Abstract
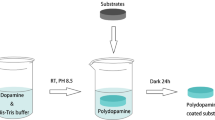
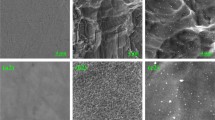
The effect of polydopamine coated titanium such as surface roughness, wettability, cell growth and toxicity, and corrosion resistance. The polydopamine-coated titanium was successfully prepared from dopamine solution and bright polydopamine granules were randomly distributed on titanium surface after coating process. The surface roughness was not significantly decreased in the pure titanium (P>0.05), but significantly decreased (P<0.05) in the spark anodized titanium after the dopamine coating treatment. The contact angle of polydopamine-coated titanium surface was found to be lower than that of the untreated titanium surface. At the potentiodynamic polarization corrosion test, polydopamine-coated titanium has better corrosion-resistance than untreated titanium. The resistance of cytotoxicity is decreased by dopamine coating surface treatment (P<0.05). Findings from this research suggested that polydopamine coating offer a versatile approach for the titanium surface modification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buser, D., Martin, W., and Belser, U. C., “Optimizing Esthetics for Implant Restorations in the Anterior Maxilla: Anatomic and Surgical Considerations,” The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, Vol. 19, pp. 43–61, 2003.
Elias, C. N., Oshida, Y., Lima, J. H. C., and Muller, C. A., “Relationship between Surface Properties (Roughness, Wettability and Morphology) of Titanium and Dental Implant Removal Torque,” Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 234–242, 2008.
Brånemark, P. I., Breine, U., Adell, R., Hansson, B., Lindström, J., and Ohlsson, Å., “Intra-Osseous Anchorage of Dental Prostheses: I. Experimental Studies,” Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Hand Surgery, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 81–100, 1969.
Coelho, P. G., Granato, R., Marin, C., Teixeira, H. S., Suzuki, M., et al., “The Effect of Different Implant Macrogeometries and Surface Treatment in Early Biomechanical Fixation: an Experimental Study in Dogs,” Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, Vol. 4, No. 8, pp. 1974–1981
Chuang, S. K. and Cai, T., “Predicting Clustered Dental Implant Survival using Frailty Methods,” Journal of Dental Research, Vol. 85, No. 12, pp. 1147–1151, 2006.
Levine, R. A., Clem, D., Beagle, J., Ganeles, J., Johnson, P., et al., “Multicenter Retrospective Analysis of the Solid-Screw ITI Implant for Posterior Single-Tooth Replacements,” The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, Vol. 17, No. 4, pp. 550–556, 2001.
Zupnik, J., Kim, S.-W., Ravens, D., Karimbux, N., and Guze, K., “Factors Associated with Dental Implant Survival: a 4-Year Retrospective Analysis,” Journal of Periodontology, Vol. 82, No. 10, pp. 1390–1395, 2011.
Park, J. W., Park, K. B., and Suh, J. Y., “Effects of Calcium Ion Incorporation on Bone Healing Of Ti6Al4V Alloy Implants in Rabbit Tibiae,” Biomaterials, Vol. 28, No. 22, pp. 3306–3313, 2007.
Le Guéhennec, L., Soueidan, A., Layrolle, P., and Amouriq, Y., “Surface Treatments of Titanium Dental Implants for Rapid Osseointegration,” Dental Materials, Vol. 23, No. 7, pp. 844–854, 2007.
Stanford, C., Johnson, G., Fakhry, A., Gartton, D., Mellonig, J., and Wagner, W., “Outcomes of a Fluoride Modified Implant One Year after Loading in the Posterior-Maxilla when Placed with the Osteotome Surgical Technique,” Appl Osseointegration Res, Vol. 5, pp. 50–55, 2006.
Hayashi, K., Inadome, T., Mashima, T., and Sugioka, Y., “Comparison of Bone-Implant Interface Shear Strength of Solid Hydroxyapatite and Hydroxyapatite Coated Titanium Implants,” Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, Vol. 27, No. 5, pp. 557–563, 1993.
Hanawa, T., Asami, K., and Asaoka, K., “Microdissolution of Calcium Ions from Calciumion-Implanted Titanium,” Corrosion Science, Vol. 38, No. 9, pp. 1579–1594, 1996.
Rabiei, A., Thomas, B., Jin, C., Narayan, R., Cuomo, J., et al., “A Study on Functionally Graded HA Coatings Processed Using Ion Beam Assisted Deposition with in Situ Heat Treatment,” Surface and Coatings Technology, Vol. 200, No. 20, pp. 6111–6116, 2006.
Kim, H. M., Miyaji, F., Kokubo, T., and Nakamura, T., “Bonding Strength of Bonelike Apatite Layer to Ti Metal Substrate,” Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, Vol. 38, No. 2, pp. 121–127, 1997.
