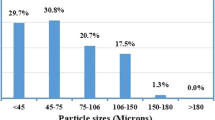
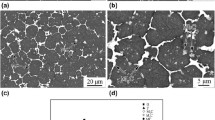
Abstract
A novel technology which was characterized by the vacuum solid state sintering was developed for powder metallurgy high speed steels production. During sintering, both the WC and Mo2C reacted with Fe and transformed to W and Mo rich M6C carbides which were the common hard phases in high speed steels. Also, a high number of W, Mo and Fe were dissolved in VC, forming the MC carbides. The densification of the material mainly relied on the solubility effect during the M6C and MC carbides formation. By alloying with a 0.1 wt% of LaB6 to the steel, the bending strength and the fracture toughness were improved from 3290 MPa and 25.6 MPam1/2 to 4018 MPa and 29.4 MPam1/2, respectively. The TEM analysis demonstrated three types of reaction products by the LaB6 addition: the amorphous phase, the core-shell structure and the La2O3 phase. The impurity elements such as the Mg, Al, Si, S, Ca, and O were absorbed following the LaB6 addition. Moreover, the deoxidization effect caused by the LaB6 addition promoted the sintering at a high-temperature period which contributed to the bending strength and fracture toughness improvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. F. Plankensteiner, H. J. Böhm, F. G. Rammerstorfer, V. A. Buryachenko, and G. Hackl, Acta Mater. 45, 1875 (1997).
S. Gimenez, C. Zubizarreta, V. Trabadelo, and I. Iturriza, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 480, 130 (2008).
V. Trabadelo, S. Gimenez, and I. Iturriza, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 202, 521 (2008).
Y. Pan, H. Yang, X. Liu, and X. Bian, Mater. Lett. 58, 1912 (2004).
K. C. Hwang, S. Lee, and H. C. Lee, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 254, 282 (1998).
S Wei, J. Zhu, L. Xu, and R. Long, Mater. Design 27, 58 (2006).
V. Vitry, S. Nardone, J. P. Breyer, M. Sinnaeve, and F. Delaunois, Mater. Design 34, 372 (2012).
C. Rodenburg and W. M. Rainforth, Acta Mater. 55, 2443 (2007).
E. Pippel, J. Woltersdorf, G. Pöckl, and G. Lichtenegger, Mater. Charact. 43, 41 (1999).
W. Rong, H. O. Andren, H. Wiséll, and G. L. Dunlop, Acta Metall. Mater. 40, 1727 (1992).
M. M. Serna and J. L. Rossi, Mater. Lett. 63, 691 (2009).
F.-S. Pan, W.-Q. Wang, A.-T. Tang L.-Z. Wu, T.-T. Liu, and R.-J. Cheng, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. 21, 180 (2011).
M. Wieβner, M. Leisch, H. Emminger, and A. Kulmburg, Mater. Charact. 59, 937 (2008).
C. Tornberg and P. Billgren, Met. Powder Rep. 47, 19 (1992).
Z. Y. Liu, N. H. Loh, K. A. Khor, and S. B. Tor, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 293, 46 (2000).
T. B. Sercombe, Mat. Sci. Eng. A 363, 242 (2003).
J. Lentz, A. Röttger, and W. Theisen, Acta Mater. 99, 119 (2015).
M. Wang, S. Mu, F. Sun, and Y. Wang, J. Rare Earth 25, 490 (2007).
X. Zhou, X. Yin, F. Fang, J. Jiang, and W. Zhu, J. Rare Earth 30, 1075 (2012).
R. H. Palma, V. Martinez, and J. J. Urcola, Powder Metall. 32, 291 (1989).
J. O. Andersson, Calphad 12, 9 (1988).
C. B. Pollock and H. H. Stadelmaier Metall. Trans. B 1, 767 (1970).
R. M. German and K. A. D'Angelo Int. Meter. Rev. 29, 249 (1983).
R. M. German and B. H. Rabin, Powder Metall. 28, 7 (1985).
C. H. Hsueh, A. G. Evans, and R. L. Coble, Acta Metall. 30, 1269 (1982).
R. Wähling, P. Beiss, and W. J. Huppmann, Powder Metall. 29, 53 (1986).
C. H. Wen, T. M. Wu, and W. C. J. Wei, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 3235 (2004).
C.-M. Chen, L. T. Zhang, W. C. Zhou, and M. Q. Lib, Acta Mater. 47, 1945 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, W., Yu, L., Li, Z. et al. In situ synthesis and strengthening of powder metallurgy high speed steel in addition of LaB6 . Met. Mater. Int. 23, 1150–1157 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-7116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-017-7116-8