Abstract
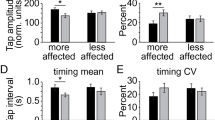
Although differential effects of medication and deep brain stimulation (DBS) on bradykinesia have been addressed in the literature, speed and amplitude have not been separated. This study investigated the differential effects of medication and DBS on quantitative measures of speed and amplitude, as well as on proximal and distal muscles of upper extremities. Fourteen upper limbs affected by Parkinson’s disease were tested. Finger tapping and forearm rotation were performed to investigate distal and proximal bradykinesia, respectively. Test conditions included off-treatment, DBS only, medication only, and medication + DBS. Quantitative outcome measures included root-mean-square average of speed and amplitude. Two-way and one-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) were performed to investigate the effects of medication and DBS, and to compare the performance in four test conditions, respectively. Speed was improved at both body parts, whereas amplitude was improved only at the proximal forearm (p < 0.01). Medication tended to be better than DBS at distal speed, whereas DBS tended to be better than medication at proximal amplitude. Medication + DBS resulted in the best average performance in all outcome measures. Improvement in speed and amplitude in each body parts are differentially associated with medication and DBS. Medication and DBS have complementary effects in amelioration of bradykinesia. The findings may be helpful for clinical interventions and evaluations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Espay, A. J., Beaton, D. E., Morgante, F., Gunraj, C. A., Lang, A. E., and Chen, R., “Impairments of speed and amplitude of movement in Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 24, No.7, pp. 1001–1008, 2009.
Lyons, K. E., Pahwa, R., Troster, A. I., and Koller, W. C., “A comparison of Parkinson’s disease symptoms and self-reported functioning and well being,” Parkinsonism. Relat. Disord., Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 207–209, 1997.
Dural, A., Atay, M. B., Akbostanci, C., and Kucukdeveci, A., “Impairment, disability, and life satisfaction in Parkinson’s disease,” Disabil. Rehabil., Vol. 25, No. 7, pp. 318–323, 2003.
Vaillancourt, D. E., Prodoehl, J., Verhagen Metman, L., Bakay, R. A., and Corcos, D. M., “Effects of deep brain stimulation and medication on bradykinesia and muscle activation in Parkinson’s disease,” Brain, Vol. 127, No. 3, pp. 491–504, 2004.
Sturman, M. M., Vaillancourt, D. E., Metman, L. V., Bakay, R. A., and Corcos, D. M., “Effects of five years of chronic STN stimulation on muscle strength and movement speed,” Exp Brain Res, Vol. 205, No. 4, pp. 435–443, 2010.
Vaillancourt, D. E., Prodoehl, J., Sturman, M. M., Bakay, R. A., Metman, L. V., and Corcos, D. M., “Effects of deep brain stimulation and medication on strength, bradykinesia, and electromyographic patterns of the ankle joint in Parkinson’s disease,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 21, No. 1, pp. 50–58, 2006.
Wenzelburger, R., Kopper, F., Zhang, B. R., Witt, K., Hamel, W., Weinert, D., Kuhtz-Buschbeck, J., Golge, M., Illert, M., Deuschl, G., and Krack, P., “Subthalamic nucleus stimulation for Parkinson’s disease preferentially improves akinesia of proximal arm movements compared to finger movements,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 18, No. 10, pp. 1162–1169, 2003.
Timmermann, L., Braun, M., Groiss, S., Wojtecki, L., Ostrowski, S., Krause, H., Pollok, B., Sudmeyer, M., Ploner, M., Gross, J., Maarouf, M., Voges, J., Sturm, V., and Schnitzler, A., “Differential effects of levodopa and subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation on bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 23, No. 2, pp. 218–227, 2008.
Goetz, C. G., Tilley, B. C., Shaftman, S. R., Stebbins, G. T., Fahn, S., Martinez-Martin, P., Poewe, W., Sampaio, C., Stern, M. B., Dodel, R., Dubois, B., Holloway, R., Jankovic, J., Kulisevsky, J., Lang, A. E., Lees, A., Leurgans, S., LeWitt, P. A., Nyenhuis, D., Olanow, C. W., Rascol, O., Schrag, A., Teresi, J. A., Van Hilten, J. J., and LaPelle, N., “Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 23, No. 15, pp. 2129–2170, 2008.
Kim, J. W., Lee, J. H., Kwon, Y., Kim, C. S., Eom, G. M., Koh, S. B., Kwon, D. Y., and Park, K. W., “Quantification of bradykinesia during clinical finger taps using a gyrosensor in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., Vol. 49, No. 3, pp. 365–371, 2011.
