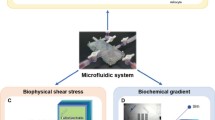
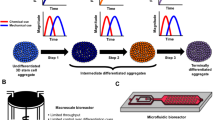
Abstract
Three-dimensional cell culture and the forming multicellular aggregates are superior over traditional monolayer approaches due to better mimicking of in vivo conditions and hence functions of a tissue. A considerable amount of attention has been devoted to devising efficient methods for the rapid formation of uniform-sized multicellular aggregates. Microfluidic technology describes a platform of techniques comprising microchannels to manipulate the small number of reagents with unique properties and capabilities suitable for biological studies. The focus of this review is to highlight recent studies of using microfluidics, especially droplet-based types for the formation, culture, and harvesting of mesenchymal stem cell aggregates and their subsequent application in stem cell biology, tissue engineering, and drug screening. Droplet-based microfluidics can be used to form microgels as carriers for delivering cells and to provide biological cues to the target tissue so as to be minimally invasive. Stem cell-laden microgels with a shape-forming property can be used as smart building blocks by injecting them into the injured tissue thereby constituting the cornerstone of tissue regeneration.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulghani S, Morouço PG (2019) Biofabrication for osteochondral tissue regeneration: bioink printability requirements. J Mater Sci Mater Med 30(2):20
Aijian AP, Garrell RL (2015) Digital microfluidics for automated hanging drop cell spheroid culture. J Lab Autom 20:283–295
Albritton JL, Roybal JD, Paulsen SJ, Calafat NJ, Flores-Zaher JA, Farach-Carson MC et al (2016) Ultrahigh-throughput generation and characterization of cellular aggregates in laser-ablated microwells of poly (dimethylsiloxane). RSC Adv 6:8980–8991
Alessandri K, Sarangi BR, Gurchenkov VV, Sinha B, Kießling TR, Fetler L et al (2013) Cellular capsules as a tool for multicellular spheroid production and for investigating the mechanics of tumor progression in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:14843–14848
Alhasan L, Qi A, Al-Abboodi A, Rezk AR, Chan PPY, Iliescu C, et al. 2016. Rapid enhancement of cellular spheroid assembly by acoustically-driven microcentrifugation, ACS Biomater Sci Eng
Al-Hetlani E, Amin MO (2019) Continuous magnetic droplets and microfluidics: generation, manipulation, synthesis, and detection. Microchim Acta 186(2):55
Allazetta S, Lutolf MP (2015) Stem cell niche engineering through droplet microfluidics. Curr Opin Biotechnol 35:86–93
Altmann B, Löchner A, Swain M, Kohal RJ, Giselbrecht S, Gottwald E et al (2014) Differences in morphogenesis of 3D cultured primary human osteoblasts under static and microfluidic growth conditions. Biomaterials 35:3208–3219
Amaral AJ, Pasparakis G (2016) Rapid formation of cell aggregates and spheroids induced by a “smart” boronic acid copolymer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(35):22930–22941
Anada T, Masuda T, Honda Y, Fukuda J, Arai F, Fukuda T et al (2010) Three-dimensional cell culture device utilizing thin membrane deformation by decompression. Sensors Actuators B Chem 147:376–379
Ananthanarayanan A, Nugraha B, Triyatni M, Hart S, Sankuratri S, Yu H (2014) Scalable spheroid model of human hepatocytes for hepatitis C infection and replication. Mol Pharm 11:2106–2114
Ashammakhi N, Elkhammas E, Hasan A (2018) Translating advances in organ-on-a-chip technology for supporting organs. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 107(6):2006–2018
Ashida T, Sakai S, Taya M (2013) Competing two enzymatic reactions realizing one-step preparation of cell-enclosing duplex microcapsules. Biotechnol Prog 29(6):1528–1534
