Abstract
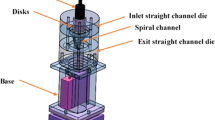
The severe plastic deformation (SPD) processes used for applying an extensive shear plastic strain in the material and consequently grain refinement and increase in the strength of materials. The strain distribution is very important and more homogenous plastic strain is desired in SPD process modifications. In this article, four different die configurations will be investigated during the hollow twist extrusion (HTE) process and the plastic strain distribution will be compared within a hollow section. The die configurations are similar slope line angle of inner and outer dies (SD), opposite slope line angle between the inner and outer dies (OD), outer die with twist zone and flat inner die (FI) and inner die with twist zone and flat outer die (FO). The Von-Mises stress, plastic strain, and material deformation are studied by using a finite element model which was developed in the ABAQUS finite element software. The results show that the FI and FO die configuration produce higher plastic strains than SD die configuration, but the strain homogeneity is not satisfactory. The plastic strain is higher and more homogenous for OD die configuration in comparison to the other die configurations. The required force for twist extrusion of the billet is almost equal for FI and FO die configuration (~ 216 kN) and increases to about 256 kN for SD die configuration (16% increase). The required force for OD die configuration increased once more to 370 kN (44.5% increase). The element distortion along the two defined paths determined the material flow during the HTE process. The flat die retards the material flow for FI and FO die configurations. A significantly material flow will happen for OD die configuration. The element distortion leads to better material mixing in OD die configuration and consequently higher magnitude and more homogenous plastic strain distribution and higher grain refinement will be obtained.
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.Z. Valiev, The new trends in fabrication of bulk nanostructured materials by SPD processing. J. Mater. Sci. 42(5), 1483–1490 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-1281-3
V.M. Segal, Materials processing by simple shear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 197(2), 157–164 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(95)09705-8
A. Khosravifard, M. Jahedi, A.H. Yaghtin, Three dimensional finite element study on torsion extrusion processing of 1050 aluminum alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(11), 2771–2776 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61531-8
D.J. Lee, H.S. Kim, Finite element analysis for the geometry effect on strain inhomogeneity during high-pressure torsion. J. Mater. Sci. 49(19), 6620–6628 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8283-3
N. Tsuji, Y. Saito, H. Utsunomiya, S. Tanigawa, Ultra-fine grained bulk steel produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Scr. Mater. 40(7), 795–800 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00015-9
N. Pardis, B. Talebanpour, R. Ebrahimi, S. Zomorodian, Cyclic expansion-extrusion (CEE): a modified counterpart of cyclic extrusion-compression (CEC). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528(25–26), 7537–7540 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.06.059
M.I. Latypov, I.V. Alexandrov, Y.E. Beygelzimer, S. Lee, H.S. Kim, Finite element analysis of plastic deformation in twist extrusion. Comput. Mater. Sci. 60, 194–200 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.03.035
Y. Beygelzimer, D. Orlov, V. Varyukhin, A new severe plastic deformation method twist extrusion, in Ultrafine Grained Materials II, ed. by Y.T. Zhu, T.G. Langdon, R.S. Mishra, S.L. Setniatin, M.J. Saran, T.C. Lowe (Wiley, Hoboken, 2013), pp. 297–304
Y.E. Beygelzimer et al., Features of twist extrusion: method, structures & material properties. Solid State Phenom. 114, 69–78 (2006). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.114.69
Y. Beygelzimer, A. Reshetov, S. Synkov, O. Prokofeva, R. Kulagin, Kinematics of metal flow during twist extrusion investigated with a new experimental method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(7), 3650–3656 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.08.022
Y. Beygelzimer, V. Varyukhin, S. Synkov, D. Orlov, Useful properties of twist extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 503(1), 14–17 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.12.055
Y. Beygelzimer et al., Planar twist extrusion versus twist extrusion. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211(3), 522–529 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.11.006
R. Kulagin, M.I. Latypov, H.S. Kim, V. Varyukhin, Y. Beygelzimer, “Cross flow during twist extrusion: theory, experiment, and application. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44(7), 3211–3220 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1661-7
A. Reshetov, R. Kulagin, A. Korshunov, Y. Beygelzimer, The occurrence of ideal plastic state in CP titanium processed by twist extrusion. Adv. Eng. Mater. 20(5), 1–8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700899
Y. Beygelzimer, R. Kulagin, Y. Estrin, L.S. Toth, H.S. Kim, M.I. Latypov, Twist extrusion as a potent tool for obtaining advanced engineering materials: a review. Eng. Mater Adv (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201600873
