Abstract
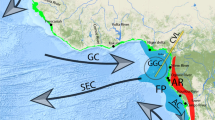
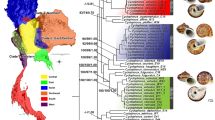
Eurycope producta Sars, 1868 and Eurycope inermis Hansen, 1916 are two widely distributed and highly abundant isopod species complexes within Icelandic waters, a region known for its highly variable environment. The two species complexes have bathymetric depth ranges from 103 to 2029 m (E. producta) and from 302 to 2113 m (E. inermis). Molecular evidence was used for species delimitation within these species complexes by analyzing nuclear (18S rDNA, H3) and mitochondrial (16S rDNA, COI) sequence data. Tree-based methods (BI and ML) and four species delimitation methods (ABGD, GMYC, NDT, PTP) were applied, in order to disentangle the two species complexes. A total of eight and four species clades could be identified within samples of the E. producta and E. inermis complexes and respectively included the closely related species E. dahli Svavarsson, 1987; E. hanseni Ohlin, 1901; and E. cornuta Sars, 1864. The morphological findings coincide with the observed molecular species clades. The elucidated species clades were geographically and bathymetrically much more restricted than previously assumed. Eight species clades featured depth spans of less than 400 m and only four species clades featured depth spans of 1000 to 1500 m. Only two species clades (E. producta sensu stricto and E. inermis sensu stricto) were found on both sides of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge. Further, species distribution maps were generated using random forest, to predict potential distributional patterns for the resolved species clades of the two species complexes. We present the first attempt of combining morphological, molecular, and species distribution models in marine isopods thus far.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABGD:
-
Automated Barcoding Gap Discovery
- AWTY:
-
Are We There Yet
- BI:
-
Bayesian inference
- DZMB:
-
German Centre for Marine Biodiversity Research
- GMYC:
-
Generalized mixed Yule coalescent
- GSR:
-
Greenland-Scotland Ridge
- IFR:
-
Iceland-Faroe Ridge
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- NDT:
-
Nucleotide divergence threshold
- OOB:
-
Out-of-the-box error
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reactions
- PTP:
-
Poisson tree process
- RF:
-
Random forest
- SDM:
-
Species distribution modeling
- SQ:
-
Sequencing
- ZMH:
-
Zoological Museum of Hamburg
References
Altabet MA, Deuser WG, Honjo S, Stienen C (1991) Seasonal and depth-related changes in the source of sinking particles in the North Atlantic. Nature 354:136–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/354136a0
Altschul S, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E, Lipman D (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Baird HP, Miller KJ, Stark JS (2011) Evidence of hidden biodiversity, ongoing speciation and diverse patterns of genetic structure in giant Antarctic amphipods. Mol Ecol 20:3439–3454
Barnard KH (1920) Contributions to the crustacean fauna of South Africa. 6. Further additions to the list of marine isopods. Ann S Afr Mus 17:319–438
Barrowclough GF, Zink RM (2009) Funds enough, and time: mtDNA, nuDNA and the discovery of divergence. Mol Ecol 18(14):2934–2936. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04271.x
Bik HM, Thomas WK, Lunt DH, Lambshead PJ (2010) Low endemism, continued deep-shallow interchanges, and evidence for cosmopolitan distributions in free-living marine nematodes (order Enoplida). BMC Evol Biol 10:389. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-389
Birky CW Jr, Wolf C, Maughan H, Herbertson L, Henry E (2005) Speciation and selection without sex. Hydrobiologia 546:29–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-4408-9_3
Birstein JA (1971) Additions to the fauna of isopods (Crustacea, Isopoda) of the Kurile-Kamtchatka Trench. Part II. Asellota 2. J Inst Oceanol Russ Acad Sci 92:162–198
Bober S, Brix S, Riehl T, Schwentner M, Brandt A (2018) Does the Mid-Atlantic Ridge affect the distribution of abyssal benthic crustaceans across the Atlantic Ocean? Deep Sea Res PT II. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2018.02.007
Bonnier J (1896) Edriophthalmes. In: Koehler R (ed) Résultats Scientifiques de la Campagne du “Caudan” dans le Golfe de Gascogne: Annelides, Poissons, Edriophthalmes, Diatomees, Debris Vegetaux et Roches, Liste des especes recueillies. Annales de l’Université de Lyon, pp 527–689
