Abstract
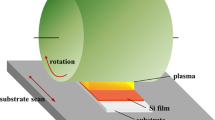
For the mass production of silicon thin film solar cell, it is a key issue to increase deposition rate of microcrystalline silicon film on a large area substrate. One of the most effective methods to increase deposition rate of the film is using high frequency and high power plasma. However, high frequency plasma leads to plasma non uniformity in large area deposition, and high power plasma induces substrate heating during deposition of microcrystalline silicon film and degrades the film quality. In this study, we developed a shaped electrode for spatially uniform plasma and a susceptor cooling system for preventing substrate heating by plasma. And also we investigated the influences of deposition parameters on the microcrystalline silicon single junction cell efficiency with high frequency and high power plasma. Glass substrate was 1.1 m × 1.3 m and plasma excitation frequency was 40 MHz. Capacitively coupled parallel plates RF reactor with concave shaped electrode was used. For the high deposition rate of the microcrystalline films, plasma powers of 0.8∼1.1W/cm2 were used. The highest deposition rate of microcrystalline silicon was 2nm/s. The increases of temperature of susceptor were monitored by two thermocouples which were installed at center and outer side of the susceptor. The temperature increases were suppressed to almost zero with liquid cooling systems. Multiple step deposition was performed which means the higher H2/SiH2 ratio at the initial stage of film growth was used and the ratio gradually decreased during deposition in order to eliminate the amorphous layer at the interface between substrate and film. We also achieved microcrystalline single junction cell efficiencies above 6% on large area substrate at high deposition rate of 1.5nm/s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meier, J., Kroll, U., Spitznagel, J., Benagli, S., Roschek, T., Pfanner, G., Ellert, C., Androutsopoulos, G., Hügli, A., Nagel, M., Bucher, C., Feitknecht, L., Büchel, G., and Büchel, A., “Progress in Up-scaling of Thin Film Silicon Solar Cells by Large-Area PECVD KAI Ssytems,” Proc. of 31st IEEE PVSC, pp. 1464–1467, 2005.
Shah, A., Meier, J., Buechel, A., Kroll, U., Steinhauser, J., Meillaud, F., Schade, H., and Domine, D., “Towards Very Low-Cost Mass Production of Thin-Film Silicon Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Modules on Glass,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 502, No. 1–2, pp. 292–299, 2006.
Aya, Y., Katayama, H., Murata, K., Shinohara, W., Nakagawa, M., Terakawa, A., and Tanaka, M., “SANYO’s R&D on Thin-Film Si Photovoltaic Technologies,” Proc. of 24th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, pp. 2394–2397, 2009.
Takatsuka, H., Yamauchi, Y., Takeuchi, Y., Fukagawa, M., Kawamura, K., Goya, S., and Takano, A., “The World’s Largest High Efficiency Thin Film Silicon Solar Cell Module,” Proc. of IEEE 4th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, pp. 2628–2633, 2006.
Niikura, C., Kondo, M., and Matsuda, A., “Preparation of Microcrystalline Silicon Films at Ultra High-Rate of 10 nm/s Using High-Density Plasma,” J. Non-Crys. Solids, Vol. 338–340, pp. 42–46, 2004.
Lieberman, M. A., Booth, J. P., Chabert, P., Rax, J. M., and Turner, M. M., “Standing Wave and Skin Effects in Large-Area, High-Frequency Capacitive Discharge,” Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 283–293, 2002.
Sansonnens, L., Pletzer, A., Magni, D., Howling, A. A., Hollesnstein, C., and Schmitt, J. P. M., “A Voltage uniformity Study in Large-Area Reactors for RF Plasma Deposition,” Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 170–178, 1997.
Schade, K., Stahr, F., Kuske, J., Rohlecke, S., Steinke, O., Stephan, U., and Dekkers, H. F. W., “High Temperature Line Electrode Assembly for Continuous Substrate Flow VHF PECVD,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 502, No. 1–2, pp. 59–62, 2006.
Hwang, D. S., Lee, S. Y., Lee, H. M., Kim, S. J., and Kim, G. J., “Dual comb-type electrodes as a plasma source for very high frequency plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 518, No. 8, pp. 2124–2127, 2010.
Takagi, T., Ueda, M., Ito, N., Watabe, Y., Sato, H., and Sawaya, K., “Large area VHF plasma sources,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 502, No. 1–2, pp. 50–54, 2006.
Chaudhary, D., Jost, S., Klindworth, M., Leu, F., Martin, J., Martinek, M., Novak, S., Salabas, A., Schrader, N., Taha, A., Wettler, D., Wieland, W., Zorzi, D., and Ellert, C., “Development of PECVD Reactor for Thin Film Solar Applications,” Proc. of 24th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, pp. 2839–2841, 2009.
van den Donkera, M. N., Schmitza, R., Appenzellera, W., Recha, B., Kesselsb, W. M. M., and van de Sanden, M. C. M., “The Role of Plasma Induced Substrate Heating during High Rate Deposition of Microcrystalline Silicon Solar Cells,” Thin Solid Films, Vol. 511–512, pp. 562–566, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, D.S., Lee, C.H., Lee, J.O. et al. Influences of deposition parameters on micro-crystalline silicon single junction cell efficiency in large-area and high rate deposition. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 13, 1113–1116 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0146-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0146-8