Abstract
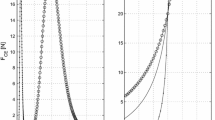
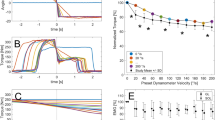
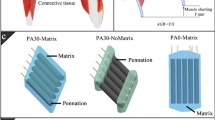
In this study, the effects of various pennation models on predictions of total fiber force and fiber length were compared. Four different pennation models were assumed, and musculotendon dynamics was performed with each pennation model for two different simulations: (1) isokinetic contraction at angular velocities of 1, 50, 100, and 500°/s with fully-activated tibialis anterior (TA) muscle; and (2) isometric contraction at -30°, -15°, 0°, and 15° with altered TA muscle activation. Total fiber force and fiber length obtained from each model were compared. Results from the isokinetic simulation showed that errors in the peak normalized fiber force were approximately ±1%, and the operating range of the normalized fiber length was the narrowest in the realistic model. Pennation angles from the realistic model showed a considerable variation compared with the variable model in isometric simulation; moreover, the realistic model predicted the largest forces and the narrowest operating range of the normalized fiber length. From this study, the variable pennation model was good for the condition of fixed muscle activation, but rather underestimated the force when the muscle activation varied. In addition, it was confirmed that the changes in pennation angle mainly result in the operating range of the fiber length.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott, S. H. and Winter, D. A., “A Comparison of Three Muscle Pennation Assumptions and their Effect on Isometric and Isotonic Force,” Journal of Biomechanics, Vol. 24, No. 2, pp. 163–167, 1991.
Huijing, P. A. and Woittiez, R. D., “The Effect of Architecture on Skeletal Muscle Performance: A Simple Planimetric Model,” Netherlands Journal of Zoology, Vol. 34, No. 1, pp. 21–32, 1983.
Hodges, P. W., Pengel, L. H. M., Herbert, R. D., and Gandevia, S. C., “Measurement of Muscle Contraction with Ultrasound Imaging,” Muscle & Nerve, Vol. 27, No. 6, pp. 682–692, 2003.
Kim, S., Son, J., Yi, C., Kim, D., and Kim, Y., “Pennation Angles of Ankle Dorsiflexor and Plantarflexors Depending on Muscle Contraction Intensity,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 14, No. 5, pp. 855–858, 2013.
Manal, K., Roberts, D. P., and Buchanan, T. S., “Optimal Pennation Angle of the Primary Ankle Plantar and Dorsiflexors: Variations with Sex, Contraction Intensity, and Limb,” Journal of Applied Biomechanics, Vol. 22, No. 4, pp. 255–263, 2006.
Arnold, E. M., Ward, S. R., Lieber, R. L., and Delp, S. L., “A Model of the Lower Limb for Analysis of Human Movement,” Annals of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 38, No. 2, pp. 269–279, 2010.
Thelen, D. G., “Adjustment of Muscle Mechanics Model Parameters to Simulate Dynamic Contractions in Older Adults,” Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, Vol. 125, No. 1, pp. 70–77, 2003.
Delp, S. L., Anderson, F. C., Arnold, A. S., Loan, P., Habib, A., et al., “Opensim: Open-Source Software to Create and Analyze Dynamic Simulations of Movement,” IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 54, No. 11, pp. 1940–1950, 2007.
Arnold, E. M. and Delp, S. L., “Fibre Operating Lengths of Human Lower Limb Muscles during Walking,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, Vol. 366, No. 1570, pp. 1530–1539, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, J., Kim, Y. A comparison of four different muscle pennation models and their effects on predictions in peak fiber force and operating range of fiber length. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 1179–1185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0152-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0152-8