Lee, M. H., Park, I. S., Min, K. S., Ahn, S. G., Park, J. M., et al., “Evaluation of in Vitro and in Vivo Tests for Surface-Modified Titanium by H2SO4 and H2O2 Treatment,” Metals and Materials International, Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 109–115, 2007.
Lee, M. H., Yoon, D. J., Won, D. H., Bae, T. S., and Watari, F., “Biocompatibility of Surface Treated Pure Titanium and Titanium Alloy Byin Vivo Andin Vitro Test,” Metals and Materials International, Vol. 9, No. 1, pp. 35–42, 2003.
Lee, I. G., Kim, Y. K., Park, I. S., Park, J. M., Lee, M. H., et al., “Influence of Electrolyte Temperature on Pure Titanium Modified by Electrochemical Treatment for Implant,” Surface and Interface Analysis, Vol. 40, No. 12, pp. 1538–1544, 2008.
Lee, H., Lee, B. P., and Messersmith, P. B., “A Reversible Wet/Dry Adhesive Inspired by Mussels and Geckos,” Nature, Vol. 448, No. 7151, pp. 338–341, 2007.
Waite, J. H., “Adhesion in Byssally Attached Bivalves,” Biological Reviews, Vol. 58, No. 2, pp. 209–231, 1983.
Waite, J. H., “Nature’s Underwater Adhesive Specialist,” International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, Vol. 7, No. 1, pp. 9–14, 1987.
Cha, H. J., Hwang, D. S., and Lim, S., “Development of Bioadhesives from Marine Mussels,” Biotechnology Journal, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 631–638, 2008.
Ryu, J., Ku, S. H., Lee, H., and Park, C. B., “MusselInspired Polydopamine Coating as a Universal Route to Hydroxyapatite Crystallization,” Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 20, No. 13, pp. 2132–2139, 2010.
Berglundh, T. and Lindhe, J., “Healing around Implants Placed in Bone Defects Treated with Bio-Oss®. An Experimental Study in the Dog,” Clinical Oral Implants Research, Vol. 8, No. 2, pp. 117–124, 1997.
Fei, B., Qian, B., Yang, Z., Wang, R., Liu, W., Mak, C., and Xin, J. H., “Coating Carbon Nanotubes by Spontaneous Oxidative Polymerization of Dopamine,” Carbon, Vol. 46, No. 13, pp. 1795–1797, 2008.
Ku, S. H., Ryu, J., Hong, S. K., Lee, H., and Park, C. B., “General Functionalization Route for Cell Adhesion on Non-Wetting Surfaces,” Biomaterials, Vol. 31, No. 9, pp. 2535–2541, 2010.
Park, I. S., Kim, J. J., Ahn, S. G., Lee, M. H., Seol, K. W., and Bae, T. S., “The Effect of Fluoride Treatment on Titanium Treated with Anodic Spark Oxidation,” Metals and Materials International, Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 117–122, 2007.
Bai, Y., Park, I. S., Park, H. H., Bae, T. S., and Lee, M. H., “Formation of Bioceramic Coatings Containing Hydroxyapatite on the Titanium Substrate by MicroArc Oxidation Coupled with Electrophoretic Deposition,” Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, Vol. 95, No. 2, pp. 365–373, 2010.
Ishizawa, H. and Ogino, M., “Formation and Characterization of Anodic Titanium Oxide Films Containing Ca and P,” Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 65–72, 1995.
Gottlander, M. and Albrektsson, T., “Histomorphometric Studies of Hydroxylapatite-Coated and Uncoated CP Titanium Threaded Implants in Bone,” The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 399–404, 1990.
Webb, K., Hlady, V., and Tresco, P. A., “Relative Importance of Surface Wettability and Charged Functional Groups on NIH 3T3 Fibroblast Attachment, Spreading, and Cytoskeletal Organization,” Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, Vol. 41, No. 3, pp. 422, 1998.
Ciapetti, G., Cenni, E., Pratelli, L., and Pizzoferrato, A., “In Vitro Evaluation of Cell/Biomaterial Interaction by MTT Assay,” Biomaterials, Vol. 14, No. 5, pp. 359–364, 1993.
Kostoryz, E., Tong, P., Chappelow, C., Eick, J., Glaros, A., and Yourtee, D., “In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Solid Epoxy-based Dental Resins and their Components,” Dental Materials, Vol. 15, No. 5, pp. 363–373, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JJ., Park, IS., Shin, GS. et al. Effects of polydopamine coating on the bioactivity of titanium for dental implants. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 15, 1647–1655 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0515-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-014-0515-6