Abstract
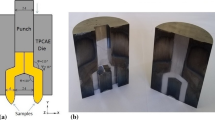
In this work, half channel angular extrusion, a recently developed severe plastic deformation (SPD) process, applied to AZ31 Mg alloy. Effects of the initial microstructure of AZ31 alloy on the microstructural development such as the grain refinement and texture evolution during the half channel angular extrusion (HCAE) has been studied. It was found that the grains of the AZ31 alloys can be refined remarkably by single pass of HCAE than other SPD techniques and not only the grain refinement but also the deformation induced textures result in a noticeable enhancement of mechanical properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lou, X. Y., Li, M., Boger, R., Agnew, S. R., and Wagoner, R. H., “Hardening Evolution of AZ31B Mg Sheet,” International Journal of Plasticity, Vol. 23, No. 1, pp. 44–86, 2007.
Khan, A. S., Pandey, A., Gnäupel-Herold, T., and Mishra, R. K., “Mechanical Response and Texture Evolution of AZ31 Alloy at Large Strains for Different Strain Rates and Temperatures,” International Journal of Plasticity, Vol. 27, No. 5, pp. 688–706, 2011.
Yoon, J., Cazacu, O., and Mishra, R. K., “Constitutive Modeling of AZ31 Sheet Alloy with Application to Axial Crushing,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 565, pp. 203–212, 2013.
Yoon, J., Lee, J., and Lee, J., “Enhancement of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in as-Forged Mg–8Al–0.5Zn Alloy using T5 Heat Treatment,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 586, pp. 306–312, 2013.
Yoon, J. and Park, S., “Forgeability Test of Extruded Mg–Sn–Al–Zn Alloys under Warm Forming Conditions,” Materials & Design, Vol. 55, pp. 300–308, 2014.
Cazacu, O. and Barlat, F., “A Criterion for Description of Anisotropy and Yield Differential Effects in Pressure-Insensitive Metals,” International Journal of Plasticity, Vol. 20, No. 11, pp. 2027–2045, 2004.
Cazacu, O., Plunkett, B., and Barlat, F., “Orthotropic Yield Criterion for Hexagonal Closed Packed Metals,” International Journal of Plasticity, Vol. 22, No. 7, pp. 1171–1194, 2006.
Zhilyaev, A., Nurislamova, G., Kim, B.-K., Baró, M., Szpunar, J., and Langdon, T., “Experimental Parameters Influencing Grain Refinement and Microstructural Evolution during high-Pressure Torsion,” Acta Materialia, Vol. 51, No. 3, pp. 753–765, 2003.
Iwahashi, Y., Wang, J., Horita, Z., Nemoto, M., and Langdon, T. G., “Principle of Equal-Channel Angular Pressing for the Processing of Ultra-Fine Grained Materials,” Scripta Materialia, Vol. 35, No. 2, pp. 143–146, 1996.
Iwahashi, Y., Horita, Z., Nemoto, M., and Langdon, T. G., “The Process of Grain Refinement in Equal-Channel Angular Pressing,” Acta Materialia, Vol. 46, No. 9, pp. 3317–3331, 1998.
Nakashima, K., Horita, Z., Nemoto, M., and Langdon, T. G., “Development of a Multi-Pass Facility for Equal-Channel Angular Pressing to high Total Strains,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 281, No. 1, pp. 82–87, 2000.
Kim, K. J., Yang, D. Y., and Yoon, J. W., “Microstructural Evolution and Its Effect on Mechanical Properties of Commercially Pure Aluminum Deformed by Ecae (Equal Channel Angular Extrusion) Via Routes A and C,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 527, No. 29, pp. 7927–7930, 2010.
Nie, K., Wu, K., Wang, X., Deng, K., Wu, Y., and Zheng, M., “Multidirectional Forging of Magnesium Matrix Composites: Effect on Microstructures and Tensile Properties,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 527, No. 27, pp. 7364–7368, 2010.
Chen, Q., Shu, D., Hu, C., Zhao, Z., and Yuan, B., “Grain Refinement in an As-Cast AZ61 Magnesium Alloy Processed by Multi-Axial Forging under the Multitemperature Processing Procedure,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 541, No. pp. 98–104, 2012.