El Assal R, Gurkan UA, Chen P, Juillard F, Tocchio A, Chinnasamy T et al (2016) 3-D microwell array system for culturing virus infected tumor cells. Scie Rep 6:39144
Bartosh TJ, Ylöstalo JH, Mohammadipoor A, Bazhanov N, Coble K, Claypool K et al (2010) Aggregation of human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) into 3D spheroids enhances their anti-inflammatory properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:13724–13729
Basova EY, Foret F (2015) Droplet microfluidics in (bio) chemical analysis. Analyst 140:22–38
Carvalho MP, Costa EC, Miguel SP, Correia IJ (2016) Tumor spheroid assembly on hyaluronic acid-based structures: a review. Carbohydr Polym 150:139–148
Carvalho MR, Lima D, Reis RL, Correlo VM, Oliveira JM (2015) Evaluating biomaterial-and microfluidic-based 3D tumor models. Trends Biotechnol 33:667–678
Cesarz Z, Tamama K (2015) Spheroid culture of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int 2016:9176357
Chan HF, Zhang Y, Ho YP, Chiu YL, Jung Y, Leong KW (2013) Rapid formation of multicellular spheroids in double-emulsion droplets with controllable microenvironment. Sci Rep 3
Charwat V, Egger D (2018) The third dimension in cell culture: from 2D to 3D culture formats, in cell culture technology. Springer, pp 75–90
Chen J, Elsayed MY, Wei Y, Mousa N (2017) Advances in micro-and nanotechnologies for stem cell-based translational applications. In: Advances in Stem Cell Therapy. Springer, pp 277–302
Chen M et al (2019a) Naked liquid marbles: a robust three-dimensional low-volume cell culturing system. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces
Chen MC, Gupta M, Cheung KC (2010) Alginate-based microfluidic system for tumor spheroid formation and anticancer agent screening. Biomed Microdevices 12:647–654
Chen R, Sun Z, Chen D (2019b) Droplet-based microfluidics for cell encapsulation and delivery, in microfluidics for pharmaceutical applications. Elsevier, pp 307–335
Ching SH, Bansal N, Bhandari B (2017) Alginate gel particles—a review of production techniques and physical properties. Crit rRev Food Sci Nutr 57(6):1133–1152
Choi A, Seo K, Kim DW, Kim BC, Kim DS (2017) Recent advances in engineering microparticles and their nascent utilization in biomedical delivery and diagnostic applications. Lab Chip 17(4):591–613
Chua KN, Lim WS, Zhang P, Lu H, Wen J, Ramakrishna S et al (2005) Stable immobilization of rat hepatocyte spheroids on galactosylated nanofiber scaffold. Biomaterials 26:2537–2547
Clausell-Tormos J, Lieber D, Baret JC, El-Harrak A, Miller OJ, Frenz L et al (2008) Droplet-based microfluidic platforms for the encapsulation and screening of mammalian cells and multicellular organisms. Chem Biol 15:427–437
Cottet J et al (2019) Dielectrophoresis-assisted creation of cell aggregates under flow conditions using planar electrodes. Electrophoresis
Du X et al (2018) Droplet array-based 3D coculture system for high-throughput tumor angiogenesis assay. Anal Chem 90(5):3253–3261
Dudani JS, Go DE, Gossett DR, Tan AP, Di Carlo D (2014) Mediating millisecond reaction time around particles and cells. Anal Chem 86:1502–1510
Egger D et al (2018) Dynamic cultivation of mesenchymal stem cell aggregates. Bioengineering 5(2):48
Elkayam T, Amitay-Shaprut S, Dvir-Ginzberg M, Harel T, Cohen S (2006) Enhancing the drug metabolism activities of C3A-a human hepatocyte cell line-by tissue engineering within alginate scaffolds. Tissue Eng 12:1357–1368
Fabisiewicz A, Grzybowska E (2017) CTC clusters in cancer progression and metastasis. Med Oncol 34:12
Fu CY, Tseng SY, Yang SM, Hsu L, Liu CH, Chang HY (2014) A microfluidic chip with a U-shaped microstructure array for multicellular spheroid formation, culturing and analysis. Biofabrication 6:015009
