Abstract
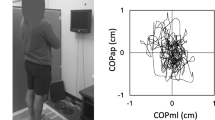
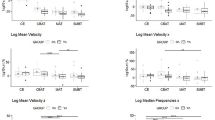
Gender differences have been reported in age-related deterioration of lateral balance, but only when subjects are assessed with their eyes open and only with global measures. The purpose of this study was to investigate the possible effects of vision on age-gender differences in static postural control with structural as well as global measures. Elderly and young subjects performed quiet natural standing on a force plate with their eyes open and closed. Structural measures based on sway-density, as well as conventional global measures, were derived from the center of pressure in both anterio-posterior (AP) and medio-lateral (ML) directions. Effects of vision, age and gender on each outcome measure were analyzed by ANOVA and post-hoc tests. Vision affected most outcome measures but gender-vision interactions could not be shown in both directions. Significant gender differences and age-gender interactions existed only in ML direction measures irrespective of vision. Specifically, women showed age-related reductions in stabilization time and increase in the distance between neighboring posturographic targets, as well as deterioration in global measures (p < 0.001). In conclusion, vision did not affect the age-gender differences in static postural control and women-specific age-related change in structural measures may suggest the deterioration in intermittent control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, J. W., Eom, G. M., Kim, C. S., Kim, D. H., Lee, J. H., Park, B. K., and Hong, J., “Gender differences in the postural sway characteristics of young and elderly subjects during quiet natural standing,” Geriatr. Gerontol. Int., Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 191–198, 2010.
Piirtola, M. and Era, P., “Force Platform measurements as predictors of falls among older people-a review,” Gerontology, Vol. 52, No. 1, pp. 1–16, 2006.
Hilliard, M. J., Martinez, K. M., Janssen, I., Edwards, B., Mille, M. L., Zhang, Y., and Rogers, M. W., “Lateral balance factors predict future falls in community-living older adults,” Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil., Vol. 89, No. 9, pp. 1708–1713, 2008.
Aoyagi, K., Ross, P. D., Davis, J. W., Wasnich, R. D., Hayashi, T., and Takemoto, T. I., “Falls Among Community-Dwelling Elderly in Japan,” J. Bone Miner. Res., Vol. 13, No. 9, pp. 1468–1474, 1998.
Cho, C. Y. and Kamen, G., “Detecting balance deficits in frequent fallers using clinical and quantitative evaluation tools,” J. Am. Geriatr. Soc., Vol. 46, No. 4, pp. 426–430, 1998.
Sattin, R. W., “Falls among older persons: a public health perspective,” Annu. Rev. Public Health, Vol. 13, pp. 489–508, 1992.
Winter, D. A., Patla, A. E., Ishac, M., and Gage, W. H., “Motor mechanisms of balance during quiet standing,” J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol., Vol. 13, No. 1, pp. 49–56, 2003.
Kim, J. W., Kwon, Y., Chung, H. Y., Eom, G. M., Jun, J. H., Chung, J. S., and Park, B. K., “Age-sex differences in the hip abductor muscle properties,” Geriatr. Gerontol. Int., Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 333–340, 2011.
Lockhart, T. E., Smith, J. L., and Woldstad, J. C., “Effects of aging on the biomechanics of slips and falls,” Hum. Factors, Vol. 47, No. 4, pp. 708–729, 2005.
Tinetti, M. E. and Speechley, M., “Prevention of falls among the elderly,” N. Engl. J. Med., Vol. 320, pp. 1055–1059, 1989.
Esteban, J. J., Martínez, M. S., Navalón, P. G., Serrano, O. P., Patiño, J. R., Purón, M. E., and Martínez-Vizcaíno, V., “Visual impairment and quality of life: gender differences in the elderly in Cuenca, Spain,” Qual. Life Res., Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 37–45, 2008.
Parsons, T. D., Rizzo, A. R., van der Zaag, C., McGee, J. S., and Buckwalter, J. G., “Gender differences and cognition among older adults,” Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, Vol. 12, pp. 78–88, 2005.