Brandt A (1992) Origin of Antarctic Isopoda (Crustacea, Malacostraca). Mar Biol 113(3):415–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00349167
Brandt A, Gooday AJ, Brandao SN, Brix S, Brökeland W, Cedhagen T, Choudhury M, Cornelius N, Danis B, De Mesel I, Diaz RJ, Gillan DC, Ebbe B, Howe JA, Janussen D, Kaiser S, Linse K, Malyutina M, Pawlowski J, Raupach M, Vanreusel A (2007) First insights into the biodiversity and biogeography of the Southern Ocean deep sea. Nature 447(7142):307–311 http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v447/n7142/suppinfo/nature05827_S1.html
Brandt A, Elsner N, Brenke N, Golovan OA, Riehl T, Schwabe E, Würzberg L (2013) Epifauna of the Sea of Japan collected via a new epibenthic sledge equipped with camera and environmental sensor systems. Deep Sea Res PT II 86-87:43–55
Brandt A, Brix S, Held C, Kihara TC (2014) Molecular differentiation in sympatry despite morphological stasis: deep-sea Atlantoserolis Wägele, 1994 and Glabroserolis Menzies, 1962 from the south-west Atlantic (Crustacea: Isopoda: Serolidae). Zool J Linnean Soc 172(2):318–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/zoj.12178
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32
Brenke N (2005) An epibenthic sledge for operations on marine soft bottom and bedrock. Mar Technol Soc J 39(2):10–19
Brix S, Svavarsson J (2010) Distribution and diversity of desmosomatid and nannoniscid isopods (Crustacea) on the Greenland–Iceland–Faeroe Ridge. Polar Biol 33(4):515–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-009-0729-8
Brix S, Riehl T, Leese F (2011) First genetic data for species of the genus Haploniscus Richardson, 1908 (Isopoda: Asellota: Haploniscidae) from neighbouring deep-sea basins. Zootaxa 2838:79–84
Brix S, Leese F, Riehl T, Kihara T (2014a) A new genus and new species of Desmosomatidae Sars, 1897 (Isopoda) from the eastern South Atlantic abyss described by means of integrative taxonomy. Mar Biodiv:1–55. doi: 10.1007/s12526-014-0218-3
Brix S, Svavarsson J, Leese F (2014b) A multi-gene analysis reveals multiple highly divergent lineages of the isopod Chelator insignis (Hansen, 1916) south of Iceland. Pol Polar Res 35(2):225–242
Brix S, Bober S, Tschesche C, Kihara T-C, Driskell A, Jennings RM (2018) Molecular species delimitation and its implications for species descriptions using desmosomatid and nannoniscid isopods from the VEMA fracture zone as example taxa. Deep-Sea Res PT II. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2018.02.004
Brökeland W, Raupach MJ (2008) A species complex within the isopod genus Haploniscus (Crustacea: Malacostraca: Peracarida) from the Southern Ocean deep sea: a morphological and molecular approach. Zool J Linnean Soc 152(4):655–706. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2008.00362.x
Buhay JE (2009) “COI-like” sequences are becoming problematic in molecular systematic and DNA barcoding studies. J Crustacean Biol 29:96–110
Carvalho GR, Piertney SB (1997) Interspecific comparisons of genetic population structure in members of the Jaera albifrons species complex. J Mar Biol Ass UK 77:77–93
Claridge MF, Dawah HA, Wilson MR (1997) Species: the units of biodiversity. Chapman & Hall, London
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9:1657–1659
Coleman CO (2003) “Digital inking”: how to make perfect line drawings on computers. Org Divers Evol 3(4):303–304. https://doi.org/10.1078/1439-6092-00081
Coleman CO (2009) Drawing setae the digital way. Zoosyst Evol 85(2):305–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoos.200900008
Colgan DJ, McLauchlan A, Wilson GDF, Livingston SP, Edgecombe GD, Macaranas J, Cassis G, Gray MR (1998) Histone H3 and U2 snRNA DNA sequences and arthropod molecular evolution. Aus J Zool 46(5):419–437. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO98048
Dauvin J-C, Alizier S, Weppe A, Guðmundsson G (2012) Diversity and zoogeography of Icelandic deep-sea Ampeliscidae (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Deep Sea Res PT I 68:12–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2012.04.013
Dayrat B (2005) Towards integrative taxonomy. Biol J Linn Soc 85(3):407–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2005.00503.x
