Abstract
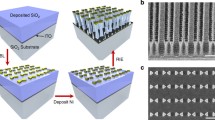
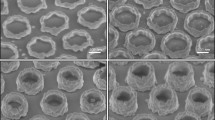
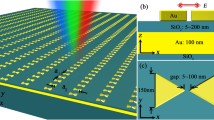
We show a novel approach to fabricate plasmonic nanoantennae based on a maskless focused ion beam nanoring patterning process. Antenna nanoarrays with desired outlines are achieved by precisely controlling the geometric parameters during the milling process. Various nanoantenna designs of bow-tie, nanoclusters (pentamers), and ellipsoid shaped satellites surrounded particle lattices are realized. The whole fabrication method is programmable and monolithic since only a one-step milling process is involved. The optical properties are experimentally characterized. Such nanoantennae may find extensive applications in chemical/bio-sensing due to remarkably enhanced near field intensity at the plasmon resonance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ri :
-
inner radius of the ring aperture for nanoantennae patterning
- ro :
-
outer radius of the ring aperture for nanoantennae patterning
References
Schuller, J. A., Barnard, E. S., Cai, W., Jun, Y. C., White, J. S., and Brongersma, M. L., “Plasmonics for Extreme Light Concentration and Manipulation,” Nature Materials, Vol. 9, No. 3, pp. 193–204, 2010.
Genet, C. and Ebbesen, T. W., “Light in Tiny Holes,” Nature, Vol. 445, No. 7123, pp. 39–46, 2007.
Huang, C. F., Cheng, H. C., Lin, Y., Wu, C. W., and Shen, Y. K., “Study on Cellar Behaviors on Different Nanostructures by Nanoporous Alumina Template,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 689–693, 2014.
Ali, M. Y., Hung, W., and Yongqi, F. Q., “A Review of Focused Ion Beam Sputtering,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 157–170, 2010.
Barnes, W. L., Dereux, A., and Ebbesen, T. W., “Surface Plasmon Subwavelength Optics,” Nature, Vol. 424, No. 6950, pp. 824–830, 2003.
Kauranen, M. and Zayats, A. V., “Nonlinear Plasmonics,” Nature Photonics, Vol. 6, No. 11, pp. 737–748, 2012.
Lal, S., Link, S., and Halas, N. J., “Nano-Optics from Sensing to Waveguiding,” Nature Photonics, Vol. 1, No. 11, pp. 641–648, 2007.
Zheludev, N. I. and Kivshar, Y. S., “From Metamaterials to Metadevices,” Nature Materials, Vol. 11, No. 11, pp. 917–924, 2012.
Ni, X., Emani, N. K., Kildishev, A. V., Boltasseva, A., and Shalaev, V. M., “Broadband Light Bending with Plasmonic Nanoantennas,” Science, Vol. 335, No. 6067, pp. 427–427, 2012.
Knight, M. W., Liu, L., Wang, Y., Brown, L., Mukherjee, S., et al., “Aluminum Plasmonic Nanoantennas,” Nano Letters, Vol. 12, No. 11, pp. 6000–6004, 2012.
Jung, H., Kim, Y., Kim, S., Jang, J., and Hahn, J. W., “Sub-Micro to Nanometer Scale Laser Direct Writing Techniques with a Contact Probe,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 877–883, 2011.
Da Yan, Y., Da Gao, W., Hu, Z. J., Zhao, X. S., and Yan, J. C., “Polymer Nanostructured Components Machined Directly by the Atomic Force Microscopy Scratching Method,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 269–273, 2012.
Kosmeier, S., De Luca, A. C., Zolotovskaya, S., Di Falco, A., Dholakia, K., and Mazilu, M., “Coherent Control of Plasmonic Nanoantennas using Optical Eigenmodes,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 3, Article No. 1808, 2013.
Kosmeier, S., De Luca, A. C., Zolotovskaya, S., Di Falco, A., Dholakia, K., and Mazilu, M., “Coherent Control of Plasmonic Nanoantennas using Optical Eigenmodes,” Scientific Reports, Vol. 3, Article No. 1808, 2013.
Wen, J., Romanov, S., and Peschel, U., “Excitation of Plasmonic Gap Waveguides by Nanoantennas,” Optics Express, Vol. 17, No. 8, pp. 5925–5932, 2009.
