hemoglobin regulation, phenomenological modeling constitutes a powerful tool for capturing essential features of these systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair GS, Bock AV, Field H (1925) The hemoglobin system. VI. The oxygen dissociation curve of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem 63:529–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(18)85018-9
Allen SJ, Curran AR, Templer RH et al (2004) Controlling the folding efficiency of an integral membrane protein. J Mol Biol 342:1293–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.07.041
Alleva K, Niemietz CM, Sutka M et al (2006) Plasma membrane of Beta vulgaris storage root shows high water channel activity regulated by cytoplasmic pH and a dual range of calcium concentrations. J Exp Bot 57:609–621. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj046
Bae C, Sachs F, Gottlieb PA (2015) Protonation of the human PIEZO1 ion channel stabilizes inactivation. J Biol Chem 290:5167–5173. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.604033
Bartoš L, Kabelka I, Vácha R (2021) Enhanced translocation of amphiphilic peptides across membranes by transmembrane proteins. Biophys J 120:2296–2305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2021.04.005
Bellati J, Alleva K, Soto G et al (2010) Intracellular pH sensing is altered by plasma membrane PIP aquaporin co-expression. Plant Mol Biol 74:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-010-9658-8
Bernard A, Peng Y, Kasumov A et al (2023) Long-lived Andreev states as evidence for protected hinge modes in a bismuth nanoring Josephson junction. Nat Phys 19:358–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-022-01858-8
Berny MC, Gilis D, Rooman M, Chaumont F (2016) Single mutations in the transmembrane domains of maize plasma membrane aquaporins affect the activity of the monomers within a heterotetramer. Mol Plant 9:986–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.04.006
Bohr C, Hasselbalch K, Krogh A (1904) Ueber einen in biologischer beziehung wichtigen einfluss, den die kohlensa¨uerspannung des blutes auf dessen sauerstoffbindung u¨bt. [On a biologically important influence that the carbon dioxide tension of the blood exerts on its oxygen binding]. Skand Arch Physiol 16:402–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1748-1716.1904.TB01382.X
Bowie JU (2001) Stabilizing membrane proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:397–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-440x(00)00223-2
Bredeston LM, González Flecha FL (2016) The promiscuous phosphomonoestearase activity of Archaeoglobus fulgidus CopA, a thermophilic Cu+transport ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr 1858:1471–1478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.04.006
Canessa Fortuna A, Zerbetto De Palma G, Aliperti Car L et al (2019) Gating in plant plasma membrane aquaporins: the involvement of leucine in the formation of a pore constriction in the closed state. FEBS J 286:3473–3487. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14922
Cantor RS (1999) Lipid composition and the lateral pressure profile in bilayers. Biophys J 76:2625–2639. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77098-0
Cantor RS (1999) Solute modulation of conformational equilibria in intrinsic membrane proteins: apparent “cooperativity” without binding. Biophys J 77:2643–2647. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77098-0
Cattoni DI, Chara O, Kaufman SB, González Flecha FL (2015) Cooperativity in binding processes: new insights from phenomenological modeling. PLoS One 10:e0146043. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146043
Chakrapani S, Cordero-Morales JF, Perozo E (2007) A quantitative description of KcsA gating I: macroscopic currents. J Gen Physiol 130:479–496. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.200709844
Chang HM, Reitstetter R, Mason RP, Gruener R (1995) Attenuation of channel kinetics and conductance by cholesterol: an interpretation using structural stress as a unifying concept. J Membr Biol 143:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232523
Chauvigné F, Zapater C, Stavang JA, Taranger GL, Cerdà J, Finn RN (2015) The pH sensitivity of Aqp0 channels in tetraploid and diploid teleosts. FASEB J 29:2172–2184. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-267625
Corradi V, Sejdiu BI, Mesa-Galloso H et al (2019) Emerging diversity in lipid-protein interactions. Chem Rev 119:5775–5848. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00451
de Almeida A, Martins AP, Mósca AF et al (2016) Exploring the gating mechanisms of aquaporin-3: new clues for the design of inhibitors? Mol Biosyst 12:1564–1573. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6MB00013D