Degraer S, Verfaillie E, Willems W, Adriaens E, Vincx M, Van Lancker V (2008) Habitat suitability modelling as a mapping tool for macrobenthic communities: an example from the Belgian part of the North Sea. Cont Shelf Res 28(3):369–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2007.09.001
Dijkstra HH, Warén A, Gudmundsson G (2009) Pectinoidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from Iceland. Mar Biol Res 5:207–243
Divins DL (2003) Total sediment thickness of the world’s oceans & marginal seas. Ver 1. World Data Service for Geophysics. http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/sedthick/sedthick.html
Dreyer H, Wägele JW (2001) Parasites of crustaceans (Isopoda: Bopyridae) evolved from fish parasites: molecular and morphological evidence. Zool 103:157–178
Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A (2012) Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol 29(8):1969–1973. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mss075
Edzard T, Fujisawa T, Barraclough TG (2009) SPLITS: SPecies’ LImits by Threshold Statistics. R package version 1.0-18/r45
Elith J, Graham CH (2009) Do they? How do they? Why do they differ? On finding reasons for differing performances of species distribution models. Ecography 32(1):66–77. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2008.05505.x
ETOPO2v2 (2006) 2-minute gridded global relief data ETOPO2v2. U.S. Department of Commerce. doi: 10.7289/V5J1012Q
Etter RJ, Rex MA, Chase MC, Quattro JM (1999) A genetic dimension to deep-sea biodiversity. Deep Sea Res PT I 46(6):1095–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0637(98)00100-9
Etter RJ, Boyle EE, Glazier A, Jennings RM, Dutra E, Chase MR (2011) Phylogeography of a pan-Atlantic abyssal protobranch bivalve: implications for evolution in the Deep Atlantic. Mol Ecol 20(4):829–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04978.x
Eustace RM, Ritchie H, Kilgallen NM, Piertney SB, Jamieson AJ (2016) Morphological and ontogenetic stratification of abyssal and hadal Eurythenes gryllus sensu lato (Amphipoda: Lysianassoidea) from the Peru–Chile Trench. Deep Sea Res PT I 109(Supplement C):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2015.11.005
Eytan RI, Hayes M, Arbour-Reily P, Miller M, Hellberg ME (2009) Nuclear sequences reveal mid-range isolation of an imperilled deep-water coral population. Mol Ecol 18(11):2375–2389. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04202.x
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408678
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondiral cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 5(3):294–299
France SC, Kocher TD (1996) Geographic and bathymetric patterns of mitochondrial 16S rRNA sequence divergence among deep-sea amphipods, Eurythenes gryllus. Mar Biol 126(4):633–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00351330
Fujita MK, Leaché AD, Burbrink FT, McGuire JA, Moritz C (2012) Coalescent-based species delimitation in an integrative taxonomy. Trends Ecol Evol 27(9):480–488
Galtier N, Nabholz B, Glemin S, Hurst GD (2009) Mitochondrial DNA as a marker of molecular diversity: a reappraisal. Mol Ecol 18(22):4541–4550. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04380.x
Gogina M, Zettler ML (2010) Diversity and distribution of benthic macrofauna in the Baltic Sea: data inventory and its use for species distribution modelling and prediction. J Sea Res 64(3):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2010.04.005
Hansen HJ (1916) Crustacea Malacostraca: the Order Isopoda. Dan Ingolf-Exp 3:1–262
Hansen B, Østerhus S (2000) North Atlantic-Nordic Seas exchanges. Prog Oceanogr 45(2):109–208
Hare MP (2001) Prospects for nuclear gene phylogeography. Trends Ecol Evol 16(12):700–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(01)02326-6
Harrison RG (1998) Linking evolutinary pattern and process. The relevance of species concepts fo the study of speciation. In: Howard DJ, Berlocher S (eds) Endless forms: species and speciation. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 19–31
Hart MW, Sunday J (2007) Things fall apart: biolgical species from unconnected parsimony networks. Biol Lett 3:509–512
Havermans C, Sonet G, d’Udekem d’Acoz C, Nagy ZT, Martin P, Brix S, Riehl T, Agrawal S, Held C (2013) Genetic and morphological divergences in the cosmopolitan deep-sea amphipod Eurythenes gryllus reveal a diverse abyss and a bipolar species. PLoS One 8(9):e74218. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0074218
