Abstract
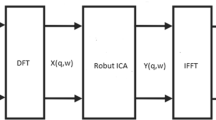
Audio source separation is the task of isolating sound sources that are active simultaneously in a room captured by a set of microphones. Convolutive audio source separation of equal number of sources and microphones has a number of shortcomings including the complexity of frequency-domain ICA, the permutation ambiguity and the problem’s scalabity with increasing number of sensors. In this paper, the authors propose a multiple-microphone audio source separation algorithm based on a previous work of Mitianoudis and Davies [IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 11(5):489–497, 2003]. Complex FastICA is substituted by Robust ICA increasing robustness and performance. Permutation ambiguity is solved using two methodologies. The first is using the Likelihood Ration Jump solution, which is now modified to decrease computational complexity in the case of multiple microphones. The application of the MuSIC algorithm, as a preprocessing step to the previous solution, forms a second methodology with promising results.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Dataset available at http://utopia.duth.gr/nmitiano/download.html.
Dataset available from http://utopia.duth.gr/nmitiano/download.html.
References
Cheney M (2001) The linear sampling method and the music algorithm. Inverse Probl 17:591–595
Comon P (1994) Independent component analysis—a new concept? Signal Process 36:287–314
Comon P, Jutten C (2010) Handbook of blind source separation: independent component analysis and applications. Academic Press, Cambridge
Févotte C, Gribonval R, Vincent E (2005) BSS EVAL toolbox user guide. Technical report, IRISA technical report 1706, Rennes. http://www.irisa.fr/metiss/bss eval/. Accessed 27 July 2017
Griffiths L, Jim C (1982) An alternative approach to linearly constrained adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans Ant Propag 30:27–34
Herbig T, Gerl F, Minker W, Haeb-Umbach R (2011) Adaptive systems for unsupervised speaker tracking and speech recognition. Evol Syst 2(3):199–214
Hyvärinen A (1999) The fixed-point algorithm and maximum likelihood estimation for independent component analysis. Neural Process Lett 10(1):1–5
Hyvärinen A (1999) Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10(3):626–634
Hyvärinen A, Karhunen J, Oja E (2001) Independent component analysis. Wiley, New York, p 481+xxii
Hyvärinen A, Oja E (2000) Independent component analysis: algorithms and applications. Neural Netw 13(4–5):411–430
Ikeda S, Murata N (1998) A method of blind separation on temporal structure of signals. In: ICONIP, vol 98, Citeseer, pp 737–742
Markovich-Golan S, Gannot S, Kellermann W (2017) Combined LCMV-TRINICON beamforming for separating multiple speech sources in noisy and reverberant environments. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 25(2):320–332
Mazur R, Mertins A (2009) An approach for solving the permutation problem of convolutive blind source separation based on statistical signal models. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 17(1):117–126
Mitianoudis N, Davies M (2003) Audio source separation of convolutive mixtures. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 11(5):489–497
Mitianoudis N, Davies M (2003) Using beamforming in the audio source separation problem. In: Proc. Int. Symp. on signal processing and its applications, Paris, pp 89 – 92
Mitianoudis N, Davies M (2004) Permutation alignment for frequency domain ICA using subspace beamforming methods. In: Proc. Int. workshop on independent component analysis and source separation (ICA2004), Granada, pp 127–132
Mitianoudis N (2004) Audio source separation using independent component analysis. PhD thesis, Queen Mary London
Moon T, Stirling W (2000) Mathematical methods and algorithms for signal processing. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Parra L, Spence C (2000) Convolutive blind separation of non-stationary sources. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 8(3):320–327
Saito S, Oishi K, Furukawa T (2015) Convolutive blind source separation using an iterative least-squares algorithm for non-orthogonal approximate joint diagonalization. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 23(12):2434–2448
Sarmiento A, Duran-Diaz I, Cichocki A, Cruces S (2015) A contrast function based on generalised divergences for solving the permutation problem in convolved speech mixtures. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 23(11):1713–1726
Sawada H, Araki S, Makino S (2011) Underdetermined convolutive blind source separation via frequency bin-wise clustering and permutation alignment. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 19(3):516 – 527
Sawada H, Mukai R, Araki S, Makino S (2003) A robust and precise method for solving the permutation problem of frequency-domain blind source separation. In: 4th Int. Symp. on independent component analysis and blind signal separation (ICA2003). Nara, Japan, pp 505–510
Simpson A, Roma G, Grais E, Mason R, Hummersone C, Liutkus A, Plumbley M (2016) Evaluation of audio source separation models using hypothesis-driven non-parametric statistical methods. In: 24th European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO 2016). Budapest, Hungary
Smaragdis P (1998) Blind separation of convolved mixtures in the frequency domain. Neurocomputing 22(1):21–34
Wang L, Ding H, Yin F (2011) A region-growing permutation alignment approach in frequency-domain blind source separation of speech mixtures. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 19(3):2434–2448
Zarzoso V, Comon P (2010) Robust independent component analysis by iterative maximization of the kurtosis contrast with algebraic optimal step size. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21(2):248–261
Zhang K, Chan L (2010) Convolutive blind source separation by efficient blind deconvolution and minimal filter distortion. Neurocomputing 73(1315):2580–2588
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mallis, D., Sgouros, T. & Mitianoudis, N. Convolutive audio source separation using robust ICA and an intelligent evolving permutation ambiguity solution. Evolving Systems 9, 315–329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-017-9199-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12530-017-9199-3