Dodes Traian MM, Cattoni DI, Levi V, González Flecha FL (2012) A two-stage model for lipid modulation of the activity of integral membrane proteins. PLoS One 7:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039255
Dutta, Hana (2021) Computational modeling of dynein motor proteins at work. Chem Commun 57:272–283. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC05857B
Dyla M, Kjærgaard M, Poulsen H, Nissen P (2020) Structure and mechanism of P-Type ATPase ion pumps. Annu Rev Biochem 89:583–603. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-010611-112801
Eigen M (1968) New looks and outlooks on physical enzymology. Quart Rev Biophys 1:3–33. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033583500000445
Filomatori CV, Rega AF (2003) On the mechanism of activation of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase by ATP and acidic phospholipids. J Biol Chem 278:22265–22271. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M302657200
Flittiger B, Klapperstück M, Schmalzing G, Markwardt F (2010) Effects of protons on macroscopic and single-channel currents mediated by the human P2X7 receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr 1798:947–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.01.023
Frick A, Järvå M, Törnroth-Horsefiel S (2013) Structural basis for pH gating of plant aquaporins. FEBS Lett 587:989–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.02.038
Frigg R, Hartmann S (2020) Models in science. In: Zalt EN (ed) The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2020/entries/models-science/
Gebeau P, Amodeo G, Henzler T et al (2002) The water permeability of Arabidopsis plasma membrane is regulated by divalent cations and pH. Plant J 30:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01268.x
Gimpl G, Klein U, Reilander H, Fahrenholz F (1995) Expression of the human oxytocin receptor in baculovirus-infected insect cells: high-affinity binding is induced by a cholesterol-cyclodextrin complex. Biochem 34:13794–13801. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00042a010
González W, Zúniga L, Cid LP et al (2013) An extracellular ion pathway plays a central role in the cooperative gating of a K2P K+ channel by extracellular pH. J Biol Chem 288:5984–5991. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.445528
González Flecha FL (2017) Kinetic stability of membrane proteins. Biophys Rev 9:563–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-017-0324-0
Gotfryd K, Mósca AF, Missel JW et al (2018) Human adipose glycerol flux is regulated by a pH gate in AQP10. Nat Commun 9:4749. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07176-z
Hill AV (1910) The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of hæmoglobin on its dissociation curves. J Physiol 40:iv–vii. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001386
Hill TL (1985) Cooperativity theory in biochemistry: steady-state and equilibrium systems. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-5082-1
Holt JM, Ackers GK (2009) The hill coefficient: inadequate resolution of cooperativity in human hemoglobin. Methods Enzymol. 455:193–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(08)04207-9
Hossain KR, Clarke RJ (2019) General and specific interactions of the phospholipid bilayer with P-type ATPases. Biophys Rev 11:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-019-00533-2
Huang SK, Almurad O, Pejana RJ et al (2022) Allosteric modulation of the adenosine A2A receptor by cholesterol. eLife 11:1–24. https://doi.org/10.7554/ELIFE.73901
Ikeda M, Beitz E, Kozono D, Guggino WB, Agre P, Yasui M (2002) Characterization of aquaporin-6 as a nitrate channel in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 277:39873–39879. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m207008200
Jozefkowicz C, Sigaut L, Scochera F et al (2016) PIP water transport and its pH dependence are regulated by tetramer stoichiometry. Biophys J 110:1312–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2016.01.026
Jozefkowicz C, Berny MC, Chaumont F, Alleva K (2017) Heteromerization of plant aquaporins. In: Chaumont F, Tyerman S (eds) Plant aquaporins, from transport to signalling. Springer, pp 29–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49395-4_2
Kaptan S, Assentoft M, Schneider HP et al (2015) H95 Is a pH-dependent gate in aquaporin 4. Structure 23:2309–2318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.08.020
Katano T, Ito Y, Ohta K, Yasujima T, Inoue K, Yuasa H (2014) Functional characteristics of aquaporin 7 as a facilitative glycerol carrier. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 29:244–248. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.dmpk-13-rg-121
Katz B (1978) Archibald Vivian Hill. Biogr Mems Fell R Soc 24:71–149. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbm.1978.0005