Hebert PDN, Ratnasingham S, deWaard JR (2003) Barcoding animal life: cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. P Roy Soc B Biol Sci 270(Suppl 1):S96–S99. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2003.0025
Held C (2003) Molecular evidence for cryptic speciation within the widespread Antarctic crustacean Ceratoserolis trilobitoides (Crustacea, Isopoda). In: Antarctic biology in a global context. pp 135–139
Held C, Wägele J-W (2005) Cryptic speciation in the giant Antarctic isopod Glyptonotus antarcticus (Isopoda, Valvifera, Chaetiliidae). Sci Mar 69:175–181
Hessler RR (1970) The Desmosomatidae (Isopoda, Asellota) of the gay head-bermuda transect. Bull Scripps Inst Oceanogr 15:1–185
Hessler RR (1981) Evolution of Arthropod locomotion: a crustacean model. In: Herraid CF, Fourtner CR (eds) Locomotion and exercise in arthropods. Plenum, New York, pp 9–29
Hessler RR, Strömberg JO (1989) Behavior of janiroidean isopods (Asellota), with special reference to deep-sea genera. Sarsia 74:145–159
Iverson LR, Prasad AM, Matthews SN, Peters M (2008) Estimating potential habitat for 134 eastern US tree species under six climate scenarios. For Ecol Manag 254(3):390–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2007.07.023
Jennings RM, Etter RJ, Ficarra L (2013) Population differentiation and species formation in the deep sea: the potential role of environmental gradients and depth. PLoS One 8(10):e77594. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077594
Jochumsen K, Schnurr SM, Quadfasel D (2016) Bottom temperature and salinity distribution and its variability around Iceland. Deep Sea Res PT I 111:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2016.02.009
Johnson NK, Cicero C (2002) The role of ecologic diversification in sibling speciation of Empidonax flycatchers (Tyrannidae): multigene evidence from mt DNA. Mol Ecol 11:2065–2081
Johnson SB, Young CR, Jones WJ, Warén A, Vrijenhoek RC (2006) Migration, isolation, and speciation of hydrothermal vent limpets (Gastropoda; Lepetodrilidae) across the Blanco Transform Fault. Biol Bull 210(2):140–157
Just J, Wilson GDF (2004) Revision of the Paramunna complex (Isopoda: Asellota: Paramunnidae). Invertebr Syst 18(4):377–466. https://doi.org/10.1071/IS03027
Kaiser S, Brix S, Kihara TC, Janssen A, Jennings RM (2017) Integrative species delimitation in the deep-sea genus Thaumastosoma Hessler, 1970 (Isopoda, Asellota, Nannoniscidae) reveals a new genus and species from the Atlantic and central Pacific abyss. Deep Sea Res PT II. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.05.006
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K-i, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30(14):3059–3066
Kunz W (2001) Taking more care in using different species concepts—an opinion. Parasitol Res 87(5):413–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004360000372
Kussakin OG (2003) Marine and brackishwater like-footed Crustacea (Isopoda) from the cold and temperate waters of the Northern hemisphere. III. Suborder Asellota. Part 3. Family Munnopsidae. Opredeliteli po faune, izdavaemie Zoologicheskim Institutom Rossiyskoy Academii Nauk
Leaché AD, Koo MS, Spencer CL, Papenfuss TJ, Fisher RN, McGuire JA (2009) Quantifying ecological, morphological, and genetic variation to delimit species in the coast horned lizard species complex (Phrynosoma). Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(30):12418–12423. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906380106
Leese F, Kop A, Wägele J-W, Held C (2008) Cryptic speciation in a benthic isopod from Patagonian and Falkland Island waters and the impact of glaciations on its population structure. Front Zool 5(1):19
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2(3):18–22
Lilljeborg W (1864) Bidrag till Kannedomen om de inom Sverige och Norrige frekommende Crustaceen af Isopodernas underordning och Tanaidernas familj. Inbjudningsskrift till hrande af de Offentliga Frelsninger 1:1–32
Lörz A-N, Smith P, Linse K, Steinke D (2012) High genetic diversity within Epimeria georgiana (Amphipoda) from the southern Scotia Arc. Mar Biodivers 42(2):137–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-011-0098-8