Guiro K, Arinzeh TL (2015) Bioengineering models for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer: Basic Clin Res 9:57
Hamilton GA, Westmoreland C, George E (2001) Effects of medium composition on the morphology and function of rat hepatocytes cultured as spheroids and monolayers. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37:656–667
Heinemann S, Wiesmann HP (2013) 3-D osteoblast culture for biomaterials testing. J Dev Biol Tissue Eng 5:7–12
Hendriks J, Visser CW, Henke S, Leijten J, Saris DB, Sun C et al (2015) Optimizing cell viability in droplet-based cell deposition. Sci Rep 5:11304
Henke S, Leijten J, Kemna E, Neubauer M, Fery A et al (2016) Enzymatic crosslinking of polymer conjugates is superior over ionic or UV crosslinking for the on-chip production of cell-laden microgels. Macromol Biosci 16(10):1524–1532
Higuchi A, Ling QD, Chang Y, Hsu ST, Umezawa A (2013) Physical cues of biomaterials guide stem cell differentiation fate. Chem Rev 113:3297–3328
Huang G, Li M, Yang Q, Li Y, Liu H, Yang H et al (2016) Magnetically actuated droplet manipulation and its potential biomedical applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces
Hsiao AY, Ys T, Tung YC, Sud S, Taichman RS, Pienta KJ et al (2009) Microfluidic system for formation of PC-3 prostate cancer co-culture spheroids. Biomaterials 30:3020–3027
Huang H, He X (2014) Interfacial tension based on-chip extraction of microparticles confined in microfluidic stokes flows. Appl Phys Lett 105:143704
Imaninezhad M et al (2018) Templated macroporous polyethylene glycol hydrogels for spheroid and aggregate cell culture. Bioconjug Chem 30(1):34–46
Ito K, Sakuma S, Kimura M, Takebe T, Kaneko M, Arai F (2016) Temporal transition of mechanical characteristics of HUVEC/MSC spheroids using a microfluidic chip with force sensor probes. Micromachines 7:221
Jackson E, Lu H (2016) Three-dimensional models for studying development and disease: moving on from organisms to organs-on-a-chip and organoids. Integr Biol 8(6):672–683
Jang M, Yang S, Kim S (2016) Microdroplet-based cell culture models and their application. BioChip J 10:310–317
Jeong SY, Lee JH, Shin Y, Chung S, Kuh HJ (2016) Co-culture of tumor spheroids and fibroblasts in a collagen matrix-incorporated microfluidic chip mimics reciprocal activation in solid tumor microenvironment. PLoS One 11:e0159013
Jin HJ, Cho YH, Gu JM, Kim J, Oh YS (2010) A multicellular spheroid formation and extraction chip using removable cell trapping barriers. Lab Chip 11:115–119
Kamperman T, Henke S, Van den Berg A, Shin S, Tamayol A et al (2017a) Single cell microgel based modular bioinks for uncoupled cellular micro-and macroenvironments. Adv Healthc Mater 6(3)
Kamperman T, Henke S, Visser C, Karperien M, Leijten J (2017b) Centering single cells in microgels via delayed crosslinking supports long-term 3D culture by preventing cell escape. Small 13(22)
Kamperman T, Henke S, Zoetebier B, Ruiterkamo N, Wang R et al (2017c) Nanoemulsion-induced enzymatic crosslinking of tyramine-functionalized polymer droplets. J Mater Chem B
Kang E, Choi YY, Jun Y, Chung BG, Lee SH (2010) Development of a multi-layer microfluidic array chip to culture and replate uniform-sized embryoid bodies without manual cell retrieval. Lab Chip 10:2651–2654
Kashaninejad N, Nikmaneshi MR, Moghadas H, Kiyoumarsi Oskouei A, Rismanian M, Barisam M et al (2016) Organ-tumor-on-a-chip for chemosensitivity assay: a critical review. Micromachines 7:130
Kelm JM, Djonov V, Ittner LM, Fluri D, Born W, Hoerstrup SP et al (2006) Design of custom-shaped vascularized tissues using microtissue spheroids as minimal building units. Tissue Eng 12:2151–2160
