Abstract
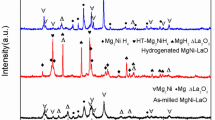
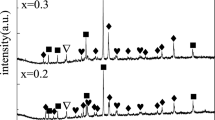
Samples with the compositions of 76.5 wt%Mg-23.5 wt%Ni (Mg-Ni), 71.5 wt%Mg-23.5 wt%Ni-5 wt% Fe2O3 (Mg-Ni-Fe2O3) and 71.5 wt%Mg-23.5 wt%Ni-5 wt% Fe2O3 (spray conversion) (Mg-Ni-scFe2O3), 71.5 wt%Mg-23.5 wt%Ni-5 wt% Fe (Mg-Ni-Fe) and 80 wt%Mg-13.33 wt%Ni-6.67 wt%Fe (Mg-13Ni-7Fe) were prepared by reactive mechanical grinding. Mg-13Ni-7Fe has the highest hydriding and dehydriding rates. After hydriding-dehydriding cycling, all the samples contain the Mg2Ni phase. The samples with Fe2O3 and Fe2O3(spray conversion) as starting materials contain the Mg(OH)2 phase after hydriding-dehydriding cycling as well as after reactive mechanical grinding. Mg-Ni-Fe and Mg-13Ni-7Fe contain the MgH2 phase after reactive mechanical grinding. Phases, space groups, cell parameters, contents and crystallite sizes were analyzed by Full Pattern Matching Refinement program, one of the Rietveld analysis programs, from the XRD powder patterns of Mg-Ni-scFe2O3 after reactive mechanical grinding and after hydriding-dehydriding cycling. The MgH2 phase formed in the Mg-Ni-Fe and Mg-13Ni-7Fe mixtures after reactive mechanical grinding is considered to help the pulverization of the materials during reactive mechanical grinding, leading to the high hydriding and dehydriding rates of these mixtures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. H. Hong, S.N. Kwon, and M. Y. Song, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 298 (2011).
M. Y. Song, Y. J. Kwak, B. S. Lee, H. R. Park, and B. G. Kim, Korean J. Met. Mater. 49, 989 (2011).
J. Huot, M. L. Tremblay, R. Schulz, J. Alloys Compd. 356–357, 603 (2003).
H. Imamura, M. Kusuhara, S. Minami, M. Matsumoto, K. Masanari, Y. Sakata, K. Itoh, T Fukunaga, Acta Mater. 51, 6407 (2003).
A. R. Yavari, A. LeMoulec, F. R. de Castro, S. Deledda, O. Friedrichs, W. J. Botta, G. Vaughan, T. Klassen, A. Fernandez, A. Kvick, Scr. Mater. 52, 719 (2005).
H. C. Zhong, H. Wang, L. Z. Ouyang, and M. Zhu, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 4268 (2011).
P. Pei, X. Song, J. Liu, A. Song, P. Zhang, and G. Chen, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 984 (2012).
Z. Li, X. Liu, Z. Huang, L. Jiang, S. Wang, Rare Metals 25, 247 (2006).
M. Lucaci, Al. R. Biris, R. L. Orban, G. B. Sbarcea, V. Tsakiris, J. Alloys Compd. 488, 163 (2009).
J. J. Reilly and R. H. Wiswall Jr, Inorg. Chem. 7, 2254 (1968).
F. G. Eisenberg, D. A. Zagnoli and J. J. Sheridan Ø, J. Less-Common Met. 74, 323 (1980).
J.-L. Bobet, E. Akiba, Y. Nakamura and B. Darriet, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 25, 987 (2000).
S. Aminorroaya, A. Ranjbar, Y. H. Cho, H. K. Liu, A. K. Dahle, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36, 571 (2011).
Y. H. Cho, S. Aminorroaya, H. K. Liu, A. K. Dahle, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36, 4984 (2011).
C. Milanese, A. Girella, G. Bruni, P. Cofrancesco, V. Berbenni, P. Matteazzi, A. Marini, Intermetallics 18, 203 (2010).
Z. Li, X. Liu, L. Jiang, S. Wang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 32, 1869 (2007).
W. Oelerich, T. Klassen, and R. Bormann, J. Alloys Compd. 322, L5 (2001).
Z. Dehouche, T. Klassen, W. Oelerich, J. Goyette, T. K. Bose, and R. Schulz, J. Alloys Compd. 347, 319 (2002).
G. Barkhordarian, T. Klassen, R. Bormann, Scr. Mater. 49, 213 (2003).
M. Y. Song, E. I. Ivanov, B. Darriet, M. Pezat, and P. Hagenmuller, J. Less-Common Met. 131, 71 (1987).
M. Y. Song, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 20, 221 (1995).
C. D. Yim, B. S. You, Y. S. Na, and J. S. Bae, Catal. Today 120, 276 (2007).
M. Y. Song, I. H. Kwon, S. N. Kwon, C. G. Park, S. H. Hong, D. R. Mumm and J. S. Bae, J. Alloys Compd. 415, 266 (2006).
M. Y. Song, S. H. Baek, J.-L. Bobet, J. Song, and S. H. Hong, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35, 10366 (2010).
M. Y. Song, J. Mater. Sci. 30, 1343 (1995).
M. Y. Song, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 28, 403 (2003).
M. Y. Song, J. P. Manaud, and B. Darriet, J. Alloys Compd. 282, 243 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, M.Y., Baek, S.H., Bobet, JL. et al. Phase transformations and hydrogen-storage characteristics of Mg-transition metal-oxide alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 237–244 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-2017-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-2017-y