Lutz MJ, Caldeira K, Dunbar RB, Behrenfeld MJ (2007) Seasonal rhythms of net primary production and particulate organic carbon flux to depth describe the efficiency of biological pump in the global ocean. J Geophys Res 112(C10):C10011. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006jc003706
Malyutina M, Brandt A (2006) A revaluation of the Eurycopinae (Crustacea, Isopoda, Munnopsidae) with a description of Dubinectes gen. nov. from the southern Atlantic deep sea. Zootaxa 1272:1–44
Marlétaz F, Le Parco Y, Liu S, Peijnenburg KTCA (2017) Extreme mitogenomic variation in natural populations of chaetognaths. GBE 9(6):1374–1384. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evx090
Marshall N, Diebel C (1995) Deep-sea spiders’ that walk through the water. J Exp Biol 198(Pt 6):1371–1379
McCallum KP, Guerin GR, Breed MF, Lowe AJ (2014) Combining population genetics, species distribution modelling and field assessments to understand a species vulnerability to climate change. Austral Ecol 39(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/aec.12041
McClain CR, Hardy SM (2010) The dynamics of biogeographic ranges in the deep sea. P Roy Soc B Biol Sci 277:3533–3546
Meier R, Kwong S, Vaidya G, Ng PKL (2006) DNA barcoding and taxonomy in Diptera: a tale of high intraspecific variability and low identification success. Syst Biol 55:715–728
Meißner K, Darr A, Rachor E (2008) Development of habitat models for Nephtys species (Polychaeta: Nephtyidae) in the German Bight (North Sea). J Sea Res 60(4):276–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2008.08.001
Meißner K, Fiorentino D, Schnurr S, Martinez Arbizu P, Huettmann F, Holst S, Brix S, Svavarsson J (2014) Distribution of benthic marine invertebrates at northern latitudes―an evaluation applying multi-algorithm species distribution models. J Sea Res 85:241–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2013.05.007
Menzel L, George KH, Arbizu PM (2011) Submarine ridges do not prevent large-scale dispersal of abyssal fauna: a case study of Mesocletodes (Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Deep Sea Res PT I 58(8):839–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2011.05.008
Menzies RJ (1962) The isopods of the abyssal depths in the Atlantic Ocean. Vema Res Ser 1:79-206
Monaghan MT, Wild R, Elliot M, Fujisawa T, Balke M, Inward DJG, Lees DC, Ranaivosolo R, Eggleton P, Barraclough TGB, Vogler AP (2009) Accelerated species inventory on Madagascar using coalescent-based models of species delineation. Syst Biol 58(3):298–311
Nilsen J, Hátún H, Mork K, Valdimarsson H (2008) The NISE dataset. Technical Report 08-07. Tórshavn, Faroe Islands
Nylander JAA (2004) MrAIC.pl. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University, Uppsala
Ohlin A (1901) Arctic Crustacea collected during the Swedish Arctic Expeditions 1898 and 1899 under the Direction of Professor A G Nathorst. Leptostraca, Isopoda, Cumacea. Bihang till Kungliga Svenska Vetenskaps-Akademiens Handlingar 26:1–54
Osborn KJ (2009) Relationships within the Munnopsidae (Crustacea, Isopoda, Asellota) based on three genes. Zool Scr 38(6):617–635. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.2009.00394.x
Padial JM, Miralles A, DeLaRiva I, Vences M (2010) The integrative future of taxonomy. Front Zool 7(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-9994-7-16
Palumbi SR, Martin A, Romanos S, McMillan WO, Stice L (1991) The simple fool’s guide to PCR. Version 2. University of Hawaii Press, Hawaii, Honolulu
Petit RJ, Excoffier L (2009) Gene flow and species delimitation. Trends Ecol Evol 24(7):386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2009.02.011
Pons J, Barraclough TG, Gomez-Zurita J, Cardoso A, Duran DP, Hazell S, Kamoun S, Sumlin WD, Vogler AP (2006) Sequence-based species delimitation for the DNA taxonomy of undescribed insects. Syst Biol 55(4):595–609
Puillandre N, Lambert A, Brouillet S, Achaz G (2012) ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol Ecol 21(8):1864–1877. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05239.x
Radulovici AE, Sainte-Marie B, Dufresne F (2009) DNA barcoding of marine crustaceans from the Estuary and Gulf of St Lawrence: a regional-scale approach. Mol Ecol Resour 9(Suppl s1):181–187. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02643.x
Rambaut A, Drummond AJ (2007) Tracer v1.5.0