Kelm JM, Fussenegger M (2010) Scaffold-free cell delivery for use in regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:753–764
Khanmohammadi M, Sakai S, Ashida T, Taya M (2016) Production of hyaluronic-acid-based cell-enclosing microparticles and microcapsules via enzymatic reaction using a microfluidic system. J Appl Polym Sci 133(16)
Khoury M, Bransky A, Korin N, Konak LC, Enikolopov G, Tzchori I et al (2010) A microfluidic traps system supporting prolonged culture of human embryonic stem cells aggregates. Biomed Microdevices 12:1001–1008
Kim C, Lee KS, Bang JH, Kim YE, Kim MC, Oh KW et al (2011) 3-dimensional cell culture for on-chip differentiation of stem cells in embryoid body. Lab Chip 11:874–882
Kim JB, Stein R, O'Hare MJ (2004) Three-dimensional in vitro tissue culture models of breast cancer—a review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 85:281–291
Kim JB (2005) Three-dimensional tissue culture models in cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol 5(5):365–377
Kim JH, Jeon TY, Choi TM, Shim TS, Kim SH, Yang SM (2013) Droplet microfluidics for producing functional microparticles. Langmuir 30:1473–1488
Kim S, Oh J, Cha C (2016) Enhancing the biocompatibility of microfluidics-assisted fabrication of cell-laden microgels with channel geometry. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 147:1–8
Kim T, Doh I, Cho YH (2012) On-chip three-dimensional tumor spheroid formation and pump-less perfusion culture using gravity-driven cell aggregation and balanced droplet dispensing. Biomicrofluidics 6:034107
Knight E, Przyborski S (2015) Advances in 3D cell culture technologies enabling tissue-like structures to be created in vitro. J Anat 227:746–756
Knowlton S, Cho Y, Li XJ, Khademhosseini A, Tasoglu S (2016) Utilizing stem cells for three-dimensional neural tissue engineering. Biomater Sci 4:768–784
Kojima R, Yoshimoto K, Takahashi E, Ichino M, Miyoshi H, Nagasaki Y (2009) Spheroid array of fetal mouse liver cells constructed on a PEG-gel micropatterned surface: upregulation of hepatic functions by co-culture with nonparenchymal liver cells. Lab Chip 9:1991–1993
Kwak B et al (2018) Mass fabrication of uniform sized 3D tumor spheroid using high-throughput microfluidic system. J Control Release 275:201–207
Labusca L 2015. Scaffold free 3D culture of mesenchymal stem cells; implications for regenerative medicine. J. Transpl. Stem Cell Biol. 2(1):1-5
Landry J, Bernier D, Ouellet C, Goyette RA, Marceau N (1985) Spheroidal aggregate culture of rat liver cells: histotypic reorganization, biomatrix deposition, and maintenance of functional activities. J Cell Biol 101:914–923
Langenbach F, Naujoks C, Smeets R, Berr K, Depprich R, Kübler N et al (2013) Scaffold-free microtissues: differences from monolayer cultures and their potential in bone tissue engineering. Clin Oral Investig 17:9–17
Laschke M, Schank T, Scheuer C, Kleer S, Schuler S, Metzger W et al (2013) Three-dimensional spheroids of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are potent initiators of blood vessel formation in porous polyurethane scaffolds. Acta Biomater 9:6876–6884
Lazar A, Mann HJ, Remmel RP, Shatford RA, Cerra FB, Hu WS (1995) Extended liver-specific functions of porcine hepatocyte spheroids entrapped in collagen gel. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 31:340–346
Lee D, Cha C (2018) The combined effects of co-culture and substrate mechanics on 3D tumor spheroid formation within microgels prepared via flow-focusing microfluidic fabrication. Pharmaceutics 10(4):229