Ünlü, E. S., Tok, R. U., and Şendur, K., “Broadband Plasmonic Nanoantenna with an Adjustable Spectral Response,” Optics Express, Vol. 19, No. 2, pp. 1000–1006, 2011.
Chen, Y. Q. and Lu, C. J., “Surface Modification on Silver Nanoparticles for Enhancing Vapor Selectivity of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 135, No. 2, pp. 492–498, 2009.
Chen, C. D., Cheng, S. F., Chau, L. K., and Wang, C. C., “Sensing Capability of the Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanorods,” Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Vol. 22, No. 6, pp. 926–932, 2007.
Endo, T., Shibata, A., Yanagida, Y., Higo, Y., and Hatsuzawa, T., “Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Optical Characteristics for Hydrogen Peroxide Using Polyvinylpyrrolidone Coated Silver Nanoparticles,” Materials Letters, Vol. 64, No. 19, pp. 2105–2108, 2010.
Rani, M., Sharma, N. K., and Sajal, V., “Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance based Fiber Optic Sensor with Nanoparticles,” Optics Communications, Vol. 292, No. pp. 92–100, 2013.
Tu, M. H., Sun, T., and Grattan, K. T. V., “LSPr Optical Fibre Sensors based on Hollow Gold Nanostructures,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Vol. 191, pp. 37–44, 2014.
Anker, J. N., Hall, W. P., Lyandres, O., Shah, N. C., Zhao, J., and Van Duyne, R. P., “Biosensing with Plasmonic Nanosensors,” Nature Materials, Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 442–453, 2008.
Zhao, Y., Chen, D., Yue, H., Spiering, M. M., Zhao, C., et al., “Dark-Field Illumination on Zero-Mode Waveguide/Microfluidic Hybrid Chip Reveals T4 Replisomal Protein Interactions,” Nano Letters, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 1952–1960, 2014.
Si, G., Zhao, Y., Liu, H., Teo, S., Zhang, M., et al., “Annular Aperture Array based Color Filter,” Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 99, No. 3, Paper No. 033105, 2011.
Si, G., Zhao, Y., Lv, J., Lu, M., Wang, F., et al., “Reflective Plasmonic Color Filters based on Lithographically Patterned Silver Nanorod Arrays,” Nanoscale, Vol. 5, No. 14, pp. 6243–6248, 2013.
Si, G., Zhao, Y., Leong, E. S. P., and Liu, Y. J., “Liquid-Crystal- Enabled Active Plasmonics: A Review,” Materials, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 1296–1317, 2014.
Si, G., Teo, E. J., Bettiol, A. A., Teng, J., and Danner, A. J., “Suspended Slab and Photonic Crystal Waveguides in Lithium Niobate,” Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, Vol. 28, No. 2, pp. 316–320, 2010.
Jiang, X., Gu, Q., Wang, F., Lv, J., Ma, Z., and Si, G., “Fabrication of Coaxial Plasmonic Crystals by Focused Ion Beam Milling and Electron-Beam Lithography,” Materials Letters, Vol. 100, pp. 192–194, 2013.
Si, G., Danner, A. J., Teo, S. L., Teo, E. J., Teng, J., and Bettiol, A. A., “Photonic Crystal Structures with Ultrahigh Aspect Ratio in Lithium Niobate Fabricated by Focused Ion Beam Milling,” Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, Vol. 29, No. 2, Paper No. 021205, 2011.
JunáLiu, Y., “Direct and Accurate Patterning of Plasmonic Nanostructures with Ultrasmall Gaps,” Nanoscale, Vol. 5, No. 10, pp. 4309–4313, 2013.
Chang, W. S., Lassiter, J. B., Swanglap, P., Sobhani, H., Khatua, Set al., “A Plasmonic Fano Switch,” Nano Letters, Vol. 12, No. 9, pp. 4977–4982, 2012.
Pakizeh, T. and Kall, M., “Unidirectional Ultracompact Optical Nanoantennas,” Nano Letters, Vol. 9, No. 6, pp. 2343–2349, 2009.
Piao, X., Yu, S., and Park, N., “Control of Fano Asymmetry in Plasmon Induced Transparency and Its Application to Plasmonic Waveguide Modulator,” Optics Express, Vol. 20, No. 17, pp. 18994–18999, 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, JT., Yan, Y., Zhang, WK. et al. Plasmonic nanoantennae fabricated by focused Ion beam milling. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 16, 851–855 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0112-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-015-0112-3