Abstract
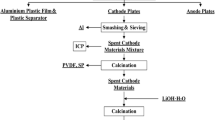
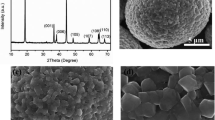
A recycling process involving chemical, mechanical, and electrochemical steps has been applied to recover cobalt from spent lithium ion batteries and resynthesize cathode active materials. LiCo1−xMnxO2 powders using Co salt including Mn from the leach liquor were resynthesized by solid-state reaction as cathode active materials. When the powder mixture with added Li salt was calcined at 950 °C for 8 hours, well crystallined LiCo1−xMnxO2 was successfully obtained. The LiCo1−xMnxO2 powders with a ratio of Co:Mn=10:1 has a discharge capacity of 156.3 mAh/g at a rate of 20 mA/g with no perceptible capacity loss, in sharp contrast to the pure LiCoO2 as active materials. The resynthesized LiCo1−xMnxO2 was proven to have good characteristics as cathode active materials in charge/discharge capacity and cyclic performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Ammann, J. Power Sources 57, 41 (1995).
C. J. Rydh and B. Svard, Science of the Total Environment 302, 167 (2003).
M. J. Lain, J. Power Sources 97–98, 736 (2001).
P. Ammann, J. Power Sources 57, 41 (1995).
C. K. Lee and K. I. Rhee, J. Power Sources 109, 17 (2002).
A. Lundblad and B. Bergman, Solid Stats Ionics 96, 173 (1977).
E. Antolini, J. Solid State Chemistry 170, 159 (2004).
M. R. Gennero de Chialvo, and A. C. Chialvo, J. Appli. Electrochem. 19, 429 (1989).
S. P. Jiang and Y. Z. Chen, J. Electrochem. Soc. 137, 3374 (1990).
S. P. Jiang, Z. G. Lin, and A. C. C. Tesung, J. Electrochem. Soc. 137, 764 (1990).
W. K. Behl and J. E. Toni, J. Electrochem. Soc. 31, 63 (1971).
J. M. Han, J. H. Lee, Y. H. Kim, U. C. Jung, and W. S. Chung, Korean J. Met. Mater. 48, 1014 (2010).
P. Ramadass, B. Haran, R. White, and B. N. Popov, J. Power Sources 111, 210 (2002).
I. Yanase, T. Ohtaki, and M. Watanabe, Solid State Ionics 151, 189 (2002).
H. Gabrisch, R. Yazami, and B. Fultz, J. Power Sources 119–121, 674 (2003).
H. Wang, Y. I. Jang, B. Huang, D. R. Sadoway, and Y. M. Chiang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146, 473 (1999).
C. Julien, A. Rougier, and G. A. Nazri, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 453, 647 (1997).
C. Julien, Solid Stats Ionics 136–137, 887 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SK., Yang, DH., Sohn, JS. et al. Resynthesis of LiCo1−xMnxO2 as a cathode material for lithium secondary batteries. Met. Mater. Int. 18, 321–326 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-012-2016-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-012-2016-4