Saito, Y., Utsunomiya, H., Tsuji, N., and Sakai, T., “Novel Ultrahigh Straining Process for Bulk Materials—Development of the Accumulative Roll-Bonding (ARB) Process,” Acta Materialia, Vol. 47, No. 2, pp. 579–583, 1999.
Kim, K. and Yoon, J., “Evolution of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ61 Alloy Processed by Half Channel Angular Extrusion (HCAE), a Novel Severe Plastic Deformation Process,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 578, pp. 160–166, 2013.
Mabuchi, M., Ameyama, K., Iwasaki, H., and Higashi, K., “Low temperature Superplasticity of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy with Non-Equilibrium Grain Boundaries,” Acta Materialia, Vol. 47, No. 7, pp. 2047–2057, 1999.
Yamashita, A., Horita, Z., and Langdon, T. G., “Improving the Mechanical Properties of Magnesium and a Magnesium Alloy through Severe Plastic Deformation,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 300, No. 1, pp. 142–147, 2001.
Watanabe, H., Mukai, T., Ishikawa, K., and Higashi, K., “Low Temperature Superplasticity of a Fine-Grained ZK60 Magnesium Alloy Processed by Equal-Channel-Angular Extrusion,” Scripta Materialia, Vol. 46, No. 12, pp. 851–856, 2002.
Agnew, S. R., Mehrotra, P., Lillo, T. M., Stoica, G. M., and Liaw, P. K., “Texture Evolution of Five Wrought Magnesium Alloys during Route a Equal Channel Angular Extrusion: Experiments and Simulations,” Acta Materialia, Vol. 53, No. 11, pp. 3135–3146, 2005.
Suwas, S., Gottstein, G., and Kumar, R., “Evolution of Crystallographic Texture during Equal Channel Angular Extrusion (ECAE) and Its Effects on Secondary Processing of Magnesium,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 471, No. 1, pp. 1–14, 2007.
Xia, K., Wang, J. T., Wu, X., Chen, G., and Gurvan, M., “Equal Channel Angular Pressing of Magnesium Alloy AZ31,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 410, pp. 324–327, 2005.
Tang, W. N., Chen, R. S., Zhou, J., and Han, E. H., “Effects of ECAE Temperature and Billet Orientation on the Microstructure, Texture Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Mg–Zn–Y–Zr Alloy,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 499, No. 1, pp. 404–410, 2009.
Al-Maharbi, M., Karaman, I., Beyerlein, I. J., Foley, D., Hartwig, K. T., et al., “Microstructure, Crystallographic Texture, and Plastic Anisotropy Evolution in an Mg Alloy during Equal Channel Angular Extrusion Processing,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 528, No. 25, pp. 7616–7627, 2011.
Foley, D. C., Al-Maharbi, M., Hartwig, K. T., Karaman, I., Kecskes, L. J., and Mathaudhu, S. N., “Grain Refinement vs. Crystallographic Texture: Mechanical Anisotropy in a Magnesium Alloy,” Scripta Materialia, Vol. 64, No. 2, pp. 193–196, 2011.
Yamashita, A., Horita, Z., and Langdon, T. G., “Improving the Mechanical Properties of Magnesium and a Magnesium Alloy through Severe Plastic Deformation,” Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 300, No. 1, pp. 142–147, 2001.
Lapovok, R., Thomson, P. F., Cottam, R., and Estrin, Y., “The Effect of Grain Refinement by Warm Equal Channel Angular Extrusion on Room Temperature Twinning in Magnesium Alloy ZK60,” Journal of Materials Science, Vol. 40, No. 7, pp. 1699–1708, 2005.
Koike, J., Kobayashi, T., Mukai, T., Watanabe, H., Suzuki, M., et al., “The Activity of Non-Basal Slip Systems and Dynamic Recovery at Room Temperature in Fine-Grained AZ31B Magnesium Alloys,” Acta Materialia, Vol. 51, No. 7, pp. 2055–2065, 2003.
Kim, W. J., An, C. W., Kim, Y. S., and Hong, S. I., “Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of an AZ61 Mg Alloy Produced by Equal Channel Angular Pressing,” Scripta Materialia, Vol. 47, No. 1, pp. 39–44, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K., Yoon, J. Effect of the initial crystallographic texture on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-3Al-1Zn sheet alloy processed by half channel angular extrusion (HCAE). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 1021–1027 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0132-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0132-z