Lee K, Kim C, Yang JY, Lee H, Ahn B, Xu L et al (2012) Gravity-oriented microfluidic device for uniform and massive cell spheroid formation. Biomicrofluidics 6:014114
Lee KH, Kim S-H, Ryoo JH, Wong SF, Lee S-H (2011) Diffusion-mediated in situ alginate encapsulation of cell spheroids using microscale concave well and nanoporous membrane. Lab Chip 11:1168–1173
Lienemann PS, Rossow T, Mao AS, Vallmajo-Martin Q, Ehrbar M, Mooney D (2017) Single cell-laden protease-sensitive microniches for long-term culture in 3D. Lab Chip 17(4):727–737
Lin RZ, Chou LF, Chien CCM, Chang HY (2006) Dynamic analysis of hepatoma spheroid formation: roles of E-cadherin and β1-integrin. Cell Tissue Res 324:411–422
Lin RZ, Chang HY (2008) Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol J 3:1172–1184
Liu K, Deng Y, Zhang N, Li S, Ding H, Guo F et al (2012) Generation of disk-like hydrogel beads for cell encapsulation and manipulation using a droplet-based microfluidic device. Microfluid Nanofluid 13:761–767
Liu W et al (2019) A microfluidic platform for multi-size 3D tumor culture, monitoring and drug resistance testing. Sens Actuators B Chem
Mao AS, Shin JW, Utech S, Wang H, Uzun O, Li W et al (2017) Deterministic encapsulation of single cells in thin tunable microgels for niche modelling and therapeutic delivery. Nat Mater 16(2):236
Marsano A, Conficconi C, Lemme M, Occhetta P, Gaudiello E, Votta E et al (2016) Beating heart on a chip: a novel microfluidic platform to generate functional 3D cardiac microtissues. Lab Chip 16:599–610
Mazzitelli S, Capretto L, Quinci F, Piva R, Nastruzzi C (2013) Preparation of cell-encapsulation devices in confined microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1533–1555
Mei C et al (2019) Three-dimensional spherical gelatin bubble-based scaffold improves the myotube formation of H9c2 myoblasts. Biotechnol Bioeng
Naruse K (2018) Mechanomedicine. Biophys Rev 10(5):1257–1262
Nyberg SL, Hardin J, Amiot B, Argikar UA, Remmel RP, Rinaldo P (2005) Rapid, large-scale formation of porcine hepatocyte spheroids in a novel spheroid reservoir bioartificial liver. Liver Transpl 11:901–910
Okuyama T, Yamazoe H, Mochizuki N, Khademhosseini A, Suzuki H, Fukuda J (2010) Preparation of arrays of cell spheroids and spheroid-monolayer cocultures within a microfluidic device. J Biosci Bioeng 110:572–576
Ota H, Yamamoto R, Deguchi K, Tanaka Y, Kazoe Y, Sato Y et al (2010) Three-dimensional spheroid-forming lab-on-a-chip using micro-rotational flow. Sens Actuators B Chem 147:359–365
Ota H, Kodama T, Miki N (2011a) Rapid formation of size-controlled three-dimensional hetero-cell aggregates using micro-rotation flow for spheroid study. Biomicrofluidics 5:034105
Ota H, Kodama T, Yamato M, Okano T, and Miki N. 2011b. Micro-rotation flow chamber rapidly forming collagen gel-mediated hetero-spheroids, in Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science (MHS), 2011 International Symposium on, pp. 94-98
Ota H, Miki N (2011) Microfluidic experimental platform for producing size-controlled three-dimensional spheroids. Sensors Actuators A Phys 169:266–273
Pajoumshariati SR et al (2018) Microfluidic-based cell-embedded microgels using nonfluorinated oil as a model for the gastrointestinal niche. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(11):9235–9246
Patra B, Chen YH, Peng CC, Lin SC, Lee CH, Tung YC (2013) A microfluidic device for uniform-sized cell spheroids formation, culture, harvesting and flow cytometry analysis. Biomicrofluidics 7:054114
Patra B, Peng CC, Liao WH, Lee CH, Tung YC (2016) Drug testing and flow cytometry analysis on a large number of uniform sized tumor spheroids using a microfluidic device. Sci Rep 6