Koch S, Exterkate M, López CA, Patro M, Marrink SJ, Driessen AJM (2019) Two distinct anionic phospholipid-dependent events involved in SecA-mediated protein translocation. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1861:183035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183035
Koshland DE, Némethy G, Filmer D (1966) Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochem 5:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00865a047
Kosk-Kosicka D (1990) Comparison of the red blood cell Ca2+-ATPase in ghost membranes and after purification. Mol Cell Biochem 99:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230336
Lacroix J, Poët M, Maehrel C, Counillon L (2004) A mechanism for the activation of the Na/H exchanger NHE-1 by cytoplasmic acidification and mitogens. EMBO Rep 5:91–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400035
Lange Y, Steck TL (2016) Active membrane cholesterol as a physiological effector. Chem Phys Lipids 199:74–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2016.02.003
Lee AG (2011) Lipid-protein interactions. Biochem Soc Trans 39:761–766. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0390761
Levental I, Lyman E (2023) Regulation of membrane protein structure and function by their lipid nano-environment. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 24:107–122. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-022-00524-4
Levi V, Rossi JPFC, Echarte MM et al (2000) Thermal stability of the plasma membrane calcium pump. Quantitative analysis of its dependence on lipid-protein interactions. J Membr Biol 173:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002320001021
Levi V, Rossi JPFC, Castello PR, González Flecha FL (2002) Structural significance of the plasma membrane calcium pump oligomerization. Biophys J 82:437–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75408-8
Levi V, Rossi JPFC, Castello PR, González Flecha FL (2003) Quantitative analysis of membrane protein-amphiphile interactions using resonance energy transfer. Anal Biochem 317:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2697(03)00132-5
Liao SY, Yang Y, Tietze D, Hong M (2015) The influenza M2 cytoplasmic tail changes the proton-exchange equilibria and the backbone conformation of the transmembrane histidine residue to facilitate proton conduction. J Am Chem Soc 137:6067–6077. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b02510
Loura LMS, Prieto M, Fernandes F (2010) Quantification of protein-lipid selectivity using FRET. Eur Biophys J 39:565–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0532-z
Loutchko D, Flechsig H (2020) Allosteric communication in molecular machines via information exchange: what can be learned from dynamical modeling. Biophys Rev 12:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-020-00667-8
Machamer P, Darden L, Craver CF (2000) Thinking about mechanisms. Philos Sci 67:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1086/392759
MacIver B, Cutler CP, Yin J, Hill MG, Zeidel ML, Hill WG (2009) Expression and functional characterization of four aquaporin water channels from the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). J Exp Biol 212:2856–2863. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.025882
Marsh D (2008) Electron spin resonance in membrane research: protein–lipid interactions. Methods 46:83–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2008.07.001
Marty MT, Hoi KK, Gault J, Robinson CV (2016) Probing the lipid annular belt by gas-phase dissociation of membrane proteins in nanodiscs. Angew Chemie - Int Ed 55:550–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201508289
Monod J, Wyman J, Changeux JP (1965) On the nature of allosteric transitions: a plausible model. J Mol Biol 12:88–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(65)80285-6
Mósca A, de Almeida A, Wragg D et al (2018) Molecular basis of aquaporin-7 permeability regulation by pH. Cells 7:207. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7110207
Muth S, Fries A, Gimpl G (2011) Cholesterol-induced conformational changes in the oxytocin receptor. Biochem J 437:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20101795
Németh-Cahalan KL, Hall JE, Ne KL (2000) pH and calcium regulate the water permeability of aquaporin 0. J Biol Chem 275:6777–6782. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.10.6777
Németh-Cahalan KL, Kalman K, Hall JE (2004) Molecular basis of pH and Ca2+ regulation of aquaporin water permeability. J Gen Physiol 123:573–580. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.200308990
Németh-Cahalan KL, Clemens DM, Hall JE (2013) Regulation of AQP0 water permeability is enhanced by cooperativity. J Gen Physiol 141:287–295. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201210884
Niu Y, Tao X, Touhara KK, MacKinnon R (2020) Cryo-EM analysis of PIP2 regulation in mammalian GIRK channels. eLife 9:e60552. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.60552