Raupach MJ, Wägele JW (2006) Distinguishing cryptic species in Antarctic Asellota (Crustacea: Isopoda)—a preliminary study of mitochondrial DNA in Acanthaspidia drygalskii. Antarct Sci 18:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954102006000228
Raupach MJ, Malyutina M, Brandt A, Wägele J-W (2007) Molecular data reveal a highly diverse species flock within the munnopsoid deep-sea isopod Betamorpha fusiformis (Barnard, 1920) (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota) in the Southern Ocean. Deep-Sea Res PT II 54(16–17):1820–1830
Raupach MJ, Mayer C, Malyutina M, Wägele JW (2009) Multiple origins of deep-sea Asellota (Crustacea: Isopoda) from shallow waters revealed by molecular data. Proc Biol Sci 276(1658):799–808
Reiss H, Cunze S, König K, Neumann H, Kröncke I (2011) Species distribution modelling of marine benthos: a North Sea case study. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 442:71–86
Reveillaud J, Remerie T, van Soest R, Erpenbeck D, Càrdenas P, Derycke S, Xavier JR, Rigaux A, Vanreusel A (2010) Species boundaries and phylogenetic relationships between Atlanto-Mediterranean shallow-water and deep-sea coral associated Hexadella species (Porifera, Ianthellidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 56:104–114
Rex MA, Etter RJ (2010) Deep-sea biodiversity: pattern and scale. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Riehl T, Brand A (2013) Southern Ocean Macrostylidae reviewed with a key to the species and new descriptions from Maud Rise. Zootaxa 3692(1):160–203. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3692.1.10
Riehl T, Kaiser S (2012) Conquered from the deep sea? A new deep-sea isopod species from the Antarctic shelf shows pattern of recent colonization. PLoS One 7(11):e49354. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049354
Riehl T, Brenke N, Driskell A, Kaiser S, Brand A (2014) Field and laboratory methods for DNA studies on deep-sea isopod crustaceans. Pol Polar Res 35(2):203–224
Riehl T, Lins L, Brandt A (2017) The effects of depth, distance, and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on genetic differentiation of abyssal and hadal isopods (Macrostylidae). Deep Sea Res PT II. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2017.10.005
Rogers AD (2003) Molecular ecology and evolution of slope species. In: Wefer G, Billett D, Hebbeln D, Jørgensen B, Schlüter M, van Weering TE (eds) Ocean margin systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 323–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-05127-6_20
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Rothlisberg PC, Pearcy WG (1977) An epibenthic sampler used to study the ontogeny of vertical migration of Pandalus jordani (Decapoda, Caridea). Fish Bull 74:994–997
Rubinoff D, Holland BS (2005) Between two extremes: mitochondrial DNA is neither the panacea nor the nemesis of phylogenetic and taxonomic inference. Syst Biol 54(6):952–961. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150500234674
Sanders HL, Hessler RR (1969) Ecology of the deep-sea benthos. Science 163(3874):1419–1424
Sanders HL, Hessler RR, Hampson GR (1965) An introduction to the study of deep-sea benthic faunal assemblages along the Gay Head-Bermuda transect. Deep Sea Res Oceanogr Abstr 12(6):845–867
Sars GO (1864) On en anomal Gruppe af Isopoder. Forh Vidensk Selsk Kristiania 1863:1–16
Sars GO Beretning om en i Sommeren 1865 foretagan zoologisk Reise ved Kysterne af Christianias og Christiansands Stifter-Crustaceer. Forh Vidensk Selsk Kristiania 1868, 1868:1–47
Schnurr S, Malyutina M (2014) Two new species of the genus Eurycope (Isopoda, Munnopsidae) from Icelandic waters. Pol Polar Res 35(2):361–388
Schnurr S, Brandt A, Brix S, Fiorentino D, Malyutina M, Svavarsson J (2014) Composition and distribution of selected munnopsid genera (Crustacea, Isopoda, Asellota) in Icelandic waters. Deep Sea Res PT I 84:142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2013.11.004
Schüller M (2011) Evidence for a role of bathymetry and emergence in speciation in the genus Glycera (Glyceridae, Polychaeta) from the deep Eastern Weddell Sea. Polar Biol 34(4):549–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-010-0913-x
Schüller M, Hutchings PA (2012) New species of Terebellides (Polychaeta: Trichobranchidae) indicate long-distance dispersal between western South Atlantic deep-sea basins. Zootaxa 3254:1–31