Porto DA, Rouse TM, San-Miguel A, Lu H (2016) Microfluidic platforms for quantitative biology studies in model organisms. In: Microfluidic Methods for Molecular Biology. Springer, pp 1–18
Qiu X et al (2018) Microfluidic channel optimization to improve hydrodynamic dissociation of cell aggregates and tissue. Sci Rep 8(1):2774
Rimann M, Laternser S, Gvozdenovic A, Muff R, Fuchs B, Kelm JM et al (2014) An in vitro osteosarcoma 3D microtissue model for drug development. J Biotechnol 189:129–135
Rossow T, Lienemann PS, Mooney D (2017) Cell microencapsulation by droplet microfluidic templating. Macromol Chem Phys 218(2)
Sabhachandani P, Motwani V, Cohen N, Sarkar S, Torchilin V, Konry T (2016) Generation and functional assessment of 3D multicellular spheroids in droplet-based microfluidics platform. Lab Chip 16:497–505
Sakai S, Ashida T, Ogino S, Taya M (2014) Horseradish peroxidase-mediated encapsulation of mammalian cells in hydrogel particles by dropping. J Microencapsul 31(1):100–104
Salim A, Fourar M, Pironon J, Sausse J (2008) Oil–water two-phase flow in microchannels: flow patterns and pressure drop measurements. Can J Chem Eng 86:978–988
Samal P et al (2019) Grow with the flow: when morphogenesis meets microfluidics. Adv Mater:1805764
Sarem M et al (2019) Cell number in mesenchymal stem cell aggregates dictates cell stiffness and chondrogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther 10(1):10
Sart S, Agathos SN, Li Y, Ma T (2016) Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell 3D microenvironment: from macro to microfluidic bioreactors. Biotechnol J 11:43–57
Sart S, et al. 2019. Mapping structure and biological functions within mesenchymal bodies using microfluidics bioRxiv p 514158
Schultz KM, Furst EM (2011) High-throughput rheology in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 11:3802–3809
Shamloo A (2014) Cell-cell interactions mediate cytoskeleton organization and collective endothelial cell chemotaxis. Cytoskeleton 71:501–512
Shao C et al (2019) Droplet microarray on patterned butterfly wing surfaces for cell spheroid culture. Langmuir
Shi W, Weng D, Niu W (2016) Nanoparticle drug delivery systems and three-dimensional cell cultures in cancer treatments and research. Cancer Transl Med 2:154
Silva TP et al (2019) Design principles for pluripotent stem cell-derived organoid engineering. Stem Cells Int 2019:4508470
Skardal A, Shupe T, Atala A (2016) Organoid-on-a-chip and body-on-a-chip systems for drug screening and disease modeling. Drug Discov Today 21(9):1399–1411
Sudeepthi A, Sen AK, Yeo L (2019) Aggregation of a dense suspension of particles in a microwell using surface acoustic wave microcentrifugation. Microfluid Nanofluid 23(5):76
Sun D, Lu J, Chen Z, Yu Y, Li Y (2014) A novel three-dimensional microfluidic platform for on-chip multicellular tumor spheroid formation and culture. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:831–842
Torisawa Y, Chueh B, Huh D, Ramamurthy P, Roth TM, Barald KF et al (2007) Efficient formation of uniform-sized embryoid bodies using a compartmentalized microchannel device. Lab Chip 7:770–776
Torres A et al (2018) Guiding morphogenesis in cell-instructive microgels for therapeutic angiogenesis. Biomaterials 154:34–47
Tung Y-C et al (2011) High-throughput 3D spheroid culture and drug testing using a 384 hanging drop array. Analyst 136(3):473–478
Verboet PE, Borovinskaya O, Meyer N, Günther D, Dittrich PS (2014) A new microfluidics-based droplet dispenser for ICPMS. Anal Chem 86:6012–6018
Visone R, Gilardi M, Marsano A, Rasponi M, Bersini S, Moretti M (2016) Cardiac meets skeletal: what’s new in microfluidic models for muscle tissue engineering. Molecules 21:1128