Öjemyr NL, von Ballmoos C, Faxén K, Svahn E, Brzezinski P (2012) The membrane modulates internal proton transfer in cytochrome c oxidase. Biochem 51:1092–1100. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi201795c
Ottolenghi P (1979) The relipidation of delipidated Na, K-ATPase. Eur J Biochem 99:113–131. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13238.x
Patrick JW, Boone CD, Liu W et al (2018) Allostery revealed within lipid binding events to membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:2976–2981. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719813115
Perutz MF (1963) X-ray analysis of hemoglobin. Science 140:863–869. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.140.3569.863
Phillips R, Ursell T, Wiggins P, Sens P (2009) Emerging roles for lipids in shaping membrane-protein function. Nature 459:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08147
Pignataro MF, Dodes-Traian MM, González-Flecha FL et al (2015) Modulation of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase by neutral phospholipids: effect of the micelle-vesicle transition and the bilayer thickness. J Biol Chem 290:6179–6190. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.585828
Pintado C, Santos J, Iglesias V, Ventura S (2021) SolupHred: a server to predict the pH-dependent aggregation of intrinsically disordered proteins. Bioinform 37:1602–1603. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa909
Placenti MA, Roman EA, González Flecha FL, González-Lebrero RM (2022) Functional characterization of Legionella pneumophila Cu+ transport ATPase. The activation by Cu+ and ATP. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr 1864:183822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183822
Posson DJ, Thompson AN, McCoy JG, Nimigean CM (2013) Molecular interactions involved in proton-dependent gating in KcsA potassium channels. J Gen Physiol 142:613–624. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201311057
Ratkeviciute G, Cooper BJ, Knowles TJ (2021) Methods for the solubilisation of membrane proteins: the micelle-aneous world of membrane protein solubilisation. Biochem Soc Trans 49:1763–1777. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20210181
Recoulat Angelini AA (2020) Efecto de surfactantes sobre la estabilidad y actividad catalítica de una proteína de membrana hipertermófila. [Effect of surfactants on the stability and catalytic activity of a hyperthermophilic membrane protein] PhD thesis, Universidad de Buenos Aires
Reed LJ, Berkson J (1928) The application of the logistic function to experimental data. J Phys Chem 33:760–779. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150299a014
Rodrigues C, Mósca AF, Martins AP et al (2016) Rat aquaporin-5 is pH-gated induced by phosphorylation and is implicated in oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci 17:12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122090
Rothert M, Rönfeldt D, Beitz E (2017) Electrostatic attraction of weak monoacid anions increases probability for protonation and passage through aquaporins. J Biol Chem 292:9358–9364. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.782516
Rusinova R, Kim DM, Nimigean CM, Andersen OS (2014) Regulation of ion channel function by the host lipid bilayer examined by a stopped-flow spectrofluorometric assay. Biophys J 106:1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2014.01.027
Santos HL, Lopes ML, Maggio B, Ciancaglini P (2005) Na, K-ATPase reconstituted in liposomes: effects of lipid composition on hydrolytic activity and enzyme orientation. Coll Surf B 41:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2004.12.013
Santos J, Iglesias V, Santos-Suárez J, Mangiagalli M, Brocca S, Pallarès I, Ventura S (2020) pH-dependent aggregation in intrinsically disordered proteins is determined by charge and lipophilicity. Cells 9:145. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010145
Scochera F, Zerbetto De Palma G, Canessa Fortuna A et al (2022) PIP aquaporin pH sensing is regulated by the length and charge of the C-terminal region. FEBS J 289:246–261. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16134
Sun C, Gennis RB (2019) Single-particle cryo-EM studies of transmembrane proteins in SMA copolymer nanodiscs. Chem Phys Lipids 221:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2019.03.007
Tan CLJ, Torres J (2021) Positive cooperativity in the activation of E. coli aquaporin Z by cardiolipin: potential for lipid-based aquaporin modulators. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1866:158899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2021.158899
Törnroth-Horsefield S, Wang Y, Hedfalk K et al (2006) Structural mechanism of plant aquaporin gating. Nature 439:688–694. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04316