Schwentner M, Timms BV, Richter S (2011) An integrative approach to species delineation incorporating different species concepts: a case study of Limnadopsis (Branchiopoda: Spinicaudata). Biol J Linn Soc 104(3):575–599. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2011.01746.x
Seiter K, Hensen C, Zabel M (2005) Benthic carbon mineralization on a global scale. Glob Biogeochem Cy 19(1):GB1010. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004gb002225
Shaw KL (2002) Conflict between nuclear and mitochondrial DNA phylogenies of a recent species radiation: what mtDNA reveals and conceals about modes of speciation in Hawaiian crickets. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99(25):16122–16127. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.242585899
Sites JW, Marshall JC (2004) Operational criteria for delimiting species. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 35:199–227. https://doi.org/10.2307/30034115
Somero GN (1992) Adaptations to high hydrostatic pressure. Annu Rev Physiol 54:557–577
Song H, Buhay JE, Whiting MF, Crandall KA (2008) Many species in one: DNA barcoding overestimates the number of species when nuclear mitochondrial pseudogenes are coamplified. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(36):13486–13491. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803076105
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. Syst Biol 57(5):758–771. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150802429642
Svavarsson J (1987) Eurycopidae (Isopoda, Asellota) from bathyal and abyssal depths in the Norwegian, Greenland, and North Polar Seas. Sarsia 72:183–196
Svavarsson J (1997) Diversity of isopods (Crustacea): new data from the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans. Biodivers Conserv 6:1571–1579
Svavarsson J, Brattegard T, Strömberg JO (1990) Distribution and diversity patterns of asellote isopods (Crustacea) in the deep Norwegian and Greenland Seas. Prog Oceanogr 24:297–310
Svavarsson J, Strömberg JO, Brattegard T (1993) The deep-sea asellote (Isopoda, Crustacea) fauna of the Northern Seas: species composition, distributional patterns and origin. J Biogeogr 20(5):537–555
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tang CQ, Leasi F, Obertegger U, Kieneke A, Barraclough TG, Fontaneto D (2012) The widely used small subunit 18S rDNA molecule greatly underestimates true diversity in biodiversity surveys of the meiofauna. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(40):16208–16212. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209160109
Templeton AR (2001) Using phylogeographic analyses of gene trees to test species status and processes. Mol Ecol 10(3):779–791. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294x.2001.01199.x
Teske PR, Papadopoulos I, Zardi GI, McQuaid CD, Edkins MT, Griffiths CL, Barker NP (2007) Implications of life history for genetic structure and migration rates of southern African coastal invertebrates: planktonic, abbreviated and direct development. Mar Biol 152(3):697–711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-007-0724-y
Tsang LM, Chan BKK, Shih F-L, Chu KH, Allen Chen C (2009) Host-associated speciation in the coral barnacle Wanella milleporae (Cirripedia: Pyrgomatidae) inhabiting the Millepora coral. Mol Ecol 18(7):1463–1475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2009.04090.x
Vrijenhoek RC (2009) Cryptic species, phenotypic plasticity, and complex life histories: assessing deep-sea faunal diversity with molecular markers. Deep Sea Res PT II 56(19–20):1713–1723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.05.016
Watling L, Guinotte J, Clark MR, Smith CR (2013) A proposed biogeography of the deep ocean floor. Prog Oceanogr 111:91–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2012.11.003
Whittaker JM, Muller RD, Roest WR, Wessel P, Smith WHF (2008) How supercontinents and superoceans affect seafloor roughness. Nature 456 (7224):938–941. doi:http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v456/n7224/suppinfo/nature07573_S1.html
Wilgenbusch JC, Warren DL, Swofford DL (2004) AWTY: a system for graphical exploration of MCMC convergence in Bayesian phylogenetic inference. http://ceb.csit.fsu.edu/awty