Wagner O, Thiele J, Weinhart M, Mazutis L, Weitz DA, Huck WT et al (2016) Biocompatible fluorinated polyglycerols for droplet microfluidics as an alternative to PEG-based copolymer surfactants. Lab Chip 16:65–69
Walser R, Metzger W, Görg A, Pohlemann T, Menger M, Laschke M (2013) Generation of co-culture spheroids as vascularisation units for bone tissue engineering. Eur Cell Mater 26:222–233
Wang J, Cheng Y, Yu Y, Fu F, Chen Z, Zhao Y et al (2015a) Microfluidic generation of porous microcarriers for three-dimensional cell culture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:27035–27039
Wang J, Li Y, Wang X, Wang J, Tian H, Zhao P et al (2017) Droplet microfluidics for the production of microparticles and nanoparticles. Micromachines 8(1):22
Wang W, Itaka K, Ohba S, Nishiyama N, Chung UI, Yamasaki Y et al (2009) 3D spheroid culture system on micropatterned substrates for improved differentiation efficiency of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 30:2705–2715
Wang Y, Wang J (2014) Mixed hydrogel bead-based tumor spheroid formation and anticancer drug testing. Analyst 139:2449–2458
Wang Y, Zhao L, Tian C, Ma C, Wang J (2015b) Geometrically controlled preparation of various cell aggregates by droplet-based microfluidics. Anal Methods 7:10040–10051
Wilson JL, Najia MA, Saeed R, McDevitt TC (2014) Alginate encapsulation parameters influence the differentiation of microencapsulated embryonic stem cell aggregates. Biotechnol Bioeng 111:618–631
Winter A, Breit S, Parsch D, Benz K, Steck E, Hauner H et al (2003) Cartilage-like gene expression in differentiated human stem cell spheroids: a comparison of bone marrow-derived and adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Arthritis Rheum 48:418–429
Wu J, Chen Q, Liu W, He Z, Lin JM (2016) Recent advances in microfluidic 3D cellular scaffolds for drug assays. TrAC Trends Anal Chem
Wu LY, Di Carlo D, Lee LP (2008) Microfluidic self-assembly of tumor spheroids for anticancer drug discovery. Biomed Microdevices 10:197–202
Yamaguchi Y, Ohno J, Sato A, Kido H, Fukushima T (2014) Mesenchymal stem cell spheroids exhibit enhanced in-vitro and in-vivo osteoregenerative potential. BMC Biotechnol 14:1
Yang S, Fu C, Tseng S, Srinivasu V, Shilpa S, Chang H, et al. 2012. NUSAS: negative pressure driving HEPG2/3T3 cells mixing/gradient co-culture inside U trapper array on rapid multicellular spheroid assembling system, in Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), 2012 IEEE 25th International Conference on, pp. 1077-1080
Yap KK, Dingle AM, Palmer JA, Dhillon RS, Lokmic Z, Penington AJ et al (2013) Enhanced liver progenitor cell survival and differentiation in vivo by spheroid implantation in a vascularized tissue engineering chamber. Biomaterials 34:3992–4001
Yoon S, Kim JA, Lee SH, Kim M, Park TH (2013) Droplet-based microfluidic system to form and separate multicellular spheroids using magnetic nanoparticles. Lab Chip 13:1522–1528
Yu L, Chen MC, Cheung KC (2010) Droplet-based microfluidic system for multicellular tumor spheroid formation and anticancer drug testing. Lab Chip 10:2424–2432
Zhu K et al (2019) All-aqueous phase microfluidics for cell encapsulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(5):4826–4832
Ziółkowska K, Stelmachowska A, Kwapiszewski R, Chudy M, Dybko A, Brzózka Z (2013) Long-term three-dimensional cell culture and anticancer drug activity evaluation in a microfluidic chip. Biosens Bioelectron 40:68–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, S.S., Shamloo, A. & Hannani, S.K. Microfluidic technologies to engineer mesenchymal stem cell aggregates—applications and benefits. Biophys Rev 12, 123–133 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-020-00613-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-020-00613-8