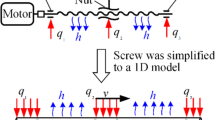
Abstract
In general, in order to compensate the thermal error or the positioning error of a ball screw feed drive system, the actual temperature or positioning data feedback was needed. The traditional thermal error compensation system of ball screw feed drive is highly dependent on the feedback temperature or positioning data. Because of the overdependence to measuring technique, increasing of compensation system cost and decreasing of productivity level will be an inevitable trend in a machine tool. This paper presents a new approach in ball screw thermal error compensation system which can work without any temperature or positioning feedback. As the parts of the thermal error compensation system, component heat generation, compensation method, thermal model, mathematic model and calculation method were studied respectively. In order to verify correctness and generality of the developed thermal model and the thermal error compensation system, a series of simulations was carried out in several kinds of working condition. Through the series of simulations with the thermal model, calculation method and simulation conditions, deformation characteristics and thermal behavior of the prototype ball screw system have been obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramesh, R., Mannan, M. A., and Poo, A. N., “Thermal Error Measurement and Modelling in Machine Tools.: Part I. Influence of Varying Operating Conditions,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 43, No. 4, pp. 391–404, 2003.
Ramesh, R., Mannan, M. A., Poo, A. N., and Keerthi, S. S., “Thermal Error Measurement and Modelling in Machine Tools. Part II. Hybrid Bayesian Network-Support Vector Machine Model,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 43, No. 4, pp. 405–419, 2003.
Ramesh, R., Mannan, M., and Poo, A., “Error Compensation in Machine Tools-A Review: Part I: Geometric, Cutting-Force Induced and Fixture-Dependent Errors,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 40, No. 9, pp. 1235–1256, 2000.
Ramesh, R., Mannan, M. A., and Poo, A. N., “Error Compensation in Machine Tools-A Review: Part II: Thermal Errors,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 40, No. 9, pp. 1257–1284, 2000.
Bryan, J., “International Status of Thermal Error Research,” CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 39, No. 2, pp. 645–656, 1990.
Kim, S. and Cho, D., “Real-Time Estimation of Temperature Distribution in a Ball-Screw System,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 37, No. 4, pp. 451–464, 1997.
Huang, S.-C., “Analysis of a Model to Forecast Thermal Deformation of Ball Screw Feed Drive Systems,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 35, No. 8, pp. 1099–1104, 1995.
Harris, T. A., “Rolling Bearing Analysis,” John Wiley and Sons, pp. 540–560, 1991.
Xu, Z. Z., Liu, X. J., Kim, H. K., Shin, J. H., and Lyu, S. K., “Thermal Error Forecast and Performance Evaluation for an Air- Cooling Ball Screw System,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 51, No. 7, pp. 605–611, 2011.
Verl, A. and Frey, S., “Correlation between Feed Velocity and Preloading In Ball Screw Drives,” CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 59, No. 1, pp. 429–432, 2010.
Xu, M., Jiang, S.Y., Cai, Y., “An Improved Thermal Model for Machine Tool Bearings,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 47, No. 1, pp. 53–62, 2007.
Li, H. and Shin, Y. C., “Integrated Dynamic Thermo-Mechanical Modeling of High Speed Spindles, Part 1: Model Development,” Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, Vol. 126, No. 1, pp. 148–158, 2004.
Yun, W. S., Kim, S. K., and Cho, D. W., “Thermal Error Analysis for a CNC Lathe Feed Drive System,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, Vol. 39, No. 7, pp. 1087–1101, 1999.
Wei, J., Lv, C., Sun, W., Li, X., and Wang, Y., “A Study on Optimum Design Method of Gear Transmission System for Wind Turbine,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 14, No. 5, pp. 767–778, 2013.
Wei, J., Sun, Q., Sun, X., and Sun, W., “A Study on Rotor Profiles Design for a Novel Twin-Screw Kneader,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 14, No. 3, pp. 451–459, 2013.
Wei, J., Liang, X. L., Chen, D. B., Yang, Y. L., and Zhou, D. M., “Evaluation of the Mixing Performance for One Novel Twin Screw Kneader with Particle Tracking,” Polymer Engineering & Science, Vol. 54, No. 10, pp. 2407–2419, 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, ZZ., Choi, C., Liang, Lj. et al. Study on a novel thermal error compensation system for high-precision ball screw feed drive (1st report: Model, calculation and simulation). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 2005–2011 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0261-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0261-4