Baratto, L., Morasso, P. G., Re, C., and Spada, G., “A new look at posturographic analysis in the clinical context: sway-density versus other parameterization techniques,” Motor Control, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 246–270, 2002.
Jacono, M., Casadio, M., Morasso, P. G., and Sanguineti, V., “The sway-density curve and the underlying postural stabilization process,” Motor Control, Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 292–311, 2004.
Zatsiorsky, V. M. and Duarte, M., “Rambling and trembling in quiet standing,” Motor Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, pp. 185–200, 2000.
Loram, I. D. and Lakie, M., “Human balancing of an inverted pendulum: position control by small, ballistic-like, throw and catch movements,” J. Physiol., Vol. 540, pp. 1111–1124, 2002.
Prieto, T. E., Myklebust, J. B., Hoffmann, R. G., Lovett, E. G., and Myklebust, B. M., “Measures of postural steadiness: differences between healthy young and elderly adults,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., Vol. 43, No. 9, pp. 956–966, 1996.
Perneger, T. V., “What’s wrong with Bonferroni adjustments,” BMJ, Vol. 316, pp. 1236–1238, 1998.
Winter, D. A., Patla, A. E., Prince, F., Ishac, M., and Gielo-Perczak, K., “Stiffness control of balance in quiet standing,” J. Neurophysiol., Vol. 80, No. 3, pp. 1211–1221, 1998.
Winter, D. A., Patla, A. E., Rietdyk, S., and Ishac, M. G., “Ankle muscle stiffness in the control of balance during quiet standing,” J. Neurophysiol., Vol. 85, No. 6, pp. 2630–2633, 2001.
Loram, I. D. and Lakie, M., “Direct measurement of human ankle stiffness during quiet standing: the intrinsic mechanical stiffness is insufficient for stability,” J. Physiol., Vol. 545, pp. 1041–1053, 2002.
Casadio, M., Morasso, P. G., and Sanguineti, V., “Direct measurement of ankle stiffness during quiet standing: implications for control modelling and clinical application,” Gait & Posture, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 410–424, 2005.
Bottaro, A., Casadio, M., Morasso, P. G., and Sanguineti, V., “Body sway during quiet standing: is it the residual chattering of an intermittent stabilization process?” Hum. Mov. Sci., Vol. 24, No. 4, pp. 588–615, 2005.
Asai, Y., Tasaka, Y., Nomura, K., Nomura, T., Casadio, M., and Morasso, P., “A model of postural control in quiet standing: Robust compensation of delay-induced instability using intermittent activation of feedback control,” PLoS One, Vol. 4, No. 7, Paper No. e6169, 2009.
de Zee, M. and Voigt, M., “Moment dependency of the series elastic stiffness in the human plantar flexors measured in vivo,” J. Biomech., Vol. 34, No. 11, pp. 1399–1406, 2001.
de Zee, M. and Voigt, M., “Assessment of functional series elastic stiffness of human dorsiflexors with fast controlled releases,” J. Appl. Physiol., Vol. 93, No. 1, pp. 324–329, 2002.
Park, B. K., Kim, J. W., Eom, G. M., Won, S. J., Kwon, Y., Hong, J., Jun, J. H., and Eom, J. S., “Effects of age and gender on the delay in initiation and termination of tibialis anterior contraction,” J. Korean Acad. Rehab. Med., Vol. 35, pp. 229–235, 2011.
Conforto, S., Schmid, M., Camomilla, V., D’Alessio, T., and Cappozzo, A., “Hemodynamics as a possible internal mechanical disturbance to balance,” Gait & Posture, Vol. 14, No. 1, pp. 28–35, 2001.
Wiinberg, N., Høegholm, A., Christensen, H. R., Bang, L. E., Mikkelsen, K. L., Nielsen, P. E., Svendsen, T. L., Kampmann, J. P., Madsen, N. H., and Bentzon, M. W., “24-h ambulatory blood pressure in 352 normal Danish subjects, related to age and gender,” Am. J. Hypertens., Vol. 8, pp. 978–986, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Kwon, Y., Eom, GM. et al. Effects of vision, age and gender on structural and global posturographic features during quiet standing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 13, 969–975 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0126-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-012-0126-z