Abstract
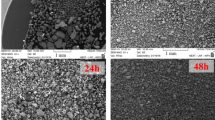
Severe cold-rolling was applied on solution annealed Fe-Ni-Mn steel with fully lath martensite structure to obtain ultrafine-grained structure. Field emission scanning electron microscopy and high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) were employed to investigate the microstructural evolution after severe cold-rolling. HRTEM images showed the typical deformed structure consisting of lamellar dislocation cell blocks. HRTEM study also revealed strain-induced reverse martensitic transformation (activated during grain refinement). It was assumed that severe plastic deformation route and related deformation mode were responsible for microstructural evolutions. X-ray diffraction (XRD) diagram revealed 7% (volume fraction) reverted austenite after final deformation pass. Moreover, HRTEM images revealed nano-void nucleation at the interface of severely deformed martensite and reverted austenite presumably due to high strain energy of misfit and molar volume difference between the austenite and the martensite. It seems that the coalescence of nano-voids could lead to the formation of microvoids in the microstructure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Z. Valiev, R. K. Islamgaliev, and I. V. Alexandrov IV, Prog. Mater. Sci. 45, 103 (2000).
N. Tsuji, Y. Saito, S. H. Lee, and Y. Minamino, Adv. Eng. Mater. 5, 338 (2003).
R. Z. Valiev and T. G. Langdon, Prog. Mater. Sci. 51, 881 (2006).
A. P. Zhilyaev, and T. G. Langdon, Prog. Mater. Sci. 53, 893 (2008).
D. R. Fang, Y. Z. Tian, Q. Q. Duan, S. D. Wu, F. Zhang, N. Q. Zhao, and J. J. Li, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 5002 (2011).
R. Lapovok, D. Tomus, J. Mang, Y. Estrin, and T.C. Lowe, Acta Mater. 57, 2909 (2009).
S. V. Divinski, K. A. Padmanabhan, and G. Wilde, Phil. Magazine 91–36, 4574 (2011).
S. V. Divinski, J. Ribbe, D. Baither, G. Schmitz, G. Reglitz, H. Rösner, K. Sato, Y. Estrin, and G. Wilde, Acta Mater. 57, 5706 (2009).
B. Oberdorfer, B. Lorenzoni, K. Unger, W. Sprengel, M. Zehetbauer, R. Pippanc, and R. Würschuma, Scripta Mater. 63, 452 (2010).
H. Ghasemi-Nanesa, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, and H. Shirazi, Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 240, 012117 (2010).
M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, H. Shirazi, H. Ghasemi-Nanesa, S. Hossein Nedjad, B. Poorganji, and T. Furuhara, Mater. Design 32, 3526 (2011).
H. Ghasemi-Nanesa, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, H. Shirazi, S. Hossein Nedjad, and S. H. Pishbin, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 527, 7552 (2010).
A. Mirsepasi, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, M. Habibi-Parsa, H. Ghasemi-Nanesa, and A. F. Dizaji, Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 551, 32 (2012).
A. H. Cottrell, Trans. Metal Soc. AIME. 212, 192 (1958).
K. D. Amar, D. C. Murdock, M. C. Mataya, J. G. Speer, and D. K. Matlock, Scripta Mater. 50, 1445 (2004).
B. D. Cullity, and S. R. Stock, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 3rd ed., Prentice Hall, NewJersey (2001).
H. Ghasemi-Nanesa, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, H. Shirazi, and T. Furuhara, Proc, 4th Int. Conf. on Nanostructures (A. Z. Moshfegh), p.594, Kish Island, Iran (2012).
Y. Ivanisenko, I. MacLaren, X. Sauvage, R. Z. Valiev, and H. J. Fecht, Acta Mater. 54–6, 1659 (2006).
E. V. Kozlov, L. A. Teplyakova, N. A. Popova, Y. F. Ivanov, D. V. Lychagin, L. N. Ignatenko, and N. A. Koneva, Russian Physics Journal. 35–10, 906 (1992).
E. V. Kozlov, N. A. Popova, N. A. Grigor’eva, L. No Ignatenko, T. A. Kovalevskaya, L. A. Teplyakova, and B. D. Chukhin, Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii Fizika. 3, 112(1991).
E. V. Kozlov, A. N. Zhdanov, and N. Koneva, Physical Mesomechanics. 11, 42 (2008).
H. Ghasemi-Nanesa, M. Nili-Ahmadabadi, H. R. Koohdar, M. Habibi-Parsa, S. Hossein Nedjad, S. A. Alidokht, and T. G. Langdon, to be published in Phil. Magazine (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi-Nanesa, H., Nili-Ahmadabadi, M., Mirsepasi, A. et al. Nano- and microvoid formation in ultrafine-grained martensitic Fe-Ni-Mn steel after severe cold rolling. Met. Mater. Int. 20, 201–205 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-014-2002-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-014-2002-0