S.A.A. Akbari Mousavi, S. Ranjbar Bahadori, A.R. Shahab, Numerical and experimental studies of the plastic strains distribution using subsequent direct extrusion after three twist extrusion passes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527(16–17), 3967–3974 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.077
S.A.A. Akbari Mousavi, A.R. Shahab, M. Mastoori, Computational study of Ti-6Al-4V flow behaviors during the twist extrusion process. Mater. Des. 29(7), 1316–1329 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2007.07.009
S.A.A. Akbari Mousavi, S.R. Bahadori, The effects of post annealing on the mechanical properties, microstructure and texture evolutions of pure copper deformed by twist extrusion process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528(3), 1242–1246 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.10.007
S.R. Bahadori, S.A.A.A. Mousavi, Examination of an aluminum alloy behavior under different routes of twist extrusion processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528(21), 6527–6534 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.04.092
Y.E. Beygelzimer, O.V. Prokofeva, V.N. Varyukhin, Structural changes in metals subjected to direct or twist extrusion: mathematical simulation. Russ. Metall. 2006(1), 25–32 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029506010058
J.G. Kim, M. Latypov, N. Pardis, Y.E. Beygelzimer, H.S. Kim, Finite element analysis of the plastic deformation in tandem process of simple shear extrusion and twist extrusion. Mater. Des. 83, 858–865 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.06.034
F.J. Kalahroudi, A.R. Eivani, H.R. Jafarian, A. Amouri, R. Gholizadeh, Inhomogeneity in strain, microstructure and mechanical properties of AA1050 alloy during twist extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 667, 349–357 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.04.087
U. Mohammed Iqbal, V.S. Senthil Kumar, An analysis on effect of multipass twist extrusion process of AA6061 alloy. Mater. Des. 50, 946–953 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.066
U. Mohammed Iqbal, V.S. Senthil Kumar, S. Gopalakannan, Application of response surface methodology in optimizing the process parameters of Twist extrusion process for AA6061-T6 aluminum alloy. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 94, 126–138 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.07.085
V. Beloshenko, I. Vozniak, Y. Beygelzimer, Y. Estrin, R. Kulagin, Severe plastic deformation of polymers. Mater. Trans. 60(7), 1192–1202 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MF201912
V.Q. Vu et al., Obtaining hexagon-shaped billets of copper with gradient structure by twist extrusion. Mater. Charact. 153, 215–223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.04.042
L. Kunčická, R. Kocich, V. Ryukhtin, J.C.T. Cullen, N.P. Lavery, Study of structure of naturally aged aluminium after twist channel angular pressing. Mater. Charact. 152, 94–100 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2019.03.045
R. Ebrahimi, A. Rezvani, E. Bagherpour, Circular simple shear extrusion as an alternative for simple shear extrusion technique for producing bulk nanostructured materials. Procedia Manuf. 15, 1502–1508 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.328
A.W. Hussein, M.A. Mahdi, R.S. Abid, Helical extrusion process of general polygonal section shapes through curved dies. J. Manuf. Process. 38, 38–48 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.12.032
S.M. Alavizadeh, K. Abrinia, A. Parvizi, Twisted multi channel angular pressing (TMCAP) as a novel severe plastic deformation method. Met. Mater. Int. 26(2), 260–271 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00319-x
G. Ranjbari, A. Doniavi, M. Shahbaz, Numerical modelling and simulation of vortex extrusion as a severe plastic deformation technique using response surface methodology and finite element analysis. Mater. Int. Met. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00635-7
J. Joudaki, M. Safari, S.M. Alhosseini, Hollow twist extrusion: introduction, strain distribution, and process parameters investigation. Met. Mater. Int. 25(6), 1593–1602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00301-7
Y. Estrin, Y. Beygelzimer, R. Kulagin, Design of architectured materials based on mechanically driven structural and compositional patterning. Adv. Eng. Mater. 21(9), 1900487 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201900487
R. Kulagin, Y. Beygelzimer, A. Bachmaier, R. Pippan, Y. Estrin, Benefits of pattern formation by severe plastic deformation. Appl. Mater. Today 15, 236–241 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2019.02.007
Y. Beygelzimer, R. Kulagin, Y. Estrin, Severe plastic deformation as a way to produce architectured materials, in Architectured Materials in Nature and Engineering, ed. by Y. Estrin, Y. Bréchet, J. Dunlop, P. Fratzl (Springer, New York, 2019), pp. 231–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joudaki, J., Safari, M. & Alhosseini, S.M. New Die Design Configuration for Grain Refinement by Hollow Twist Extrusion (HTE) Process. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 667–675 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00725-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00725-6