Abstract
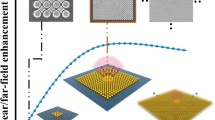
In this study, we present a description of an Au nanobead array-based optical recoding mechanism using the near-field strong enhancement induced by localized surface plasmon resonance. Through a numerical Finite-Difference Time-Domain simulation, we find that a strong field enhancement by originating from the coupled plasmon mode can be induced between closely spaced Au nanoparticles (NPs) arranged on the top surface of a recording medium. The calculated maximum power density inside the recording layer in the case of the Au NPs’ density = 55% (λ = 658 nm) is ~ 56% higher than that of the case without the Au NP array. Moreover, our phase-change recording experiment using an Au NP array verifies the functionality of localized surface plasmon resonance-based optical recording.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- λ :
-
Wavelength
- k:
-
Wave vector
- c :
-
Velocity of electromagnetic wave
- \(\tilde{\varepsilon }\) :
-
Complex relative permittivity
- εα :
-
Infinite permittivity
- εs :
-
Static permittivity
- ω:
-
Angular frequency
- σ:
-
Conductivity
- τ:
-
Relaxation time
- E :
-
Electric field amplitude
- S:
-
Power density
- R:
-
Reflectance
References
Csáki, A., Möller, R., & Fritzsche, W. (2002). Gold nanoparticles as novel label for DNA diagnotics. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics, 2, 187–193.
Fritzsche, W., Csáki, A., & Möller, R. (2002). Nanoparticle-based optical detection of molecular interactions for DNA-Chip technology. Proceedings of SPIE, 4626, 17.
Csáki, A., Möller, R., Köhler, J. M., & Fritzsche, W. (2001). DNA monolayer on gold substrate characterized by nanoparticle labeling and scanning force microscopy. Nucleic Acids Research, 29(16), e81.
Köhler, J. M., Csáki, A., Reichert, J., Möller, R., Straube, W., & Fritzsche, W. (2001). Selective labeling of oligonucleotide monolayers by metallic nanobeads for fast optical readout of DNA-chips. Sensors and Actuators B, 76, 166–172.
Hutter, E., & Fendler, J. H. (2004). Exploitation of localized surface plasmon resonance. Advanced Material, 16(19), 1685–1706.
Haes, A. J., Haynes, C. L., McFarland, A. D., Schatz, G. C., Van Duyne, R. P., & Zou, S. (2005). Plasmonic material for surface-enhanced sensing and spectroscopy. MRS Bulletin, 30, 368–375.
Barnes, W. L., Dereux, A., & Ebbesen, T. W. (2003). Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature, 424, 824–830.
Kottmann, J. P., & Martin, O. J. F. (2001). Retardation-induced plasmon resonances in coupled nanoparticles. Optics Letter, 26(14), 1096–1098.
Bohren, C. F., & Huffman, D. R. (1983). Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. New York: Wiley.
Kreibig, U., & Vollmer, M. (1995). Optical properties of metal clusters (Vol. 25). Berlin: Springer.
Blab, G. A., Cognet, L., Berciaud, S., Alexandre, I., Husar, D., Remacle, J., et al. (2006). Optical readout of gold nanoparticle-based DNA microarrays without silver enhancement. Biophysical Journal: Biophysical Letters, 90, L13.
Haes, A. J., Hall, W. P., Chang, L., Klein, W. L., & Van Duyne, R. P. (2004). A localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor: First steps toward an assay for alzheimer’s disease. Nano Letters, 4(6), 1029–1034.
Arai, T., Kumar, P. K. R., Rockstuhl, C., Awazu, K., & Tominaga, J. (2007). An optical biosensor based on localized surface plasmon resonance of silver nanostructured films. Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics, 9, 699–703.
Endo, T., Yamamura, S., Nagatani, N., Morita, Y., Takamura, Y., & Tamiya, E. (2005). Localized surface plasmon resonance based optical biosensor using surface modified nanoparticle layer for label-free monitoring of antigen-antibody reaction. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 6, 491–500.
Kim, K.-H., Lee, S.-Y., Kim, S.-K., Lee, S.-H., & Jeong, S.-G. (2007). A new DNA chip detection mechanism using optical pick-up actuators. Microsystem Technologies, 13, 1359–1369.
Kim, S.-K., Li, X.-Z., Lee, S. B., Kim, K.-H., & Lee, S.-Y. (2008). Nano-pulsed laser irradiation scanning system for phase-change materials. Ultramicroscopy, 108, 1110–1114.
Park, K.-H., Lee, S.-Q., Kim, E.-K., Moon, S.-E., Cho, Y.-H., Gokarna, A., et al. (2008). Bio-information scanning technology using an optical pick-up head. Ultramicroscopy, 108, 1319–1324.
Kunz, K., & Lubbers, R. (1996). The finite difference time domain method for electromagnetics. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Remcom Inc.: XFDTD 6.4 software (2006).
Palik, E. D. (1996). Handbook of optical constants of solids. Orlando: Academic.
Wang, X., Kuwahara, M., Awazu, K., Fons, P., Tominaga, J., & Ohki, Y. (2009). Proposal of a grating-based optical reflection switch using phase change materials. Optics Express, 17(19), 1647–16956.
Long, G., & Genga, Y. (2012). Investigation of ZnS–SiO2/Ag/ZnS–SiO2 as high stable transparent and conductive multilayer films. Applied Surface Science, 263, 546–552.
Su, K.-H., Wei, Q.-H., Zhang, X., Mock, J. J., Smith, D. R., & Schultz, S. (2003). Interparticle coupling effects on plasmon resonances of nanogold particles. Nano Letters, 3(8), 1087.
Maier, S. A., Kik, P. G., & Atwater, H. A. (2002). Observation of coupled plasmon-polariton mode in Au nanoparticle chain waveguides of different length: Estimation of waveguide loss. Applied Physics Letters, 81(9), 1714–1716.
David, C., Armand, M., & Aziz, M. M. (2006). Terabit-per-square-inch data storage using phase-change media and scanning electrical nanoprobes. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 5(1), 50–61.
Hecht, E. (2002). Optics (4th ed.). Reading: Addison Wesley.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research Grants from Daegu Catholic University in 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, SM. Au Nanoparticle Array Deposited Phase-Change Material for Optical Information Recording Using Field Enhancement Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 20, 267–272 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00096-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00096-y