Kim, J. W., Kwon, Y., Kim, Y. M., Chung, H. Y., Eom, G. M., Jun, J. H., Lee, J. W., Koh, S. B., Park, B. K., and Kwon, D. K., “Analysis of lower limb bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease patients,” Geriatr. Gerontol. Int., Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 257–264, 2012.
http://www.mdvu.org/library/ratingscales/pd/ (Accessed 14 June 2013)
Chae, J., Yang, G., Park, B. K., and Labatia, I., “Delay in initiation and termination of muscle contraction, motor impairment, and physical disability in upper limb hemiparesis,” Muscle Nerve, Vol. 25, No. 4, pp. 568–575, 2002.
Potter-Nerger, M., Wenzelburger, R., Deuschl, G., and Volkmann, J., “Impact of subthalamic stimulation and medication on proximal and distal bradykinesia in Parkinson’s disease,” Eur. Neurol., Vol. 62, No. 2, pp. 114–119, 2009.
Espay, A. J., Giuffrida, J. P., Chen, R., Payne, M., Mazzella, F., Dunn, E., Vaughan, J. E., Duker, A. P., Sahay, A., Kim, S. J., Revilla, F. J., and Heldman, D. A., “Differential response of speed, amplitude, and rhythm to dopaminergic medications in Parkinson’s disease,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 26, No. 14, pp. 2504–2508, 2011.
Krakauer, J. and Ghez, C., “Voluntary Movement, In: Kandel, E. R., Schwartz, J. H., and Jessell, T. M. (eds.), Principles of Neural Science,” McGraw-Hill Companies 4th Edition, pp. 756–781, 2000.
Rascol, O., Sabatini, U., Chollet, F., Celsis, P., Montastruc, J. L., Marc-Vergnes, J. P., and Rascol, A., “Supplementary and primary sensory motor area activity in Parkinson’s disease. Regional cerebral blood flow changes during finger movements and effects of apomorphine,” Arch. Neurol., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 144–148, 1992.
Ceballos-Baumann, A. O., Boecker, H., Bartenstein, P., von Falkenhayn, I., Riescher, H., Conrad, B., Moringlane, J. R., and Alesch, F., “A positron emission tomographic study of subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson disease: enhanced movementrelated activity of motor-association cortex and decreased motor cortex resting activity,” Arch. Neurol., Vol. 56, No. 8, pp. 997–1003, 1999.
Jenkins, I. H., Fernandez, W., Playford, E. D., Lees, A. J., Frackowiak, R. S., Passingham, R. E., and Brooks, D. J., “Impaired activation of the supplementary motor area in Parkinson’s disease is reversed when akinesia is treated with apomorphine,” Ann. Neurol., Vol. 32, No. 6, pp. 749–757, 1992.
Hilker, R., Voges, J., Thiel, A., Ghaemi, M., Herholz, K., Sturm, V., and Heiss, W. D., “Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus versus levodopa challenge in Parkinson’s disease: measuring the on- and off-conditions with FDG-PET,” J. Neural. Transm., Vol. 109, No. 10, pp. 1257–1264, 2002.
Gross, J., Pollok, B., Dirks, M., Timmermann, L., Butz, M., and Schnitzler, A., “Task-dependent oscillations during unimanual and bimanual movements in the human primary motor cortex and SMA studied with magnetoencephalography,” Neuroimage, Vol. 26, No.1, pp. 91–98, 2005.
Moore, S. T., MacDougall, H. G., Gracies, J. M., Cohen, H.S., and Ondo, W. G., “Long-term monitoring of gait in Parkinson’s disease,” Gait Posture, Vol. 26, No. 2, pp. 200–207, 2007.
Jun, J. H., Kim, J. W., Kwon, Y., Eom, G. M., Koh, S. B., Lee, B. S., Kim, H. S., Yi, J. H., and Tack, G. R., “Quantification of limb bradykinesia in patients with Parkinson’s disease using a gyrosensor — Improvement and validation,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 557–563, 2011.
Brown, J. D., “Effect size and eta squared.” Shiken: JALT Testing & Evaluation SIG Newsletter, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 38–43, 2008.
Hamani, C., Richter, E., Schwalb, J. M., and Lozano, A. M., “Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review of the clinical literature,” Neurosurgery., Vol. 56, No. 6, pp. 1313–1324, 2005.
Levin, J., Krafczyk, S., Valkovic, P., Eggert, T., Claassen, J., and Botzel, K., “Objective measurement of muscle rigidity in Parkinsonian patients treated with subthalamic stimulation,” Mov. Disord., Vol. 24, No. 1, pp. 57–63, 2009.
Shapiro, M. B., Vaillancourt, D. E., Sturman, M. M., Metman, L. V., Bakay, R. A., and Corcos, D. M., “Effects of STN DBS on rigidity in Parkinson’s disease,” IEEE. Trans. Neural. Syst. Rehabil. Eng., Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 173–181, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors equally contributed as corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JW., Kwon, Y., Ho, Y. et al. Effects of medication and deep brain stimulation on speed and amplitude are different between finger and forearm in patient with Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 14, 1201–1207 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0163-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-013-0163-2