Wilson GDF (1982) Systematics of a species complex in the deep-sea genus Eurycope, with a revision of six previously described species (Crustacea, Isopoda, Eurycopidae). Bull Scripps Inst Oceanogr 25:1–64
Wilson GDF (1983a) An unusual species complex in the genus Eurycope (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota) from the deep north Atlantic Ocean. P Biol Soc Wash 96(3):452–467
Wilson GDF (1983b) Variation in the deep-sea isopod Eurycope iphthima (Asellota, Eurycopidae): depth related clines in rostral morphology and in populations structure. J Crustacean Biol 3(1):127–140
Wilson GDF (1985) The distribution of eurycopid species complexes (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota). In: Laubier L, Monniot C (eds) Peuplements profonds du Golfe de Gascogne. Brest, pp 630–468
Wilson GDF (1989) A systematic revision of the deep-sea subfamily Lipomerinae of the isopod crustacean family Munnopsidae. Bull Scripps Inst Oceanogr 27:1–138
Wilson GDF (2008) A review of taxonomic concepts in the Nannoniscidae (Isopoda, Asellota), with a key to the genera and a description of Nannoniscus oblongus Sars. Zootaxa 1680:1–24
Wilson GDF, Hessler RR (1981) A revision of the genus Eurycope (Isopoda, Asellota) with descriptions of three new genera. J Crustacean Biol 1(3):401–423
Wilson GDF, Hessler RR (1987) Speciation in the deep sea. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:185–207
Wilson GDF, Schotte M (2017) Munnopsidae Lilljeborg, 1864. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=118264. Accessed 2017-12-14 2017
Wilson AC, Cann RL, Carr SM, George M, Gyllensten UB, Helm-Bychowski KM, Higuchi RG, Palumbi SR, Prager EM, Sage RD, Stoneking M (1985) Mitochondrial DNA and two perspectives on evolutionary genetics. Biol J Linn Soc 26(4):375–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.1985.tb02048.x
Wolff T (1962) The systematics and biology of bathyal and abyssal Isopoda Asellota. Galathea Rep 6:1–320
Zardus JD, Etter RJ, Chase MR, Rex MA, Boyle EE (2006) Bathymetric and geographic population structure in the pan-Atlantic deep-sea bivalve Deminucula atacellana (Schenck, 1939). Mol Ecol 15(3):639–651. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02832.x
Zhang J, Kapli P, Pavlidis P, Stamatakis A (2013) A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 29(22):2869–2876. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt499
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the crew and participants of the IceAGE expeditions, as well as all pickers and sorters at the DZMB in Hamburg, Germany, and the Nature Centre in Sandgerði, Iceland. Special thanks go to Dr. Herman Wirshing for his help during S. Schnurr’s stays at the facilities of the Laboratories of Analytical Biology (LAB) at the Smithonian National Museum of Natural History, Washington, DC. We thank Karen Jeskulke for introducing lab workflow, Lukas Rischke for solving hardware problems, and Falk Huettmann for his introduction to random forest models.
Funding
S. Schnurr was partly funded by the German Science Foundation (DFG) under contract 2843/4-1 and BR3843/6-1, as well as by the Census of the Diversity of Abyssal Marine Life (CeDAMar), the Smithsonian’s Rathbun Fund for Crustacean Research, and the Annette Barthelt Stiftung. The IceAGE cruises were funded by the DFG contract BR3843/3-1 (IceAGE1) and 4-1 (IceAGE2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the authors.
Sampling and field studies
All necessary permits for sampling and observational field studies have been obtained by the authors from the competent authorities and are mentioned in the acknowledgements, if applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by K. Halanych
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
Uncorrected pairwise p-distances for the 16S gene of all evaluated E. producta complex specimens. (XLSX 26.8 kb)
Online Resource 2
Uncorrected pairwise p-distances for the 16S gene of all evaluated E. inermis complex specimens. (XLSX 33.7 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schnurr, S., Osborn, K.J., Malyutina, M. et al. Hidden diversity in two species complexes of munnopsid isopods (Crustacea) at the transition between the northernmost North Atlantic and the Nordic Seas. Mar Biodiv 48, 813–843 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-018-0877-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-018-0877-6