Tournaire-Roux C, Sutka M, Javot H et al (2003) Cytosolic pH regulates root water transport during anoxic stress through gating of aquaporins. Nature 425:393–397. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01853
van der Does C, Swaving J, Van Klompenburg W, Driessen AJM (2000) Non-bilayer lipids stimulate the activity of the reconstituted bacterial protein translocase. J Biol Chem 275:2472–2478. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.4.2472
Verdoucq L, Grondin A, Maurel C (2008) Structure-function analysis of plant aquaporin AtPIP2;1 gating by divalent cations and protons. Biochem J 415:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20080275
Virginio C, Church D, North RA, Surprenant A (1997) Effects of divalent cations, protons and calmidazolium at the rat P2X7 receptor. Neuropharm 36:1285–1294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0028-3908(97)00141-X
Virkki LV, Cooper GJ, Boron WF (2001) Cloning and functional expression of an MIP (AQP0) homolog from killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) lens. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281:R1994–R2003. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.2001.281.6.r1994
Vitali V, Jozefkowicz C, Canessa Fortuna A et al (2019) Cooperativity in proton sensing by PIP aquaporins. FEBS J 286:991–1002. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14701
Wang Y, Bianchi L (2009) Insights into the molecular determinants of proton inhibition in an acid-inactivated degenerins and mammalian epithelial Na+ channel. Biochem 48:10005–10013. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9014902
Wang W, Whorton MR, MacKinnon R (2014) Quantitative analysis of mammalian GIRK2 channel regulation by G proteins, the signaling lipid PIP2 and Na+ in a reconstituted system. eLife 3:e03671. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03671
Weber G (1992) Protein interactions. Chapman and Hall, New York
Wyman J (1964) Linked functions and reciprocal effects in hemoglobin: a second look. Adv Protein Chem 19:223–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3233(08)60190-4
Wyman J, Gill S (1990) Binding and linkage: functional chemistry of biological macromolecules. University Science Books
Yaneff A, Sigaut L, Marquez M et al (2014) Heteromerization of PIP aquaporins affects their intrinsic permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1316537111
Yasui M, Hazama A, Kwon TH, Nielsen S, WmB G, Agre P (1999) Rapid gating and anion permeability of an intracellular aquaporin. Nature 402:184–187. https://doi.org/10.1038/46045
Yu C, Yu I, King TE (1975) Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome. J Biol Chem 250:1383–1392. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(19)41825-5
Zelazny E, Borst JW, Muylaert M et al (2007) FRET imaging in living maize cells reveals that plasma membrane aquaporins interact to regulate their subcellular localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:12359–12364. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701180104
Zelenina M, Bondar AA, Zelenin S, Aperia A (2003) Nickel and extracellular acidification inhibit the water permeability of human aquaporin-3 in lung epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:30037–30043. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m302206200
Zeuthen T, Klaerke DA (1999) Transport of water and glycerol in aquaporin 3 is gated by H+. J Biol Chem 274:21631–21636. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.31.21631
Zhang H, Zhou YH (2023) Unveiling the spectrum of electrohydrodynamic turbulence in dust storms. Nat Commun 14:408. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36041-x
Zhou HX, Cross TA (2013) Modeling the membrane environment has implications for membrane protein structure and function: influenza A M2 protein. Prot Sci 22:381–394. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2232
Zimmer J, Doyle DA (2006) Phospholipid requirement and pH optimum for the in vitro enzymatic activity of the E. coli P-type ATPase ZntA. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr 1758:645–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.04.008
Funding
This work was supported by ANPCYT (PICT 2019- 02768 to FLGF and PICT 2017–0244 and PICT 2019–00387 to KA) and UBA (UBACYT 2018 0178 to KA and 0306 to FLGF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FLGF and KA contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by GZDP, AR, and VV. The first draft of the manuscript was written by KA and FLGF and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zerbetto De Palma, G., Recoulat Angelini, A.A., Vitali, V. et al. Cooperativity in regulation of membrane protein function: phenomenological analysis of the effects of pH and phospholipids. Biophys Rev 15, 721–731 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-023-01095-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-023-01095-0