Abstract
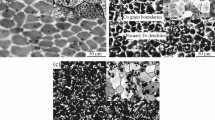
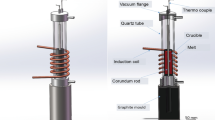
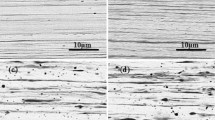
Heavily drawn Cu-6 wt% Ag-2 wt% Fe, Cu-6 wt% Ag-4 wt% Fe and Cu-6 wt% Ag-6 wt% Fe were prepared by melting, homogenizing and cold drawing processes. The homogenizing treatment promotes the precipitation of secondary particles in the matrix, which results in finer and more uniform composite filaments in the drawn microstructure. With the increase of Fe content, the tensile strength increases but the electrical conductivity decreases. The strengthening of the composites and the decrease of the conductivity could be divided into two stages, which is explained by the non-homogeneous deformation model. At η = 5.6, dynamic recovery is thought to occur due to the temperature rise associated with severe deformation, leading to the sudden increase of the conductivity. A dislocation mechanism or an interface obstacle mechanism could be considered to be responsible for the strengthening and conducting behaviors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. W. Wu, Y. Chen, and L. Meng, J. Alloys Compd. 481, 236 (2009).
Z. W. WU, J. J. Liu, Y. Chen, and L. Meng, J. Alloys Compd. 467, 213 (2009).
Z. W. Wu, Y. Chen, and L. Meng, J. Alloys Compd. 477, 198 (2009).
S. I. Hong and M. A. Hill, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 264, 151 (1999).
M. S. Lim, J. S. Song, and S. I. Hong, J. Mater. Sci. 35, 4557 (2000).
A. Benghalem and D. G. Morris, Acta Mater. 45, 397 (1997).
S. I. Hong and M. A. Hill, Acta Mater. 46, 4111 (1998).
W. A. Spitzig, Acta Metall. Mater. 39, 1085 (1991).
C. L. Trybus and W. A. Spitzig, Acta Metall. 37, 1971 (1989).
S. J. Sun, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 1225 (2001).
J. B. Liu, L. Meng and Y. W. Zeng, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 435–436, 237 (2006).
L. Zhang, L. Meng and J. B. Liu, Scr. Mater. 52, 587 (2005).
L. Zhang and L. Meng, Scr. Mater. 52, 1187 (2005).
Y. Sakai, K. Inoue, and H. Maeda, Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 1517 (1995).
W. A. Spitzig, A. R. Pelton, and F. C. Laabs, Acta Metall. 35, 2427 (1987).
P. D. Funkenbusch and T. H. Courtney, Acta Metall. 33, 913 (1985).
D. Mattissen, D. Raabe, and F. Heringhaus, Acta Mater. 47, 1627 (1999).
A. Gaganov, J. Freudenberger, E. Botcharova, and L. Schultz, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 437, 313 (2006).
J. S. Song, S. I. Hong, and Y. G. Park, J. Alloys Compd. 388, 69 (2005).
J. S. Song, S. I. Hong, and H. S. Kim, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 113, 610 (2001).
J. S. Song and S. I. Hong, J. Alloys Compd. 311, 265 (2000).
H. Y. Gao, J. Wang, D. Shu, and B. D. Sun, Scr. Mater. 54, 1931 (2006).
H. Y. Gao, J. Wang, D. Shu, and B. D. Sun, J. Alloys Compd. 438, 268 (2007).
B. D. Sun, H. Y. Gao, J. Wang, and D. Shu, Mater. Lett. 61, 1002 (2007).
D. Raabe, S. Ohsaki, and K. Hono, Acta Mater. 57, 5254 (2009).
D. Raabe and D. Mattissen, Acta Mater. 46, 5973 (1998).
H. Y. Gao, J. Wang, D. Shu, and B. D. Sun, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 452–453, 367 (2007).
J. Lin and L. Meng, J. Alloys Compd. 454, 150 (2008).
J. D. Verhoeven, H. L. Downing, L. S. Chumbley, and E. D. Gibson, J. Appl. Phys. 65, 1293 (1989).
C. Biselli and D. G. Morris, Acta Mater. 44, 493 (1996).
J. Wang, R. G. Hoagland, J. P. Hirth, and A. Misra, Acta Mater. 56, 5685 (2008).
P. D. Funkenbusch, J. K. Lee, and T. H. Courtney, Mater. Trans. A 18, 1249 (1987).
C. W. Sinclair, J. D. Embury, and G. C. Weatherly, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 272, 90 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J.S., Yao, D.W. & Meng, L. Microstructure and properties of heavily drawn Cu-Ag-Fe composites. Met. Mater. Int. 19, 225–230 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-2015-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-2015-0