Abstract
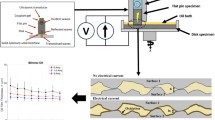
In marine engines, the wear between the piston-ring face and the cylinder liner is an extremely unpredictable and hard-to-reproduce phenomenon that significantly decreases engine performance. This study investigates the characteristics of wear arising between both hard and soft piston-ring coatings and the running surface of the cylinder liner. A detailed tribological analysis using a Pin-on-Disk (POD) testing machine compares the wear rate and the friction coefficient between piston-ring coatings and the cylinder liner for various test parameters, such as test temperature, roughness of the liner, and lubrication. The experimental results show that the wear rate and the friction coefficient of soft coatings were higher than those of hard coatings. The wear rate and the friction coefficient were also found to be influenced by test temperature, due to the lubrication effect of the wear-protective oxidized layers that developed at elevated temperatures. The surface roughness of the cylinder liner on the wear rate strongly influenced the soft coating but was much less apparent for the hard coating. The morphological features of the scuffed cylinder liner revealed that a harder piston-ring coating enhances scuffing of the cylinder liner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Pawlus, Wear 209, 69 (1997).
J. H. Hwang, M. S. Han, D. Y. Kim, and J. G. Youn, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 15, 328 (2006).
J. Jiang, F. H. Stott, and M. M. Stack, Tribo. Int. 31, 245 (1998).
D. K. Srivastava, A. K. Agarwal, and J. Kumar, Mater. Design 28, 1632 (2007).
C. Y. Son, C. K. Kim, D. J. Ha, S. H. Lee, J. S. Lee, K. T. Kim, and Y. D. Lee, J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 45, 6 (2007).
M. P. Alanou, H. P. Evans, and R. W. Snidle, Tribo. Int. 37, 93 (2004).
J. Yunxue, J. M. Lee, and S. B. Kang, J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 45, 118 (2007).
Z. Ye, C. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. S. Cheng, S. Tung, Q. J. Wang, and X. He, Wear 257, 8 (2004).
M. F. Jensen, J. Bøtiger, H. H. Reitz, and M. E. Benzon, Wear 253, 1044 (2002).
J. S. Oh and C. K. Rhee, Met. Mater. Int. 14, 425 (2008).
S. B. Park, K. H. Cho, S. Jung, and H. Jang, Met. Mater. Int. 15, 27 (2009).
F. Svahn, A. Kassman-Rudolphi, and E. Wallen, Wear 254, 1092 (2003).
S. H. Kim and Y. S. Kim, Metals and Materials 5, 267 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, J.H., Joo, B.D., Lee, J.H. et al. Effect of hardness of the piston ring coating on the wear characteristics of rubbing surfaces. Met. Mater. Int. 15, 903–908 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-009-0903-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-009-0903-0